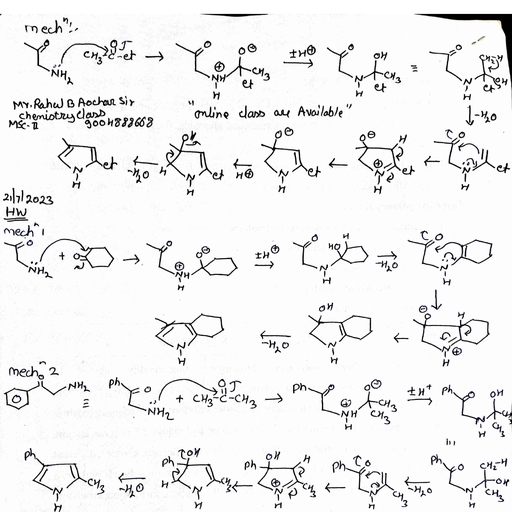
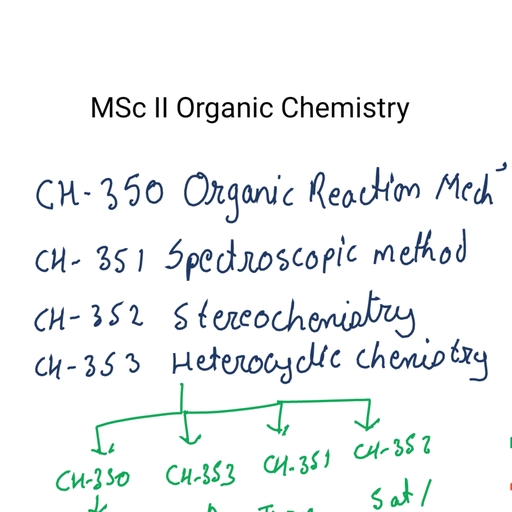
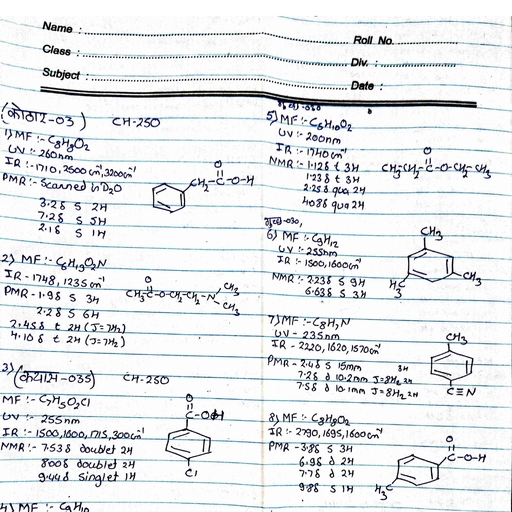
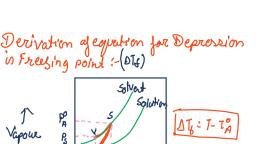
Page 1 :
Arts Commerce and Science college Bodwad, Dist: Jalgaon, Department of Chemistry, Question Bank, S.Y.B.Sc -Sem-III- 2020-21, Chemistry -I- Physical and Inorganic chemistry, -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------1. What is a substance that is dissolved in another substance?, a) solution, b) solute, c) solvent, d) compound, 2. What is a solvent?, a) The substance that does the dissolving in a other substance, b) The substance that is being dissolved in a solution., c) The mixing of different substances., d) The process in which neutral molecules loose or gain electrons, 3. What happens to vapor pressure when you add a solute to a solution?, a) It lowers the vapor pressure., b) It has no effect., c) It raises the vapor pressure., d) It causes the reaction to reach equilibrium., 4. What is osmotic pressure?, a) It is the minimum pressure that must be applied to a solution to stop osmosis from, happening., b) It is the maximum pressure that must be applied to a solution to stop osmosis from, happening., c) It is the maximum pressure of the vapor over a liquid at equilibrium., d) It is the minimum pressure of the vapor over a liquid at equilibrium., 5. PA and PB are the vapour pressure of pure liquid components, A and B, respectively of, an ideal binary solution. If XA and XB represents the mole fraction of component A and, B, the total pressure of the solution will be, a), b), c), d), , PB + XA (PB – PA), PB+ XB (PA – PB), PA+ XB (PB – PA), PA+ XA (PA – PB), , 6. A solution of two liquids boils at a temperature more than the boiling point of, either of them. Hence, the binary solution shows, a) Azeotrope with maximum boiling point, b) Azeotrope with minimum boiling point, c) No change, d) Obeys Raoult’s law, By- Smt. Kanchan Damade, Department of Chemistry, Arts, Commerce and Science College Bodwad
Page 2 :
7. Which of the following statements is false?, a) Units of atmospheric pressure and osmotic pressure are the same., b) In reverse osmosis, solvent molecules move through a semipermeable membrane from a, region of lower concentration of solute to a region of higher concentration., c) The value of molal depression constant depends on nature of solvent., d) Relative lowering of vapour pressure, is a dimensionless quantity, 8. If two liquids A and B form minimum boiling azeotrope at some specific composition, then., a) A–B interactions are stronger than those between A–A or B–B., b) vapour pressure of solution increases because more number of molecules of liquids A and, B can escape from the solution., c) vapour pressure of solution decreases because less number of molecules of only one of, the liquids escape from the solution., d) A–B interactions are weaker than those between A–A or B–B., 9. The vapor pressure of a solution containing a non-volatile solute is directly proportional, to the, a) molality of the solvent., b) osmotic pressure of the solute., c) molarity of the solvent., d) mole fraction of solvent., e) mole fraction of solute, 10. A solution made by dissolving 9.81 g of a nonvolatile nonelectrolyte in 90.0 g of water, boiled at 100.37 oC at 760 mm Hg. What is the approximate molecular weight of the, substance? (For water, Kb = 0.51 oC/m), a), 240 g/mol, b), 150 g/mol, c), 79 g/mol, d), 61 g/mol, e), 34 g/mol, 11. What is the freezing point of an aqueous 1.00 m NaCl solution? (Kf = 1.86 oC/m), (Assume complete dissociation of the salt.), a) -1.86 oC, b) +1.86 oC, c) -3.72 oC, d) -0.93 oC, e) 0.0 oC, 12. Colligative properties depend upon:, a) The type of solute particles, b) The number of solute particles, c) Both the type and number of solute particles, , By- Smt. Kanchan Damade, Department of Chemistry, Arts, Commerce and Science College Bodwad
