Page 1 :
Animal Classification, Exercise, Q. 1. A. Identify me., I am diploblastic & acoelomate. Which phylum do I belong to?, Answer : Cnidaria, Explanation- Cnidaria is diploblastic i.e. it consists of two germ layers. There is an, absence of body cavity in it which makes it an acoelomate., Q. 1. B. Identify me., My body is radially symmetrical. Water vascular system is present in my body. I, am referred as fish though I am not. What is my name?, Answer : Star fish, Explanation- Starfish belong to the phylum Echinodermata. Their body is triploblastic,, acoelomate and are radially symmetrical in the adult stage., Q. 1. C. Identify me., I live in your small intestine. Pseudocoelom is present in my thread like body. In, which phylum will you include me?, Answer : Ascaris (Intestinal worms)-Phylum Aschelminthes, Explanation- The intestinal worms belong to the Phylum Aschelminthes. Body of these, animals is triploblastic and Pseudo coelomate., Q. 1. D. Identify me., Though I am multicellular, there are no tissues in my body. What is the name of, my phylum?, Answer : Porifera, Explanation- Animals belonging to the phylum Porifera have the simplest body plan, and are called as sponges. They bear numerous pores on their body., Q. 2. Write the characters of each of the following animals with the help of, classification chart.
Page 2 :
Bath sponge, grasshopper, rohu, penguin, frog, lizard, elephant, jellyfish., Answer : 1. Bath sponge: Phylum- Porifera, These animals are with simplest body plan and are called as ‘Sponges’. They bear, numerous pores on their body. Those pores are called as ‘Ostia’ and ‘Oscula’. These, are aquatic animals and are mostly asymmetrical., 2. Grasshopper: Phylum- Arthropoda, These animals have jointed appendages. Body of these animals is triploblastic,, eucoelomate, bilaterally symmetrical and segmented., 3. Rohu: Phylum – Pisces, These are cold blooded aquatic animals living in marine and fresh waters. Their body is, spindle shaped to minimize water-resistance. They have paired & un-paired fins for, swimming. The tail fin is useful as a steering organ during swimming. They use gills for, respiration., 4. Penguin: Phylum- Aves, These vertebrates are completely adapted for aerial life. These are warm blooded i.e., they can maintain their body temperature constant and their body is spindle-shaped to, minimize air resistance during flight. Their forelimbs are modified into wings and the, digits are covered with scales and bear claws. Exoskeleton is present in the form of, feathers., 5. Frog: Phylum- Amphibia, These animals are strictly aquatic during larval life and perform only aquatic respiration, whereas they can live in water as well as on land during adult life and can perform, aquatic as well as aerial respiration. They have two pairs of appendages and their digits, are without claws., 6. Lizard: Phylum- Reptilia, These are cold blooded animals. They creep on the land as their body cannot be lifted, up. Their skin is dry and scaly., , 7. Elephant: Phylum- Mammalia
Page 3 :
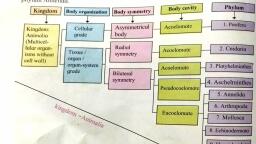
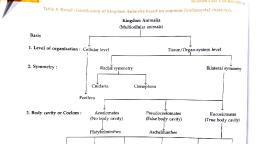
Presence of mammary glands is typical character of this phylum. These animals are, warm blooded. Their body is divided into head, neck, trunk and tail and their digits are, provided with nails, claws, or hooves., 8. Jellyfish: Phylum- Cnidaria, Body of these animals is cylindrical or umbrella-like. Most of these animals are marine., Only few are fresh-water dwellers. Their body is radially symmetrical & diploblastic., Tentacles are useful for capturing the prey whereas cnidoblasts inject the toxin in the, body of prey. Those are useful for protection too., Q. 3. Write in brief about progressive changes in animal classification., Answer : i. Greek philosopher Aristotle was the first to perform the animal classification., He classified the animals according to the criteria like body size, habits and habitats. It, is known as ‘Artificial method’., ii. Besides Aristotle, artificial method of classification was followed by Theophrastus,, Pliny, John Ray, Linnaeus, etc., iii. Later on, ‘Natural system of classification’ was followed. Natural system of, classification was based on various criteria like body organization, types of cells,, chromosomes, bio-chemical properties, etc. Dobzhansky and Meyer propagated the, use of system of classification based on evolution., iv. Recently, Carl Woese has also proposed the animal classification. This system of, animal classification was in practice till now., v. At present, according to the five kingdom classification system of Robert Whittaker,, all multicellular animals are included in Kingdom: Animalia. This system of classification, is based upon some criteria like Body organization, Body symmetry, Body cavity,, Germinal layers, Segmentation, etc., Q. 4. What is the exact difference between grades of organization and symmetry?, explain win examples., Answer : a. Body Organization, i. Body organization of unicellular animals is referred as ‘Protoplasmic grade’, organization., ii. In case of multicellular animals, if tissues are not formed, their body organization is, called as ‘Cellular grade organization’. Ex. Phylum-Porifera.
