Page 1 :
(@), , Select the correct answers from the alternatives given below in each bit :, The simplest measure of dispersion is :, (i) Inter Quartile range (ii) Quartile Deviation (iii) Range (iv) Mean Deviation, , , , , , , , (b), , (c), , @, , (e), , (f), , (g), , , , A relative measure of dispersion is :, , (i) Range (ii) Inter Quartile range (iii) Coefficient of QD, (iv) Quartile, Deviation., , An absolute measure of dispersion is :, , (i) Coefficient of range (ii) Coefficient I.Q.R (iii) Standard Deviation (iv), Coefficient of Mean Deviation, , The measure of dispersion not suitable for open-end class is :, , (i) Quartile Deviation (iii) Mean Deviation, , (ii) Range (iv) Inter Quartile Range, , An absolute measure of dispersion is expressed in :, , (i) Ratio (ii) Percentage (iii) Decimal (iv) the same unit of original data., Relative measure of dispersion can be expressed in :, , (i) Ratio/percentage/decimal (ii) the same unit of original data (iii) in, different units original data (iv) rates., , Arelative measure of dispersion is always, , (i) equal to unity (ii) more than unity (iii) Less than or equal to unity, (iv) less than zero
Page 2 :
Fill in the gaps, , (a) is the simplest measure of dispersion., , (b) Coefficient of range is called coefficient of, , (c) Range, I QR and QD are dispersions., , (d) Positional dispersions are of positional averages., , (e) Mathematical dispersion is of further mathematical analysis., (f) Range be used in open-end distributions., , (g) Range is by fluctuations of sampling., , (h) Median lies half way on the same scale from Q, to Q, in series., @Q,+QD + Q,-QDin series of distribution, , (j) QD includes atleast percent in asymmetrical series.
Page 3 :
3 From the alternatives given below in each bit, choose and write the correct answer, , @, (b), ©, , @, , ©, , ce), , along with its serial number :, , The dispersion which shows the scatterness of various items from its central value is :, @ Range Gi) Interquartilerange (iii) Quartiledeviation (iv) Mean deviation, Mean deviation is not calculated from :, , @ GeometricMean (i) ArithmeticMean (if) Median (iv) Mode, The most preferred measure of central tendency used to calculate Mean Deviation is :, @ Mean (i) Median (iii) Mode (iv) Harmonic Mean, , The unitless dispersion is :, @ Mean Deviation (i) Quartile Deviation, Gi) Range (iv) Coefficient of Mean Deviation, , Mean deviation does not give accurate result in case of :, , @ closed-end series (i) Exclusive series, , Gi) Open-end series _(iv) Inclusive series, , The dispersion which is based on all the observations ofa series :, , @ Range (ii) Interquartilerange (jij) Quartiledeviation (iv) Mean deviation
Page 4 :
(@), (b), ©, d), ©), (3), , h), @, 0, &), , tN Nk tA NS, , Fillin the gaps., Mean deviation is defined., Mean deviation affected by extreme items., Mean deviation is useful n business cycles., Mean deviation is capable of further algebraic treatment., Mean deviation is difficult to compute ifMean, Median and Mode is in, Itis to igonre ‘+’ signs in computing Mean Deviation., Mean Deviation is meaningful in studying samples., Mean deviation is rarely used in studies / surveys., is based on all the observations of the series., Mean deviation is the mean of deviations taken from a central value., Mean deviation is also known as mean deviation., Mean deviation is also known as first of dispersion.
Page 5 :
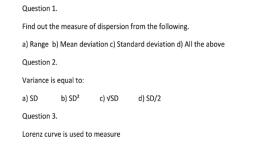
From the alternatives given below in each bit, choose and write the correct, , answer alongwith its serial numbers., , @), (b), , (c), , @, , (e), , (f), , (g), , Multiple choice questions :, , Standard deviation of 3 and 4 is :, , (i) 2 (ii) 3.5 (iii) 1.5 (iv) 5, The concept of Standard Deviation was developed by :, , (i) Croxton and Cowden (ii) Karl Pearson, , (iii) Lord Bowley (iv) Clark, , Coefficient of Standard Deviation is the :, , (i) Absolute measure of dispersion (ii) Relative measure of dispersion, , , , (iii) Square root of variance (iv) Root-mean square deviation, Coefficient of variation is :, , . o i wey ; o, ) = (ii) & Gi) 99%! =) cams, , One of the following, which is not required to compute Combined Standard, Deviation is :, , (i) Median (ii) Mean, , (iii) Standard Deviation (iv) Number of items, , The measure of dispersion suitable for studying fluctuations in share prices, is :, (i) Quartile Deviation (ii) Mean Deviation, , (iii) Range (iv) Standard Deviation, , If each of the observations of a series is divided by 3, the Standard Deviation of, the new observations is :, , (i) 3M of the S.D. of the original observations, , (ii) 3 times of the S.D. of the original observations, (iii) 6 times of the S.D. of the original observations, , (iv) Not changed.