Page 3 :
13. For a non-volatile solute, colligative properties are measured on:, a), The solvent, b), The solute, c), Both the solvent and solute, 14. The freezing point depression is defined as:, A. Tf - Tfo, B. Tf + Tfo, C. Tfo - Tf, D. Tfo × T, 15. The boiling point elevation is defined as:, a. Tb - Tbo, b. Tb + Tbo, c. Tbo - Tb, d. Tbo × Tb, 17. A semipermeable membrane allows:, a. Only solute through, b. Only solvent through, c. Both solute and solvent through, 18. The graph below plots the vapor pressure of two volatile liquids A and B that form an ideal, solution, , a. Line "A" represents:, a. Partial vapor pressure PA, , b. Partial vapor pressure PB, , c. Total vapor pressure P, , b. Partial vapor pressure PB, , c. Total vapor pressure P, , b. Line "B" represents:, a. Partial vapor pressure PA, , c. Line "C" represents:, a. Partial vapor pressure PA, , b. Partial vapor pressure PB, , c. Total vapor pressure P, , By- Smt. Kanchan Damade, Department of Chemistry, Arts, Commerce and Science College Bodwad
Page 4 :
19. The graph below contains dashed lines representing the measured vapor pressure,, and solid lines representing the ideal vapor pressure for a mixture of volatile, liquids A and B. The A-B intermolecular forces are:, , a. More attractive than A-A or B-B forces, b. Similar to A-A or B-B forces, c. More repulsive than A-A or B-B forces, 20. The graph below contains dashed lines representing the measured vapor pressure, and solid, lines representing the ideal vapor pressure for a mixture of volatile liquids A and B. The AB intermolecular forces are:, , a. More attractive than A-A or B-B forces, b. Similar to A-A or B-B forces, c. More repulsive than A-A or B-B forces, 21. Which of the following is the best description of a semipermeable membrane in the context, of osmosis?, a) A membrane that allows neither solute nor solvent particles to pass through it., b) A membrane that allows solute particles, but not solvent particles, to pass through it., c) A membrane that allows solvent particles, but not solute particles, to pass through it., d) A membrane that allows both solute and solvent particles to pass through it., 22. State the Van't Hoff factor (i) for a dilute aqueous solution of the strong electrolyte barium, hydroxide, Ba(OH)2, a) 0, , b) 1, , c) 2, , d) 3, , By- Smt. Kanchan Damade, Department of Chemistry, Arts, Commerce and Science College Bodwad
Page 5 :
23. Which of the following is a colligative property, a), b), c), d), , Osmotic pressure, Boiling point, Vapour pressure, Freezing point, , 24. The colligative properties of a solution depend on, a), b), c), d), , Nature of solute particles present in it, Nature of solvent used, Number of solute particles present in it, Number of moles of solvent only, , 25. Which of the following is not a colligative property, a), b), c), d), , Osmotic pressure, Elevation in B.P., Vapour pressure, Depression in freezing point, , 26. Colligative properties of a solution depends upon, a), b), c), d), , Nature of both solvent and solute, The relative number of solute and solvent particles, Nature of solute only, Nature of solvent only, , 27. Colligative properties are used for the determination of, a), b), c), d), e), , Molar Mass, Equivalent weight, Arrangement of molecules, Melting point and boiling point, Both A and B, , 28. Molarity of a solution is expressed as:, a) the number of moles of a solute present in one litre of the solution., b) the number of