Page 1 :
Topic: Reported Speech, Subject: English Grammar, , Direct-Indirect Speech, (Rules), BASIC RULES FOR INDIRECT SPEECH, Rule No. 1. Words of the speaker (reported speech) are not enclosed in Inverted Commas or, Quotation Marks in Indirect Speech., Rule No. 2. Usage of word “that”: The conjunction “that” is always used between, reporting verb and reported speech in indirect speech., Example:, • Direct Speech: He said, “I write a letter”., Indirect Speech: He said that he wrote a letter., Rule No. 3. Change in tense of the reported speech: A change is made in tense of reported, speech for changing a direct speech into indirect speech. Rules for tense change are given, below:, Examples:, • Direct Speech: She said, “I am watching a movie”., Indirect Speech: She said that she was watching a movie, • Direct Speech: He says, “I am playing cricket”., Indirect Speech: He says that he was playing cricket., Rule No. 4. Changes in Pronoun: The pronoun (or subject) of reported speech is sometime, changed according to the pronoun (or subject) or Object of the reported verb (first sentence, of Direct speech). The possessive pronouns (i.e. his, her, my, their, your etc.) may also change, according to subject or object of the first sentence., Examples:, • Direct Speech: He said, “I eat two apples”., Indirect Speech: He said that he ate two apples., • Direct Speech: She said to me, “I like your book”., Indirect Speech: She said to me that she liked my book., Rule No. 5. Change in Time: If there is time mentioned in the sentence of Direct speech, the, time will be changed in Indirect Speech. There are certain rules changing the time. i.e. not, into then, tomorrow into the next day, today into that day, yesterday into the previous day., Examples:, • Direct Speech: She said, “I am buying a laptop today”., Indirect Speech: She said that she was buying a laptop that day., • Direct Speech: He said, “I need your now”., Indirect Speech: He said that he needed my help then., , Change of pronouns, , Direct Speech, I, We, My, Your, Our, , Indirect Speech, He/ She, They, His/ Her, My, Their
Page 2 :
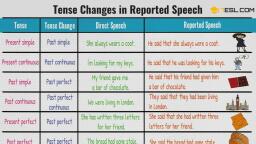
Topic: Reported Speech, Subject: English Grammar, , Change of place and time, words, , Direct Speech, Me, Us, Here, Today, Now, This, These, Thus, This morning, Yesterday, Tomorrow, Next week, Next month, , Indirect Speech, Him/ Her, Them, there, That day, Then, That, Those, So, That morning, The day before, The next day, The following week, The following month, , DIRECT SPEECH CHANGES - INTO INDIRECT SPEECH (TENSE CHANGE), (i), Present Simple Tense into Past Simple Tense, (ii) Present Progressive Tense into Past Progressive Tense, (iii) Present Perfect Tense into Past Perfect Tense, (iv) Present Perfect Progressive Tense into Past Perfect Tense, (v) Past Simple Tense into Past Perfect Tense, (vi) Past Progressive Tense into Perfect Continuous Tense, (vii) Past Perfect Tense (The tense remains unchanged), (viii) Past Perfect Progressive Tense (The tense remains unchanged), (ix) Future Simple Tense (e.g. will) into “would”, (x) Future Progressive Tense (e.g. will be) into “would be”, (xi) Future Perfect Tense (e.g. will have) into “would have”, (xii) Future Perfect Progressive Tense (e.g. will have been) into “would have been”, , RULES FOR AFFIRMATIVE/ POSITIVE SENTENCES, 1. PRESENT TENSE, PRESENT SIMPLE changes into PAST SIMPLE, She said, “I work in a hospital”., She said that she worked in a hospital., They said, “We play Football”., They said that they played Football., He said, “I love my parents”., He said that he loved his parents., She said, “I don’t waste time”., She said that she didn’t waste time., PRESENT PROGRESSIVE changes into PAST PROGESSIVE, He said, “I am waiting for someone”., He said that he was waiting for someone., I said, “She is driving a car”., I said that she was driving a car., She said, “They are enjoying the music”. She said that they were enjoying the music., David said, “I am not going to College”. David said that he was not going to College., PRESENT PERFECT changes into PAST PERFECT, She said, “ I have completed the work”, She said that she had completed the work., John said, “I have won a prize”., John said that he had won a prize., He said, “She has washed the shirts”, He said that she had washed the shirts., David said, “I have not met her”., David said that he had not met her.
