Page 1 :
NAME, , CEE QAD 2021/ZOOLOGY, , www.name.edu.np, , QAD, , Series, , Frog, Development of Frog & Bone, Frog, 1., During breeding season, nuptial pad is found the thumb, of, a) male frog b) female frog c) male toad d) female toad, 2., Croaking of frog is, a) hunger call, b) danger call, c)musical note, d) sex call for female, 3., Parotid glands are found in, a) Bufo, b) Hyla, c) Rana, d) Alytes, 4., Male frog can croak louder than female frog because, being, a) Vocal sac, b) stronger, c) larger in size, d) larger sound box, 5., Neck is absent in frog. This help frog in, a) respiration, b) catching prey, c) jumping on ground, d) swimming in water, 6., Frogs have ability to climb because they possess, a) Claws, b) adhesive skin, c) adhesive pad on finger and toes, d) glue like secretion from mucus gland, 7., The summer sleep of frog is termed as, a) neoteny, b) aestivation, c) Paedogenesis, d) hibernation, 8., , 9., , 10., , 11., , 12., , 13., 14., 15., 16., , 17., 18., 19., , 20., , 21., 22., 23., , Colouration in frog and other amphiabians is due to, a) keratin, b) algae upon skin, c) chromatophores, d) irridescenec of skin, Glands present in the skin of frog is, a) sweat and nucus, b) sweat and mammary, c) mucus and poison, d) sweat and sebaceous, The opening of rectum in frog is called, a) vestibule, b) cloaca, c) coccyx, d) nephrostome, Frog and toads belongs to the order, a) Anura, b) Apoda, c) Caudata, d) Gymnophiona, Frog is, a) arboreal, b) terrestrial, c) fully aquatic, d) both aquatic and terrestrial, Frog hibernates during, a) winter, b) spring, c) summer, d) autumn, Mucus help frog in making, a) dry skin, b) moist skin c) rough skin d) thick skin, In buccal cavity of frog, internal nares are, a) one, b) two, c) fused, d) absent, Chromatophores in skin of frog are found in stratum, a) cornaeum, b) compactum, c) germinativum, d) mostly spongiosum, Dermal plicae is found in, a) frog, b) Rabbit, c) Fish, d) Cat, No exoskeleton is found in, a) Birds, b) Mammals c) Frogs, d) Rabbit, If the skin of frog is dry, it will die due to, a) dehydrartion, b) Asphyxia, c) intoxication, d) starvation, Pigment melanin is found in, a) Xanthophore, b) Guanophore, c) melanophore, d) lipophores, The cells of stratum cornaeum bear, a) keratin, b) Eledin, c) Keratohyaline d) all, The conjunctiva of eye frog is formed from, a) skin, b) Epidermis c) Dermis, d) None, The glottis is the passage of, a) oesophagus, b) respiratory passage, , 24., , 25., 26., 27., 28., , 29., 30., , 31., 32., 33., , 34., , 35., , 36., , 37, , 38., 39., , 40., , 41., , c) Excretory passage, d) none, The teeth of frog is, a) Heterodont, b) Homodont, c) Monophyodont, d) Thecodnt, The muscular contraction of stomach are known as, a) absorption b) digestion, c) circulation d) peristalsis, The internal mucosa lining is transverse in, a) oesophagus b) stomach, c) Duodenum d) Rectum, The mucosa form well developed villi in, a) stomach, b) Rectum, c) Intestine, d) all, The chief function of bile is, a) Emulsification of fat, b) regulate digestion of fat, c) to remove waste products d) to dissolve fat in water., Oxyntic cells secrete, a) Pespin, b) trypsin, c) HCL, d) Rennin, Islets of Langerhans are found in, a) Tubule of kidney, b) Pituitory gland, c) Lymph glands, d) Endocrine part of Pancreas, In frog, protein digestion is completed in, a) duodenum b) Rectum, d) stomach, d) Ileum, Ornithin cycle occurs in, a) stomach, b) kidney, c) Pancreas, d) Liver, Layer of actively dividing cells in skin of frog is termed, as