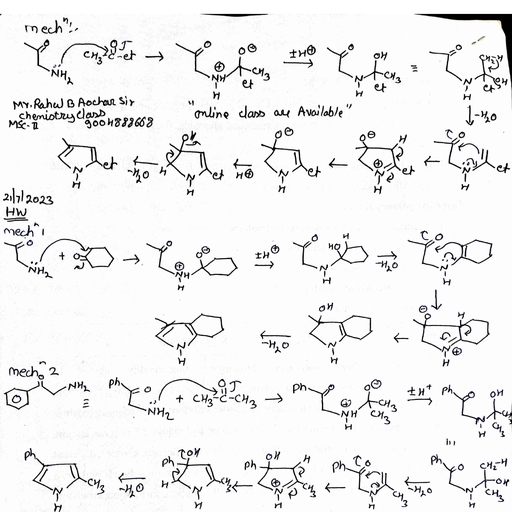
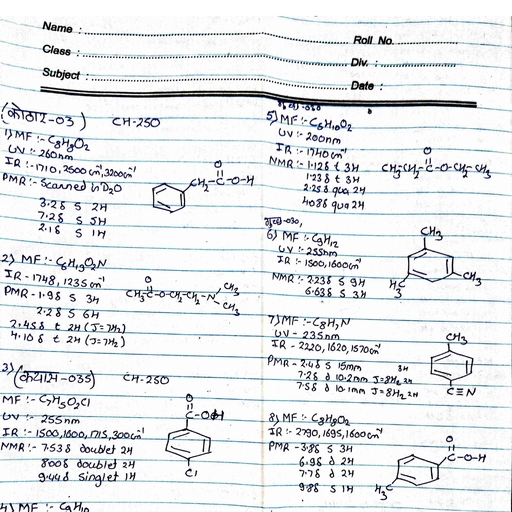
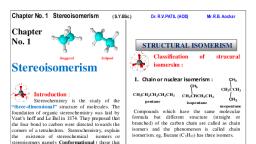
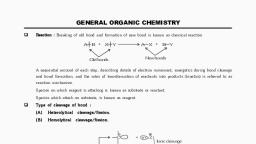
Page 1 :
Arts, Commerce and Science College, Bodwad., Question Bank, S.Y. B.Sc. Sem-III, , Subject: - Organic & Inorganic Chemistry (Chem-II), , ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------, , Multiple Choice Questions, , 1. Optical activity is shown by a molecule which--------a) Contains at least 3 asymmetric centers, b) is asymmetric or dissymmetric as whole., c) has plane of symmetry., d) has a center of symmetry., , 2. An asymmetric carbon atom has--------a) one different atom or group., b) two different atom or group., c) three different atom or group., d) four different atom or group., , 3. In the complete rotation of butane from 0o to 360o the gauche conformation appear--------a) Once, , b) Twice, , c) Thrice, , d) Four times., , 4. In structural representation of molecule the prefixes Z and E stands for --------a) Zigle - Erythro, , b) Zusammen – Estrogen, , c) Zeigle - Erhard, , d) Zusammen – Entgegen., , 5. Racemic mixture is equimolar concentration --------a) Enantiomers, , b) Diastereomers, , c) Enantiomer and meso compound, , d) None of these, , 6. The priority sequence for the hydrogen isotopes is---------
Page 2 :
a) H > D > T, , b) T > D > H, , c) H > T > D, , d) D > T > H, , 7. In the R-S notation, the prefixes R and S stands for --------a) Rectus-simiantus, , b) Rectus-sinister, , c) Rotamer-simiantus, , d) Rotamer-sinister., , 8. ---------is the most stable conformation of n-butane., a) Gauche, , b) Fully eclipsed, , c) Anti or staggered, , d) Partially eclipsed., , 9. The atoms or groups which are behind the plane of the paper are shown by -----a) Thick line, , b) Normal lines, , c) Dotted lines, , d) Zig-zag lines, , 10. The prefixes used in the nomenclature of stereoisomer of oximes are -----a) Cis-trans, , b) Z-E, , c) Syn-anti, , d) Eclipsed-Staggered., , 11. Which of the following is not a projection formula., a) Newman, , b) Wedge, , c) Fischer, , d) Newton, , 12. The light consisting of only one wavelength is called as…………………light, a) Polarized, , b) Monochromatic, , c) Visible, , d) Invisible, , 13. The plane polarized light vibrates only in ……………..plane., a) One, , b) two, , c) Many, , d) Does not vibrate, , 14. The instrument used to measure optical rotation is…….., a) Polarimeter, , b) Slit, , c) Nicol prism, , d) Microscope, , 15. The compound which contains chiral centre but, optically inactive is called…….., a) Dextrorotatory, , b) Levorotatory, , c) Enantiomer, , d) Meso compound
Page 3 :
16. The stereoisomers which are not mirror images of each other are called as……., a) Epimers, , b) Conformers, , c) Diastereomers, , d) None of these, , 17. Which of the following type of isomer contain similar group on same side of the double bond, a) Cis, , b) Trans, , c) Eclipsed, , d) Staggered, , 18. The stereoisomers which can be interconverted by rotation of single bond are called.., a) Configurational isomers, , b) Geometrical isomers, , c) Conformational isomers, , d) Chain isomers, , 19. The isomers which differ in the position of substituent are called……., a) Position isomers, , b) Chain