Page 3 :
Topic: Reported Speech, Subject: English Grammar, PRESENT PERFECT PROGRESSIVE changes into PAST PERFECT PROGRESSIVE, She said, “I have been working in a factory for, She said that she had been working in a factory, two years., for two years., David said, “he has been waiting for his brother David said that he had been waiting for his, for three hours”, brother for three hours., They said, “We have been living in America, They said that they had been living in America, since 2013”., since 2013., , 2. PAST TENSE, PAST SIMPLE changes into PAST PERFECT, He said, “I started a Job”., He said that he had started a job., She said, “I bought a new car”., She said that she had bought a new car., They said, “We went to a market”, They that they had gone to a market., He said to me, “You didn’t help me”, He said to me that I had not helped him., PAST PROGRESSIVE changes into PAST PERFECT PROGRESSIVE, He said, “I was writing a poem”, He said that he had been writing a poem., The kids said, “We were playing a game”. The kids said they had been playing a game., They said, “We were watching a movie”., They said they had been watching a movie., She said, “I was not making a noise”., She said that she had not been making a noise., PAST PERFECT changes into PAST PERFECT (No change in tense), They said, “We had won the game”, They said that they had won the game., He said, “I had gone to home”., He said that he had gone to home., David said, “I had passed the exam”., David said that he had passed the exam., She said, “I had not received the letter”., She said that she had not received the letter., , 3. FUTURE TENSE, FUTURE SIMPLE TENSE, WILL changes into WOULD, She said, “I will go to London”., She said that she would go to London., He said, “I will start a new job”., He said that he would start a new job., They said to me, “We will help you”., They said to me that they would help me., She said, “I will not waste time”., She said that she would not waste time., FUTURE CONTINUOUS TENSE, WILL BE changes into WOULD BE, He said to me, “I will be waiting for you”., He said to me that he would be waiting for me., David said, “I will be making tea”., David said that he would be making tea., She said, “I will be feeding my kids”., She said that she would be feeding her kids., They said, “We will not be driving a car”., They said that they would not be driving a car., FUTURE PERFECT TENSE, WILL HAVE changes into WOULD HAVE, She said, “I will have cooked the food”., She said that she would have cooked the food., He said, “I will have cleaned the room”., He said that he would have cleaned the room., David said, “I will have called a Doctor”. David said that he would have called a Doctor.
Page 4 :
Topic: Reported Speech, Subject: English Grammar, , RULES FOR INTERROGATIVE/ QUESTION SENTENCES, The basic rules for converting Direct Speech (question sentences) into Indirect Speech are as, follows:, (i) Comma and inverted commas will be removed., (ii) The conjunction “that” will not be used in Indirect Speech (in question sentence). The, conjunction “that” is used in Indirect speech of all positive sentences., (iii) In indirect speech, the question sentence will be expressed in assertive (positive) form, instead of interrogative form., (iv) Question mark (?) will not be used in indirect speech of interrogative sentence. ., (v) The verb such as ‘say’ or ‘tell’ (e.g. he said or she said) in direct speech is replaced with, verb such ‘ask’ or ‘inquire’ (e.g. he asked, she inquired) in indirect speech., The above rules are common for all question-sentences. Apart from these common rules, there, are a few specific rules which apply according to the type of question in sentence., There are two types of question-sentences:, 1. Question which can be answered with YES or NO, 2. Question which cannot be answered only with YES or NO, but requires a detailed answer., Such questions usually start with “what, why, how, when etc.”, Examples:, • Do you like a mango? (Such a question can be answered by saying only YES or No), • What are you doing? (Such a question cannot be answered by Yes or No but it requires, a bit explanation i.e. I am listening to music.), The specific rules according to type of question are as follows:, , Questions that CAN be answered with “YES or NO”, To make indirect speech of such questions, the word “if” or “whether” will be used in Indirect, Speech. Both the words “if” or “whether” can be used interchangeably., Examples:, Direct Speech, David said to me, “Do you like coffee?”, He said to me, “Will you help me?”, She said to me, “Can I use your Phone?”, They told me, “Have you gone to London?”, He said to me, “Did you meet your friend?”, John said to her, “Will you buy the book?”, She said, “Are they waiting for me?”, , Indirect Speech, David asked me if I liked coffee., He asked me if I would help him., She asked me if she could use my Phone., They asked me if I had gone to London., He asked me if I had met my friend., John asked her whether she would buy the book., She asked whether they were waiting for her., , Questions that CANNOT be answered with only “YES or NO”, To make indirect speech of such questions, the word “if” or “whether” will not be used. The, question is changed into assertive(positive) form and is simply placed after the reporting verb., Examples:, Direct Speech, He said to me, “What are you doing?”, She said to me, “What is your name?”, David said to me, “How are you?”, , Indirect Speech, He asked me what I was doing., She asked me what my name was., David asked me how I was.