stratum, a) malpighi, b) cornaeum, c) compactum, d) spongiosum, In which of hese animals, skin serves as an accessory, organ of respiration, a) Bird, b) Frog, c) Lizard, d) Rabbit, Which of the following is the longest in frog, a) Ileum, b) small intestine, c) oesphagus, d) stomach, In frog which of the following is common in digestion, and respiration, a) Pharynx, b) Larynx, c) oesophagus d) Trachea, Dentition in frog is, a) Homodont, b) heterodont, c) Thecodont, d) Bunodont, How many teeth are found in lower jaw of frog?, a) no, B) 2, C) 3, D) 4, Which of the following is mainly used in capturing the, prey?, a) lips, b) teeth, c) tongue, d) hand, In frog, the surface of attachment of tongue is, a) Palatine, b) spenoid, c) pterygoid, d)hyoid apparatus., Oesophagus is extremely short in frog due to, a) carnivorous habit, b) absence of neck, c) large head, d) Herbivorous, , 42., , Carbohydrate are stored in muscles and liver as, a) glucose, b) starch, c) glycogen, d)fat, , 43., , The chief function of Bile is, a) Emulsification, b) to regulate the digestion, c) to digest fat by enzymes, d) To remove waste product., , 44., , The muscular contraction of stomach is as, a) Digestion b) twitch, c) peristalsis, , 45., , Glycogenesis is, a) hydrolysis of glycogen, b) liberation of glucose into blood, c) conversion glucose into glycogen, d) formation of glucose into liver, , d) tetanus
Page 2 :
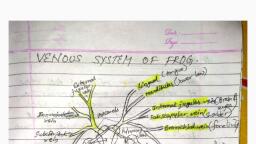
NAME, , CEE QAD 2021/ZOOLOGY, , www.name.edu.np, , 46., 47., , The insulin is produced by, a) Stomach, b) liver, , d) oval, nucleated , biconcave, c) intestine, , d) pancreas, , The alimentary canal of frog is derived from the, embryonic, a)Endoderm, mesoderm & ectoderm, b)Mesoderm & endoderm, c) endoderm & ectoderm, d) ectoderm, , 48. Chief cells secrete, a) HCl, b) Mucin, , 64., , The blood cells in frog, which is found in maximum, number & act as scavenger is, a) Neutriphils b) RBC, c) Eosinophil d) Platelets, , 65., , Inspiration in frog is brought about by the contarction of, a) Skeletal muscle, b) Lung muscle, c) pterohyal muscle, d) Sternohyal muscle, , 66., , Lungs of frog acts as, a) Airostatic organ, b) Thermostatic organ, , c) Pepsinogen d) H2O, , 49., , Stomach of frog does not have, a) fundic part b) Cardiac part c) Pyloric part d) all, , 50., , b) Hydrostatic organ, d) All, , 67., , In frog, pyloric sphincter is located in between, a)fundus & pylorus, b) cardiac & fundus, c) Oesophagus and pharynx d) stomach & duodenum, , The epithelial lining of respiratory system of frog is, derived from, a) ectoderm, b) endoderm, c) mesoderm, d) mesoderm and endoderm, , 68., , 51., , The structure present in man but absent in frog is, a) pancreas, b) thyroid gland, c) Adrenal gland, d) Salivary gland, , In frog respiration occurs by, a) lungs, b) trachea, c) gills only, d) both a & b, , 69., , 52., , The spiral valve is present in, a) Conus arteriosus, b) Bulbous arteriosus, c) In between right & Left arteries, d) Aur Icle & ventricle, , Which one is not related with respiration in frog?, a) lungs, b) skin, c) diaphragm, d) buccal cavity., , 70., , Expiration is brought about by contraction of, a) Sternohyal, b) Petrohyal, c) Lungs and abdominal cavity d) All, , 71., , Contraction of sternohyal muscles during breathing in, frog, a) Closes glottis, b) Opens the nostrils, c) raises floor of buccal cavity d) lowers floor of oral cavity, , 72., , In frog glottis is controlled by, a) Sternum, b) vocal cords, c) Pectoral girdle, d) Arytenoid cartilage, , 73., , If mouth of frog is kept open for