moles of a solute present in 1000 gm of the solvent., c) the number of gram equivalent of solute present in one litre of solution., d) the ratio of the number of moles of solute to the total number of moles of solute, 29. of the following characteristics is not possessed by an ideal solution:, a) obeys Raoult’s law., b) volume change on mixing is not equal to zero., c) there should be no chemical reaction between solute and solvent., d) only very dilute solutions behave as ideal solutions., 30. The phenomenon of lowering of vapour pressure is defined as:, a) decrease in vapour pressure of a solvent on addition of a volatile non electrolyte solute in it., By- Smt. Kanchan Damade, Department of Chemistry, Arts, Commerce and Science College Bodwad
Page 6 :
b) decrease in vapour pressure of a solvent on addition of a non-volatile non electrolyte solute in, it., c) decrease in vapour pressure of a solvent on addition of a volatile electrolyte solute in it., d) decrease in vapour pressure of a solvent on addition of a non-volatile solute in it., 31. The value of Ebullioscopic constant or boiling point elevation constant depends on:, a) amount of solute., b) nature of solute., c) amount of solvent., d) nature of solvent., 32. The unit of Cryoscopic constant is:, a) kelvin kg mol-1, b) kelvin kg-1 mol-1, c) kelvin kg mol+1, d) kelvin kg+1 mol+1, 33. Vapour pressure decreases with:, a) increase in concentration of the solution., b) decrease in solute particles in the solution., c) decrease in boiling point., d) increase in freezing point., 34. Positive deviation from Raoult’s law is observed when:, a. inter molecular forces of attraction between the two liquids is greater than that between, individual liquids., b. inter molecular forces of attraction between the two liquids is smaller than that between, individual liquids., c. force of attraction between two liquids is greater than that between individual liquids., d. force of attraction between two liquids is smaller than that between individual liquid., 35. Addition of non-volatile solute in water results in:, a) an increase in melting point of the liquid., b) a decrease in the boiling point of the liquid., c) a decrease in the vapour pressure of the liquid., d) no change in the boiling point of the liquid., 36. Which of the following pair of liquids are immiscible?, a) Acetone + water., b) Benzene + water., c) Ethanol + water., d) Acetic acid + water., 37. Osmotic pressure of a solution is:, a) Inversely proportional to its absolute temperature., b) Inversely proportional to its centigrade temperature., By- Smt. Kanchan Damade, Department of Chemistry, Arts, Commerce and Science College Bodwad
Page 7 :
c) Directly proportional to its centigrade temperature., d) Directly proportional to its absolute temperature., 38. If the solvent boils at a temperature T1 and the solution at a temperature T2 , then the, elevation of boiling point is given by:, a) T1 + T2., b) T1 – T2., c) T2 – T1., d) None of the above., 39. The ratio of elevation in B.P to molality of solution is known as:, a) Molar elevation constant., b) Mole elevation constant., c) Normal elevation constant., d) Molal elevation constant., 40. Two solutions C and D are separated by a semi-permeable membrane. If liquid flows, From D to C then., a) Both have same concentration., b) D is less concentrated than C., c) D is more concentrated than C., d) None of these., 41. Unit of molarity is:, a) Kg / litre., b) mol / litre., c) gm / litre., d) none of these., 42. Relative lowering of vapour pressure is a colligative property because __________., a) It depends on the concentration of a non electrolyte solute in solution and does not depend