Page 5 :
Topic: Reported Speech, Subject: English Grammar, They said to me, “where have you gone?”, Teacher told her, “Why did you fail the exam?, I said to her, “What were you eating?”, He said to her, “How will you help me?”, The student said, “How can I buy this book?”, They said, “How is the weather?”, She said, “Who was that fantastic man?”, , They asked me where I had gone., Teacher asked her why she had failed the exam., I asked her what she had been eating., He asked her how he would help her., The student asked how he could buy this book., They asked how the weather was., She asked me who that fantastic man had been., , INDIRECT SPEECH FOR IMPERATIVE SENTENCES, A sentence that expresses a command, a request, an advice or a suggestion is called an imperative, sentence. Examples:, • Open the door., (command), • Please help me., (request), • Quit smoking., (advice), • Don’t make a noise., (command), As imperative sentences have a command (or an order), a request, an advice or a suggestion, to, change them into Indirect Speech, some specific verbs (i.e. requested, order, advised, forbade,, suggested) replace the verbs (e.g. said, told) of reporting verb. The conjunction used used in these, sentences is “to”., Examples:, 1., 2., 3., 4., , Direct Speech, She said to me, “Please help me”., Teacher said to him, “Do not waste your time”., He said to her, “Please lend me your Camera for, one day”., Doctor said to him, “Avoid unhealthy food”., , 5. The Boss said to the employee, “Get out of the, room”, 6. He said to his servant, “Clean the room”., , 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6., , Indirect Speech, She requested me to help her., Teacher advised him not to waste his time., He requested her to lend him her camera, for one day., Doctor advised him to avoid unhealthy, food., The Boss ordered the employee to get out, of the room., He ordered his servant to clean the room., , INDIRECT SPEECH FOR MODALS, For converting direct speech into indirect speech, Present Modals (e.g. Must, Can, May) are, changed into Past Modals (i.e. Could, Might, Had to)., Examples:, Direct Speech, He said, “I can sing a song”., She said, “I can write a poem”., David said, “I can play a Guitar”., She said, “I may go to Paris”., They said, “We may buy a car”., He said, “I may call a Doctor”., , Indirect Speech, CAN changes into COULD, He said that he could sing a song., She said that she could write a poem., David said that he could play a Guitar., MAY changes into MIGHT, She said that she might go to Paris., They said that might buy a car., He said he might call a Doctor., MUST (not changed)
Page 6 :
Topic: Reported Speech, Subject: English Grammar, Direct Speech, He said, “I must study this book”., They said, “We must finish the work in time”., She said, “I must eat a healthy diet”., , Indirect Speech, He said that he must study that book., They said that they must finish the work in time., She said that she must eat a healthy diet., , Modals like Should, Might, Could, Would, Ought to are not changed in Indirect Speech., Direct Speech, He said, “I should start a Job”., She said, “I might eat a cake”., David said, “I could buy a Camera”., He said, “I would decorate the walls”., Gabbar said, “I ought to avoid unhealthy diets”., , Indirect Speech, He said that he should start a Job., She said that she might eat a cake., David said that he could buy a Camera., He said that he would decorate the walls., Gabbar said that he ought to avoid unhealthy diets.