sometime, it dies, because it is unable to, a) eat, b) drink, c) breathe, d) None, , 74., , 100 primary oocytes form, a) 100 ova, b) oviduct, , 53., , Which of the following has 3-chambered heart?, a) Frog, b) Snake, c) Crocodile, d) Lizard, , 54., , Venous system of frog differ from that of mammal in the, presence of, a) Hepatic portal system, b) Renal portal system, c) Three vanacava, d) Hepatic vein, , 55., , Blood from back side of frog is collected by, a) Iliac, b) Dorsolumber c) Femoral, , 56., , Portal system carries blood, a) to capillaries, b) from capillaries, c) from capillaries to capillaries, d) from liver to intestine, , 57., , d) Sciatic, , Anterior abdominal vein in frog is formed pelvic vein, which is, a) ventral femoral, b) dorsal femoral, c) ventral sciatic, d) Dorsal sciatic, , 58., , In frog, blood flows to right auricle from, a) Venacava, b) Sinus venosus, c) Pulmonary artery, d) all, , 60., , Brachial & Musculocutaneous veins in frog unite to form, a) Innominate vein, b) external jugular vein, c) Subclavian vein, d) Post-caval vein, , 61., , 62., , 63., , Cavum aorticum in frog’s heart is a, a) Left chamber of truncus arteriosus, b) Right chamber of truncus arteriosus, c) Left atrial chamber, d) Right atrial chamber., RBC of frog are, a) Oval and nucleated, b) Circular & nucleated, c) Oval & non-nucleated, d) Circular and non-nucleated, RBC of frog is, a) Ellipticle, non-nucleated,, b) Ellipticle, nucleated, biconvex, c) oval, non-nucleatd, biconvex, , c) 400 ova, , d) 50 ova, , 75., , The vasa efferentia in frog open into, a) cloaca, b) Bidder’s canal, c) Glomerulus, d) collecting duct, , 76., , In frog, reproduction involves, a) clasping in which the male inseminate the female, b) nest building by the male who then gets the female to lay, eggs in nest., c) a male and female pairing which is present association., d) Sperm and egg release into water., , 77., , Aqueduct of sylvius occurs in, a) Heart, b) Brain, c) ear, , d) Eye, , Cavity within spinal cord is, a) Scizocoel b) Enterocoel c) Neurocoel, , d) Blastocoel, , 78., 79., , Which one of the following is purely motor nerve?, a) Abducens b) audotory, c) facial, d) Vagus, , 80., , The cranial nerve innervating the structure beyond the, head is, a) Hypoglossal, b) auditory, c) Facial, d) Vagus, , 81., , Lateral ventricle are found in, a)Heart & Brain, b) Heart, c) Brain, d) Brain & thyroid, , 82., , IX cranial nerve of frog is named, a) trochlear, b) Vagus, c) Glossopharyngeal, d)Trigeminal
Page 3 :
NAME, , CEE QAD 2021/ZOOLOGY, , www.name.edu.np, , 83., , Which one is not a true cranial nerve?, a) Olfactory b) Vagus, c) Trochlear, , d) Abducens, , 84., , Which cranial nerves are purely sensory?, a) I, II, VIII, b) I, II, IV, c) I,V,VII, , d) None, , 85., , Glands of Swammerdam are related with, a) Spinal nerve of frog, b) Cranial nerve of frog, c) endocrine system of frog, d) alimentary canal of frog, , 86., , Which of the following is not the median part in the brain, cavity of frog?, a) Iter, b) Diocoel, c) Metacoel, d) Optocoel, , 87., , Medulla oblongata of brain passes out through, a) foramen of obturator, b) foramen Magnum, c) Foramen of Magendi, d) Foramina of Luschka, , 88., , Which part of the brain of frog is called Pallium?, a) roof of paracoel, b) floor of epicoel, c) roof of rhinocoel, d) roof of Metacoel., , 89., , Velocity of conduction of nerve impulse in frog is, a) faster than sound, b) 30 metre per second, c) 300 meter per second, d )same of that is electricity., , 90., , If cerebral hemisphere of