on, the nature of the solute molecules., b) It depends on number of particles of electrolyte solute in solution and does not depend on the, nature of the solute particles., c) It depends on the concentration of a non electrolyte solute in solution as well as on the nature, of the solute molecules., d) It depends on the concentration of an electrolyte or nonelectrolyte solute in solution as well, as on the nature of solute molecules., 43. Colligative properties are observed when ___________., a), b), c), d), , a non volatile solid is dissolved in a volatile liquid., a non volatile liquid is dissolved in another volatile liquid., a gas is dissolved in non volatile liquid., a volatile liquid is dissolved in another volatile liquid, , By- Smt. Kanchan Damade, Department of Chemistry, Arts, Commerce and Science College Bodwad
Page 8 :
44. Which of the following units is useful in relating concentration of solution with its vapour, pressure?, a), b), c), d), , mole fraction, parts per million, mass percentage, molality, , 45. The unit of ebulioscopic constant is _______________., a), b), c), d), , K/ kg mol–1 or K (molality)–1, mol kg K–1 or K–1(molality), kg mol–1 K–1 or K–1(molality)–1, K mol kg–1 or K (molality), , 46. Van’t Hoff factor (i)is given by the expression _____________., a), b), c), d), , i, i, i, i, , =, =, =, =, , Normal molar mass / Abnormal molar mass, Abnormal molar mass / Normal molar mass, Observed colligative property / Calculated colligative property, Calculated colligative property / Observed colligative property, , 47. Saturated solution is, a) Solution having same osmotic pressure at a given temperature as that of given solution., b) A solution which contains maximum amount of solute that can be dissolved in a given, amount of solvent at a given temperature, c) Solution with two components, d) solution whose osmotic pressure is less than that of another, 48. Soda water is, a) A solution of gas in solid, b) A solution of gas in gas, c) A solution of gas in liquid, d) A solution of liquid in solid, 49. the condition for ideal equation, a) mix H = zero, b) mix V = zero, c) obeys raoults law, d) all of the above, 50. Sugar solution is-----a) A solution of solid in liquid, b) A solution of liquid in solid, c) A solution of solid in solid, d) A solution of gas in gas, 51. Equation for osmotic pressure is---a) Tf = Kfm, b) = CRT, c) P = X1P1 + X2P2, d) P = KH.x, e) Tb = Kbm, By- Smt. Kanchan Damade, Department of Chemistry, Arts, Commerce and Science College Bodwad
Page 9 :
52. Equation for depression in freezing point is---a) Tf = Kf. m, b) = CRT, c) P = X1P1 + X2P2, d) P = KH. x, e) Tb = Kb . m, 53. Equation for elevation in boiling point is---a) Tf = Kf. m, b) = CRT, c) P = X1P1 + X2P2, d) P = KH. xs, e) Tb = Kb. M, 54. Match the terms given in Column I with expressions given in Column II., Column I, 1. Mass percentage, , (a), , Column II, Number of moles of the solute component, Volume of solution in litres, , 2., , Volume percentage, , (b), , 3., , Mole fraction, , (c) Volume of the solute component in solution x 100, Total volume of solution, , Number of moles of a component, Total number of moles of all the components, , 4. Molality, , (d) Mass of the solute component in solution x 100, Total mass of the solution, , 5. Molarity, , (e), , a), b), c), d), , Number of moles of the solute components, Mass of solvent in kilograms, , 1-d, 2-c, 3-b, 4-e, 5-a, 1-a, 2-c, 3-b, 4-e, 5-d, 1-b, 2-c, 3-d, 4-e, 5-a, 1-e, 2-c, 3-b, 4-d, 5-a, , 55. Azeotrope is-_______, a) At a particular conc. the mixture of two or more than two components boil at constant temp., b) A mixture of two partially miscible components, c) A mixture which can be separated by distillation., d) A type-I solution, 56. The solubility of a gas in water depends on, a) Nature of the gas, b) Temperature, c) Pressure of the gas, d) All of the above, 57. The molarity of 0.006 mole of NaCl in 100 ml solution is, (a), 0.6, (b), 0.06, By- Smt. Kanchan Damade, Department of Chemistry, Arts, Commerce and Science College Bodwad