isomers, , c) Functional isomers, , d) Metamers, , 20. The most unstable conformation of cyclohexane is, a) Boat, , b) Half chair, , c) Twist chair, , d) Chair, , 21. Eclipsed bonds are seen in ………………..conformation of cyclohexane, a) Boat, , b) Half chair, , c) Twist chair, , d) Chair, , 22. Chair-chair interconversion is possible by,, a) stretching, , b) bending, , c) ring flipping, , d) twisting, , 23. The boat conformation of cyclohexane is less stable due to…………hydrogens, a) equatorial, , b) axial, , c) all, , d) flag-pole, , 24. ………………..conformation of cyclohexane is free of angle & torsional strain, a) Boat, , b) Half chair, , c) Twist chair, , d) Chair, , 25. Dimethyl ether and ethyl alcohol are examples of ……………….isomerism, a) Position, , b) Chain, , c) Functional group, , d) Metamers
Page 4 :
26. The angle between Hydrogen on near carbon and farther carbon is called……, a) Dihedral angle, , b) rotational angle, , c) rectangle, , d) cross angle, , 27. The full form of CIP is, a) Cahn-Ingold-Prelog, , b) Cane-India-Pacific, , c) China-Indonesia-Paris, , d) None of the above, , 28. The priority sequence is given on the basis of…, a) Atomic size, , b) Atomic number, , c) Electronegativity, , d) Energy, , 29. The elements of symmetry are useful to determine…………………..of molecule., a) reactivity, , b) symmetry, , c) polarizability, , d) size, , 30. The carbon atom having four different substituents is called as…………, a) Chiral carbon, , b) Good carbon, , c) Bad carbon, , d) symmetric carbon, , 31. In polarimeter, sample is placed in……, a) Nicol prism, , b) Source, , c) Analyzer, , d) Polarimeter tube, , 32. In Newman projection formula, front carbon atom is shown by a…………., a) Circle, , b) Ellipse, , c) Dot, , d) Line, , 33. Pyridine undergo electrophilic substitution reaction at position numbera) 2, , b) 3, , c) 4, , d) 1, , 34. Furan, pyrrole and thiophene undergo substitution at ____position, a) 1, , b) 2, , c) 3, , d) 4, , 35. _____ is not a heterocyclic aromatic compound., a) Furan, , b) Pyrrole, , c) Thiophene, , d) Naphthalene
Page 7 :
a) Tetralin, , b) Decalin, , c) 1-4, dihydro naphthalene, , d) Pyrrole, , 56. Naphthalene on reduction with H2/Pt gives……, a) Tetralin, , b) Decalin, , c) 1-4, dihydro naphthalene, , d) Pyrrole, , 57. Which of the following is nitrating mixture,, a) HCl/H2SO4, , b) HNO3/H2SO4, , c) H2/Pt, , d) All of these, , 58. The reduction using Zn-Hg/HCl is called as………., a) Clemmenson’s reduction, , b) Birch reduction, , c) Catalytic reduction, , d) Total reduction, , 59. Haworth synthesis is used to synthesize………….., a) Pyridine, , b) Naphthalene, , c) Furan, , d) Pyrrole, , 60. 3-methyl pyridine is called as….., a) Pyrrolidine, , b) Piperidine, , c) Acrolein, , d) Picoline, , 61. The removal of carboxyl group in the form of CO2 by heating is called,, a) Decarboxylation, , b) Elimination, , c) Addition, , d) Substitution, , 62. The reaction using CHCl3/ KOH is called., a) Freidel-Craft reaction, , b) Hydrogenation, , c) Reimer-Tiemann reaction, , d) Sulphonation, , 63. According to solvent system concept, the compound which gives cation of solvent is…., a) acid, , b) Base, , c) Neutral, , d) Salt, , 64. According to solvent system concept, the compound which gives anion of solvent is….