frog is removed, it, a) dies at once, b) stops feeding, c) remain as it was, d) it dies after some time, , 91., , Which of the following is the part of forebrain?, a) Olfactory lobe, b) Cerebrum, c) Diencephalon, d)All of these., , 92., , Sensory nerve fibres enter Spinal cord through, a) Dorsal root b) ventral root c) both, d) none, , 93., , Rana tigrina, the Indian bull frog has, a) 10 pairs of spinal nerves, b) 9 pairs Spinal nerves, c) 8 pairs of Spinal nerves, d) 7 pairs of Spinal nerves., , 94., , If cerebral hemisphere of frogs are removed, a) it will lose body balance, b) it will stop feeding, c) it will not show reflexes, d) none of these, , 104. Endolymph is fluid present in, a) synovial fluid, b) Internal ear, c) Cnidoblast, d) posterior chamber of eye., , 95., , The outer covering of brain is, a) Choroid, b) Pia mater, c) Arachnoid, d) Dura mater, , 96., , In case of spinal nerve, the cell bodies of afferent fibres, lie in, a) white matter, b) Grey matter, c) Dorsal root, d) ventral root, , 97., , The Hind brain of frog consists of, a) Optic lobe, b) Medulla oblongata & Cerebellum, c) Optic lobe and Medulla oblongata, d) Diencephalon and Medulla oblongata, , 98., , Paracoel is found in, a) Optic lobe, c) Cerebellum, , 105. The chief function of semicircular canal is, a) To percieve sound vibration, b) To maintain balance of the body, c) To transmit sound vibration to auditory canal., d) Hearing., 106. The contraction of heart of frg commences from, a) Left auricle, b) Sinus venosus, c) Right auricles, d) Inter-auricular septum, 107. Which of the following veins break up into capillaries?, a) a) renal vein, b) Pelvic vein, c) Pulmonary vein, d) Hepatic portal vein, 108. Carotid labyrinth, a) Control the flow of blood in carotid arch, b) Controls the concentration of oxygen, c) detect the presence of respiratory gases in blood, d) Detect the presence of CO2 in blood, 109. The pylangium and synangium of fog’s heart is marked, by, a) First row of semilunar valve, b) second row of semilunar valve, c) spiral valve, d) Sinu-atrial valve, , 99., , d) Ampulla of semicircular canal., , b) cerebrum, d) Medulla oblongata, , Mammalian brain differ from frog brain in having, a) Olfactory lobe, b) Corpus callosum, c) Cerebellum, d) Hypothalamus, , 100. CNS develops at, a) Blastulation, c) Neurulation, , b) Gastrulation, d) Cleavage, , 103. One of the main function of semicircular canal is, a) Percieve sound, b) percieve pressure wave, c) to maintain balance of the body/Percieve the motion of, head, d) Percieve water wave and current, The lagena is part of the vestibular system in fish and, amphibians. It contains the otoliths asterisci. In fish, the, lagena is implicated in hearing and the registration of, vertical linear acceleration,[1] in amphibians is the latter, only., utriculus (utricle) A chamber of the inner ear from which, the semicircular canals arise. It bears patches of sensory, epithelium concerned with detecting changes in the, direction and speed of movement (see macula)., Sacculus and Lagena are concerned with hearing., , 101. A single middle ear ossicle in frog is the, a)Tripus, b) Malleus, c) Columella auris d) Incus., , 110. The surface of the eye remain moist due to the secretion of, a) Harderian gland, b) Lacrimal gland, c) Meibomian gland, d) glands o f Zeis., , 102. The sense of balance or equilibrium resides in the, a) Lagena, b) Utriculus, c) Ear ossicle, , 111. The eye of frog is adapted for, a) Monocular vision, b) Binocular vision, c) Mosaic vision, d) Telescopic vision.