Page 10 :
(c), , 0.006, , (d), , 0.066, , 58. The sum of the mole fraction of the components of a solution is, (a) 0, (b) 1, (c) 2, (d) 4, 59. Phenol water system exhibits _________ system, a) Maximum Critical solution temperature (CST), b) Minimum Critical solution temperature, c) Both Minimum and Maximum Critical solution temperature, d) Without CST, 60. A real solution is that which obeys__________, a) Raoult’s law, b) Donot obeys raoults law, c) Obeys henry’s law, d) Donot obeys henrys law, 61. Normality is a solution of number of __________ weight in 1 litres of solvents., a) Molecular, b) Moles, c) Equivalent, d) Formula weight, e) Mole fraction, 62. The temperature at which V.P f liquids is equal to atmospheric pressure is, a) Boiling point, b) Melting point, c) Freezing point, d) Fusion, 63.Unit of mole fraction is, a) Mol/ lit, b) Mol/kg, c) Mol/lit2, d) Dimensionless, 64. Nicotine- water system exhibits _________ system, a) Maximum Critical solution temperature (CST), b) Minimum Critical solution temperature, c) Both Minimum and Maximum Critical solution temperature, d) Without CST, 65. Molarity is a solution of number of __________ of solute in 1 litres of solvents., a) Molecular, b) Moles, c) Equivalent, d) Formula weight, e) Mole fraction, 66. Triethylamine- water system exhibits _________ system, a) Maximum Critical solution temperature (CST), b) Minimum Critical solution temperature, By- Smt. Kanchan Damade, Department of Chemistry, Arts, Commerce and Science College Bodwad
Page 11 :
c) Both Minimum and Maximum Critical solution temperature, d) Without CST, 67. Unit of molality is, a) Mol/ lit, b) Mol/kg, c) Mol/lit2, d) Dimensionless, 68. In fractionating column distillation is carried out by ----a) Discontinuous manner, b) Continuous manner, c) Batch wise, d) None of the above, 69. The solubility of a solid in water depends on, a) Nature of the solid, b) Temperature, c) Pressure of the solid, d) All of the above, 70. The methods by which osmotic pressure is measured_______, a) Landsberger method, b) Beckmann’s method, c) Berkley and Hertley method, d) Vant’hoff method, 71. The methods by which elevation in boiling point is measured_______, a) Landsberger method, b) Beckmann’s method, c) Berkley and Hertley method, d) Vant’hoff method, 72. The methods by which depression in Freezing point is measured_______, a) Landsberger method, b) Beckmann’s method, c) Berkley and Hertley method, d) Vant’hoff method, 73. Write the electronic configuration of chromium (Atomic number; Cr = 24)., a) [Ar], 3d5, 4s1, b) [Ar], 3d4, 4s2, c) [Ar], 3d5, 4s2, d) none of the above, 74. Write the electronic configuration of copper (Atomic number, Cu=29)., a) [Ar], 3d9, 4s2, b) [Ar], 3d10, 4s1, c) [Ar], 3d10, 4s2, d) None of the above, 75. Give the general electronic configuration of transition metals., a) [Ar], 3d1-10, 4s1 or 2, b) [Ar], 3d0-10, 4s1 or 2, By- Smt. Kanchan Damade, Department of Chemistry, Arts, Commerce and Science College Bodwad
Page 12 :