Page 4 :
iii. In case of some animals, cells come together to form tissues with the help of which, all the body functions are performed. Such animals show ‘Cell - tissue grade’, organization. Ex. Animals from phylum- Cnidaria., iv. Flat worms show ‘Tissue-Organ grade’ organization. In this type of organization,, tissues are organized to form some organs. However, complete organsystems are not, formed., v. Remaining all animals show ‘Organ-system grade organization’ in which different, organs are joined together to form organsystem that performs specific functions. Ex., Crab, Frog, Human, etc., b. Body symmetry, vi. In imaginary sense, if body of any animal is cut through imaginary axis of body, it, may or may not produce two equal halves. Depending upon this property, there are, different types of animal bodies., vii. Asymmetrical Body: In case of such body, there is no any such imaginary axis of the, body through which we can get two equal halves. Ex. Amoeba, Paramoecium, some, sponges., viii. Radial symmetry: In this type of body, if imaginary cut passes through central axis, but any plane of body, it gives two equal halves. Ex. Star fish., ix. Bilateral symmetry: In this type of body, there is only one such imaginary axis of, body through which we can get two equal halves. Ex. Insects, fishes, frog, birds,, human, etc., Q. 5. A. Answer in brief., a. Give scientific classification of shark upto class., Answer : Kingdom- Animalia, Sub-kingdom- Chordates, Phylum- Chordata, Subphylum- Vertebrata, Class- Pisces, Q. 5. B. Answer in brief., Write four distinguishing characters of phylum- Echinodermata.
Page 5 :
Answer : 1. Calcareous spines are present on the body of these animals; hence, they are called as echinoderms., 2. These animals are found only in ocean., 3. Their body is triploblastic, eucoelomate and it is radially symmetrical in adult stage., However, they show bilateral symmetry in larval stage., 4. They perform locomotion with the help of tube-feet. Tube feet are also useful for, capturing the prey. Some animals are sedentary. Examples: Star fish, sea-urchin, brittle, star, sea-cucumber, etc., Q. 5. C. Answer in brief., Distinguish between butterfly and bat with the help of four distinguishing, properties., Answer :, , Q. 5. D. Answer in brief., To which phylum does Cockroach belong? Justify your answer with scientific, reasons., Answer : 1. Cockroach belongs to the phylum Arthropoda., 2. These animals have jointed appendages., 3. They are found in all types of habitats ranging from deepest oceans to highest, mountains., 4. Body of these animals is triploblastic, eucoelomate, bilaterally symmetrical and, segmented., 5. Chitinous exoskeleton is present around their body.
Page 6 :
6. These animals are unisexual., Q. 6. A. Give scientific reasons., Though tortoise lives on land as well as in water, it cannot be included in classAmphibia., Answer : Amphibians are strictly aquatic during larval life and perform only aquatic, respiration whereas they can live in water as well as on land during adult life and can, perform aquatic as well as aerial respiration. This characteristic is not seen in tortoises, that are cold-blooded animals and are observed to creep on land. Hence, they are, included in the class Reptilia and not Mammalia., Q. 6. B. Give scientific reasons., Our body irritates if it comes in contact with jelly fish., Answer : Jellyfish belongs to the phylum Cnidaria. Cnidoblasts bearing tentacles are, present around the mouth. These tentacles are useful for capturing the prey whereas, cnidoblasts inject the toxin in the body of prey. Those are useful for protection too. The, release of the contact and its contact with the skin hence causes irritation when our, body comes in contact with the jelly fish., Q. 6. C. Give scientific reasons., All vertebrates are chordates but all chordates are not vertebrates., Answer : Chordates have a supporting notochord in the body. In sub-phylum, Vertebrata, the notochord present in embryos gets replaced by a cartilaginous or bony, vertebral column in adults. But in cephelochordates, notochord persists throughout life, as such and in urochordates, notochord is present only in larval stages and absent in, adults. Thus, it can be said that all vertebrates are chordates but all chordates are not, vertebrates., Q. 6. D. Give scientific reasons., Balanoglossus is connecting link between non-chordates & chordates., Answer : Through the view point of evolution, Balanoglossus is considered as, connecting link between non-chordates and chordates. This animal shows the, characters of both the groups. It is a chordate since it has a notochord, tubular nerve, cord and gill slits. The invertebrates character includes the phosphogens and larva., Q. 6. E. Give scientific reasons., Body temperature of reptiles in not constant.