Page 4 :
NAME, , CEE QAD 2021/ZOOLOGY, , www.name.edu.np, , a) Ectoderm & endoderm, c) Ectoderm & mesoderm, , Development of Frog, 1., , 2., , 3., , 4., , 5., , 6., , 7., , b) Ectoderm only., d) Mesoderm only., , Archenteron in frog’s embryo is developed due to:, a) Epiboly, b) Emiboly, c) Cleavage division, d) Neurulation, , 19., , Vegetal hemisphere of frog’s egg consists of:, a) Gray crescent, b) germinal vesicle, c) Melanin, d) yolk, , Vertebral column of vertebrates is originated from, a) Neural tube, b) Notochord, c) Ectodermal plate, d) Mesodermal plate, , 20., , The origin of frog’s brain is –, a)Endodermal, b) Mesodermal, c) Ectodermal, d) Endo-mesodermal, , In frog coelom is derived from, a) Ectoderm, b) Mesoderm, c) Endoderm, d) Neuroectoderm., , 21., , Type of cleavage in frog’s zygote is, a) Holoblastic & equal, b) Holoblastic & unequal, c) Meroblastic, d) Diploblastic, , _____ gives origin to nervous, a) ectoderm b) mesoderm c) endoderm, d) ectoderm & endoderm, e) Endoderm & mesoderm, , 22., , Change in sperm for fertilization is, a) capacitation, b)insemination, c)polygamy, d)sterilization, , _____gives origin to skeletal system, a) ectoderm b) mesoderm c) endoderm, d) ectoderm & endoderm e)Endoderm & mesoderm, , 23., , Segmentation is another name for, a) cleavage, b) Blastocoel, c) Archenteron, d) Body cavity., , 24., , Blastopore develops into mouth in, a) frog, b) rabbit, c) Leech, d) Human being, , 25., , Gastrulation in frog involves, a) epiboly, b) emboly, c) invagination, d) all, , 26., , During metamorphosis of tadpoe larva of frog, the, dissolution od tail takes place by, a) Ligase, b) Lipase, c) Catepsins, d) Polymerase, , The cavity that appears during embryogenesis of frog is, called, a) Mesenteron, b) Blasocoel, c) Coelenteron, d) Archenteron, Yolk plug is seen in, a) Blastula, c) Morula, , b) Gastrula, d) Cleavage, , 8., , Which of the following is outer layer of an early embryo?, a) Endoderm, b) endoderm, c) ectoderm, d)Mesoderm, , 9., , Blastopore is present in _stage, a) Morula, b) Blastula, c) Gastrula, d) Neurula, , 27., , Germ layers are seen in, a) Gastrula, c) Cleavage, , What distinguishes a morula from blastula ?, a) Presence of more yok, b) absence of yolk, c) presence of cavity, d) Absence of cavity, , 28., , Which organs come earlier during metamorphosis of frog?, a) Fore-limbs b) Hind-limbs c) both once, d) none, , 29., , In frog’s embryo presumptive area can be maped out in, a) Blastula, b) Morula, c) Gastrula, d) Neurula, , 30., , The gastric and intestinal glands of frog’s tadpole arise, from primary, a) Endoderm, b) Mesoderm, c) Ectoderm, d)Mesodermal nuclei, , 31., , Cleavage in frog’s development ends with the stage of, a) Morula, b) Blastula, c) Gastrula, d) Tadpole, , 32., , Archenteron is formed at the stage of, a) Morula, b) Blastula, c) gastrula, d) Postgastrula, , 33., , Metamorphosis occurs when, a) Growth takes place, b) Larva changes into adult, d) Development is by parthenogenesis, , 34., , Gonads are derived from, a) Mesoderm b) Endoderms c) Ectoderm, , 10., , 11., , 12., , 13., , 14., , 15., , 16., , 17., 18., , b) Blastula, d) Fertilization, , The tadpole of frog feeds upon, a) zoo plankton, b) swimming insect, c) aquatic flora, d) Smaller fishes, In frog, jelly around the eggs is deposited, a) in water after fertilization, b) in water during fertilization, c) in oviduct, d) in the ovary, Blastopore is found in, a) Blastula & is the opening of blastocoel, b) Blastula & is the opening of archenteron, c) Gastrula & is the opening of blastocoel, d) Gastrula & is the opening of archenteron, Metamorphosis in frog can be accelerated by, a) iodin, b) Phospohorous, c) Potassium, d) Calcium, Which of the following is true about mesoderm?, a) It forms CNS, b) it forms the pouches lining of the coelom, c) it has no contribution to alimentary canal, d) It