c) [Ar], 3d1-10, 4s2, d) None of the above, 76. Write the electronic configuration of Manganese (Atomic number, Mn = 25)., a) [Ar], 3d5, 4s2, b) [Ar], 3d6, 4s1, c) [Ar], 3d5, 4s1, d) None of the above, 77. 'd' block element have ability to form complexes because they have ---a) Variable oxidation no., b) Higher coordination no., c) Small size, d) All the above three, 78. Out of the following which is co-ordination compounds?, a) FeSO4, b) K4[Fe (CN)6], c) KCN, d) Fe (CN)6, 79. CuSO4 is blue in colour while ZnSO4 is colourless. Because-----a) Cu has partial filling of d orbital & in Zn d orbital is completely filled, b) Cu has filled d orbital & in Zn d orbital is completely filled, c) Cu is smaller & Zn is larger in size, d) Other than above, 80. Out of the following elements which compounds are colourless complexes?, a) Fe2+, b) Mn2+, c) Zn2+, d) Ni2+, 81. What is unit of magnetic moment?, a) Cm, b) BM, c) MM, , d) KM, , 82. Why d- block elements show variable oxidation states?, a) Energy difference between (n-1) d and ns orbitals are very small, b) Electrons from 4s & 3d energy levels can be used for bonding, c) Elements are present in transition series, d) Both a & b, 83. What is spin only formula?, a) μ = √n (n + 2), b) μ = √ n (n + 1), c) μ = √n (n x 2), d) other than above three, 84. What is magnetic moment of Mn2+ by spin only formula?, a) 5.91, b) 4.90, c) 3.87, d) 1.73, 85. What is magnetic moment of Cr3+ by spin only formula?, a) 5.91, b) 4.90, c) 3.87, d) 1.73, , By- Smt. Kanchan Damade, Department of Chemistry, Arts, Commerce and Science College Bodwad
Page 13 :
86. Which element in d block shows maximum oxidation state?, a) Fe, b) Mn, c) Zn, d) Cu, 87. Haemoglobin in blood contain -------------------- metal, a) Mn, b) Fe, c) Zn, d) Cu, 88. Which groups of elements are called d-block elements in modern periodic table?, a) 1 to 2, b) 3 to 10, c) 3 to 12, d) 13 to 18, 89. In modern periodic table, by which name d-block elements are known?, a) More electropositive elements, b) Transition elements, c) Less electropositive elements, d) Inner transition elements, 90. When d-block elements are considered as d-block elements?, a) d-orbital is fully filled in ground state., b) d-orbital is half filled in ground state., c) d-orbital is fully filled in all oxidation states., d) d-orbital is fully filled in only anyone oxidation state, 91. Which of the following does not relevant with transition elements?, a) Melting points of transition elements are high., b) Some ions of transition elements possess paramagetic properties., c) All transition elements dissolves in acid., d) Transition elements processes various oxidation state., 92. Which of following statement is wrong?, a) Atoms of all transition elements are paramagnetic., b) All transition elements are metals., c) All elements of d-block are transition elements., d) d-block elements are present in between s & p block elements in periodic table., 93. How many d-electrons are there in Fe2+ (Z = 26), (A) 4, (B) 5, (C) 6, D) 3, 94. What is oxidation no. of Cr in K2Cr2O7, (A) +2, (B) +4, (C) +6, , (D) +7, , 95. Lanthanide contraction is observed due to increase in.............., a) Atomic radii, b) Volume of 4f orbital, c) Effective nuclear charge, d) Atomic number, 96. Which block elements are more electropositive in modern periodic table?, (a) s, (b) p, (c) d, (d) f, 97. How many d-electrons are there in Ti (Z = 22), (a) 2, (b) 5, (c) 6, (d) 3, , By- Smt. Kanchan Damade, Department of Chemistry, Arts, Commerce and Science College Bodwad
Page 14 :
98. What is magnetic moment of Sc+2 by spin only formula?, a) 5.91, b) 4.90, c) 3.87, d) 1.73, 99. Which of ion has largest radii?, a)., Mn+3, b). Fe+3, , c). Cr+3, , d).Co+3, , 100. Which of the following pair are chemical twins., a) Mo and W, b) Zr and Ta, c) Mo and Hf, d) Ru and Os, , __________________________________Best of Luck________________________________, , By- Smt. Kanchan Damade, Department of Chemistry, Arts, Commerce and Science College Bodwad