Page 7 :
Answer : Reptiles are poikiolotherms, which means they are cold blooded animals., Cold-blooded animals do not maintain a constant body temperature. They get their heat, from the outside environment, so their body temperature fluctuates, based on external, temperatures. Hence, body temperature of reptiles is not constant., Q. 7. A. Answer the following questions by choosing correct option., Which special cells are present in the body of sponges (Porifera)?, A. Collar cells, B. Cnidoblasts, C. Germ cells, D. Ectodermal cells, Answer : Collar cells, Explanation: The specialized type of cells present in the body of sponges belonging to, the Phylum Porifera are known as the collar cells., Q. 7. B. Answer the following questions by choosing correct option., Which of the following animals’ body shows bilateral symmetry?, A. Star fish, B. Jelly fish, C. Earthworm, D. Sponge, Answer : Earthworm, Explanation: Earthworms belong to the Phylum Annelida. They are triploblastic,, bilaterally symmetrical and eucoelomate., Q. 7. C. Answer the following questions by choosing correct option., Which of the following animals can regenerate it’s broken body part?, A. Cockroach, B. Frog, C. Sparrow, D. Star fish, Answer : Star fish, Explanation: Star fish belongs to the Phylum Echinodermata. Animals belonging to this, phylum have a good ability of regeneration., Q. 7. D. Answer the following questions by choosing correct option.
Page 8 :
Bat is included in which class?, A. Amphibia, B. Reptilia, C. Aves, D. Mammalia, Answer : Mammalia, Explanation: Bats are warm-blooded and show the presence of mammary glands., Q. 8. Complete the following chart., , Answer :
Page 9 :
Q. 9, Complete the following chart., , Answer :, , Q. 10. Sketch, labell and classify, Hydra, Jellyfish, Planaria, Round worm, Butterfly, Earthworm, Octopus, Star fish,, Shark, Frog, Wall lizard, Pigeon., Answer : 1. Hydra
Page 11 :
Body organization- Cell tissue, Body symmetry- Radial symmetry, Body cavity- Acoelomate, Phylum- Cnidaria, 3. Planaria, , Kingdom- Animalia, Body organization- Tissue grade, Body symmetry- Bilateral symmetry
Page 12 :
Body cavity- Acoelomate, Phylum- Platyhelminthes, 4. Round worm, , Kingdom- Animalia, Body organization- Organ system grade, Body symmetry- Bilateral symmetry, Body cavity- Eucoelomate, Phylum- Annelida, 5. Butterfly
Page 13 :
Kingdom- Animalia, Body organization- Organ system grade, Body symmetry- Bilateral symmetry, Body cavity- Eucoelomate, Phylum- Arthropoda, 6. Earthworm
Page 14 :
Kingdom- Animalia, Body organization- Organ system grade, Body symmetry- Bilateral symmetry, Body cavity- Eucoelomate, Phylum- Annelida, 7. Octopus
Page 15 :
Kingdom- Animalia, Body organization- Organ system grade, Body symmetry- Bilateral symmetry, Body cavity- Eucoelomate, Phylum- Mollusca, 8. Starfish
Page 16 :
Kingdom- Animalia, Body organization- Organ system grade, Body symmetry- Bilateral symmetry, Body cavity- Eucoelomate, Phylum- Echinodermata, 9. Shark
Page 17 :
Kingdom- Animalia, Body organization- Organ system grade, Body symmetry- Bilateral symmetry, Body cavity- Eucoelomate, Phylum- Pisces, 10. Frog
Page 18 :
Kingdom- Animalia, Body organization- Organ system grade, Body symmetry- Bilateral symmetry, Body cavity- Eucoelomate, Phylum- Amphibia, 11. Wall lizard
Page 19 :
Kingdom- Animalia, Body organization- Organ system grade, Body symmetry- Bilateral symmetry, Body cavity- Eucoelomate, Phylum- Reptilia, 12. Pigeon
Page 20 :
Kingdom- Animalia, Body organization- Organ system grade, Body symmetry- Bilateral symmetry, Body cavity- Eucoelomate, Phylum- Aves
Page 21 :
Q. 11. Label the following., , Answer :, , Jellyfish
Page 22 :
Earthworm, , Tapeworm
Page 23 :
Fish