does not form blood vessel, Blastopore in the vertebrates develop into, a) Anus, b) Mouth, c) Notochord, d) Both mouth and anus., Metamorphosis in frog is regulated by the secretion of, a) Pituitary, b) Adrenal, c) Thyroxin, d) Calcitonin, Skeleton & muscles in a vertebrate embryo develop from, , d) None, , Bone, 1., , The only acoelous vertebra in frog is (MOE 2063), a) VII, b)VIII, c) IX, d) X, , 2., , The eighth vertebra of frog is (MOE 2060), a) Amphicoelous, b) Acoelous, c) Procoelous, d) Opisthocoelous, , 3., , The Urostyle of frog is supported to be made of smaller, bones Urostyle is (MOE2055), b) 8th, c)10th, d)Urostyle, a) 9th, , 4., , Ilium of pelvic girdle in frog articulate with transverse, process of (MOE 2052), a) 7th, b) 8th, c) 9th, d) Urostyle
Page 5 :
NAME, , CEE QAD 2021/ZOOLOGY, , www.name.edu.np, , 5., , 6., 7., 8., 9., 10., 11., 12., , 13., , Septo-maxillary bones are present in the skull of, (IOM1998), a) Rabbit, b) Man, c) Rat, d)Frog, Cranium consists of ______ bones ( IOM 1993), a) 6, b) 8, c) 14, d) 37, The number of spinal vertebrae ( IOM 2002), a) 26, b) 33, c) 30, d) 24, The number of cervical vertebrae in human is ( (IOM 98), a) 6, b) 7, c) 8, d) 12, The total number of thoracic vertebra in man is ( IOM 99_, a) 10, b) 12, c) 15, d) 37, Pisciform bone is located in ( IOM 98), a) Wrist bone b) Elbow joint c) Ankle joint, d) Hip joint, Incus is found in ( IOM 96), a) Skull, b) hand, c) Liver, d) Kidney, Sternum is, (IOM 96), a) Long bone, b) Flat bone, c) both of these, d) None of these, Which one of the following is sessamoid bone of our, body ( IOM 93), a) Patella, b) Talus, c) Clavicle, d) Navicular, , 14., , Lunate bone forms the part of, a) Shouldier joint, b) Ankle joint, c) wrist joint, d) knee joint, , 15., , The largest joint of human body is ( IOM 1996), a) Hip joint, b) shouldier joint, c) knee joint, d) knee joint, , 16., , An example of Hinge joint is ( IOM 94), a) Hip joint, b) shouldier joint, c) knee joint, d) Wrist joint, , 17., , 14 phallangeal bones are present in, a) Hand, b) leg, c) wrist, , 18., , 19., 20., , 21., , 22., , 23., 24., , 25., , 27., , 28., 29., , 30., 31., 32., , 33., 34., , c) tricondylic, d) Tetracondylic, Parietal bone is found (MOE 2060), a) pectoral girdle, b) Pelvic Girdle, c) Skull, d) Limb, The number of occipital condyle in mammal is, a) 3, b) 5, c) 1, d) 2, In rabbit Jaw suspensorium is, a) craniostylic, b) autostylic, c) hyostylic, d) amphistylic, Scientific term for upper jaw bone is (KU 2011), a) Maxilla, b) Mandible, c) Molar, d) Incisor, Sella turcica is found in, a) occipital, b) Parietal, c) Frontal, d)Temporal, Supratrochlear foramen is found in, a) Petoral girdle, b) Humerus, c) Femur, d) Pelvic girdle, Deltoid ridge is found in (MOE 2061, a) Humerus b) Femur, c) Tibia, d) Ulna, Wrist bones are called )(MOE 2003), a) Carpal, b) metacarpals c)Tarsal, d) Metatarsal, , d) both a & b, , One of the folloing is not a part of mammalian bone (BP, 2003), a) Periosteum b) peritoneum c) endosteum d) Lamella, A man broke his fibula, i.e; he broke his (MoE 2052), a) Head, b) pubic, c) Jaw, d) leg, Joint pain in old person are mostly due to ( IE 2009), a) Reduced synovial fluid, b) increase of synovial fluid, c) Formation of extra-osteocytes, d) all of theabove, Saddle joint present between the (Bp 2004), a) Meta carpal & Carpal, b) metacarpal & Phallanges, c) Tibia & femur, d) Humerus & Radius, The shouldier and Hip joint are of the type (IOM 2001), a) Ball & Scket, b) Hinge joint, c) Pivot joint, d) Gliding joint., Number of false ribs in rabbit : (MOE Paush 2070), a) 2 pairs, b) 3 pairs, c) 5 pairs, d) 7 pairs., Which of the following piece of bone is not the part of, Rabbit cranium? (MOE Paush 2070), a) Frontal, b) parietal, c) Occipital, d) Periotic, The skull of Frog and Rabbit is (IOM 2013), a) Dicondylic, b) Monocondylic, , Thank You