Page 8 :
a) acid, , b) Base, , c) Neutral, , d) Salt, , 65. According to solvent system concept, neutralization is, a) Reaction between acid and base to give salt, b) Reaction between acid and base to give salt and solvent, c) Reaction between acid and base to give water, d) Reaction between acid and base to give acid, , 66. Oxide ion donor is base. This is according to,, a) solvent system concept, , b) Lewis concept, , c) Lux-Flood concept, , d) Bronsted concept, , 67. Oxide ion acceptor is acid. This is according to,, a) solvent system concept, , b) Lewis concept, , c) Lux-Flood concept, , d) Bronsted concept, , 68. Electron pair acceptor species is acid. This is according to,, a) solvent system concept, c) Lux-Flood concept, , b) Lewis concept, d) Bronsted concept, , 69. According to Lewis concept base is,, a) any species capable of donating electron pair, b) Any species capable of accepting electron pair, c) Substance donating H+ ion, d) Substance accepting H+ ion, , 70. Combination of ions or molecules of solute with solvent is called,, a) Neutralization, , b) Oxidation, , 71. BF3, AlCl3, GaCl3 are…………, , c) Reduction, , d) Solvation
Page 9 :
a) Lewis acids, , b) Lewis bases, , c) Bronsted acids, , d) Bronsted bases, , 72. Combination of acid with base to form addition product or adduct. This according to,, a) solvent system concept, c) Lux-Flood concept, , b) Lewis concept, d) Bronsted concept, , 73. All cations are acids and all anions are bases. This is according to,, a) solvent system concept, c) Lux-Flood concept, , b) Lewis concept, d) Bronsted concept, , 74. NH3, H2O, ROH, ROR are……, a) Lewis acids, , b) Lewis bases, , c) Lux-Flood acids, , d) Bronsted acids, , 75. According to generalized acid-base concept,, a) H+ is a base, , b) Free electron is acid, , c) Free electron is base, , d) -OH is acid, , 76. Solvent which brings ionization of solute to same extent is called as, a) Acidic solvent., , b) Basic solvent, , 77. Acidic solvents are,, a) Levelling for acids., c) Differentiating for bases., , 78. Basic solvents are,, a) Levelling for acids., c) Differentiating for acids., , c) Differentiating solvent., , b) Levelling for bases., d) None of the above., , b) Levelling for bases., d) None of the above., , 79. Substances used to increase ionization of acids or bases in medium are,, a) Oxidizing agents., b) Reducing agents., c) Co-solvating agents., d) Redox agents., , d) Levelling solvent.
Page 10 :
80. Species having strong tendency to accept electrons & form ionic bond with base, are called, a) Hard base., b) Soft base., c) Hard acid., d) Soft acid., , 81. Species in which valence electrons are easily distorted or polarized or donated, are called, a) Hard base., b) Soft base., c) Hard acid., d) Soft acid., , 82. According to Pearson’s HSAB concept, Hard acid prefers to bind,, a) Hard base., b) Soft base., c) Hard acid., d) Soft acid., , 83. According to Pearson’s HSAB concept, the product is more stable when,, a) Hard acid combines with soft base., b) Soft acid combines with Hard base., c) Hard acid combines with Hard base., d) cannot be predicted., , 84. Solute is a substance which dissolves in solvent and forms,, a) Solution, , b) Gas, , c) Film, , d) acid, , 85. Water has ……………dielectric constant., a) Low, , b) Negative, , c) High, , d) Zero, , 86. Molten salts are,, a) Protic, , b) Aprotic, , c) Acidic, , d) Basic, , 87. Dissolved oxygen can be partly removed from solvent by, a) Exposing to sunlight, , b) Passing air, , c) By bubbling nitrogen gas, , d) Cannot be removed, , 88. According to Electronic theory, Hard-Hard interactions involve,, a) Co-ordinate bonding, , b) Ionic bonding, , c) Covalent bonding, , d) H-bonding, , 89. According to Electronic theory, Soft-Soft interactions involve,, a) Co-ordinate bonding, , b) Ionic bonding
Page 11 :
c) Covalent bonding, , d) H-bonding, , 90. HSAB concept can be used to determine,, a) Stability of complexes, , b) Predicting feasibility of reactions, , c) Solubility of compounds in a given solvent, , d) All the above, , 91. Decrease in the activity of a catalyst due to contamination is called as,, a) Poisoning of catalyst, , b) Dirtiness of catalyst, , c) Arresting of catalyst, , d) None of above, , 92. Which of the following is a disadvantage of solvent system concept,, a) It requires solvent, , b) It requires clean apparatus, , c) It requires large literature, , d) It is useless, , 93. The Lewis concept is,, a) Tedious, , b) Boring, , c) Broader, , d) Shorter, , 94. Lewis bases are ………….in complexes., a) Metal ions, , b) Counter ion, , c) whole complex, , d) Ligands, , 95. The species with highest positive charge density is,, a) Strongest acid, , b) Strongest base, , c) Weakest acid, , d) Neutral, , 96. The species with highest negative charge density is,, a) Strongest acid, , b) Strongest base, , c) Weakest base, , d) Neutral, , 97. ……………solvents are used to determine the strength of acids & bases of a given series., a) Levelling, , b) Differentiating, , 98. Solvation takes place by,, , c) Acidic, , d) Basic
Page 12 :
a) Formation od co-ordinate bond, , b) ion-dipole interaction, , c) Both a and b, , d) None of the above, , 99. In electrochemical reactions, solvent must have,, a) High dielectric constant, , b) Low dielectric constant, , c) Zero dielectric constant, , d) Negative dielectric constant, , 100. Solvent ether reacts with oxygen in air on long exposure and forms,, a) Sulphides, , b) Nitriles, , c) Peroxides, , d) Hydrides