Page 1 :
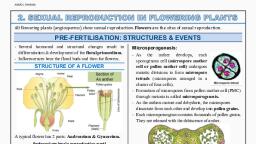
Angiosperms, , Angiosperms or flowering plants form the largest, group of plant kingdom, including about 300, families, 8000 genera and 300,000 species., They are considered to be highest evolved plants, on the surface of earth., , Angiosperms better known as flowering plants,, are vascular seed plants that produce flowers and, fruits., , They are by far the most diverse and, geographically widespread of all plants., , There are about 250,000 known species of, angiosperms., , As late as the 1990s, most plant taxonomists divided, the angiosperms into two main classes — the, monocots and dicots., , A typical angiospermic plant is sporophytic (2n), and have both vegetative parts and reproductive, parts., , Vegetative parts or organs of an angiospermic, plant are root, stem and leaves., , Roots collectively constitute root system, which, generally constitute the under ground portion of, the plant., , The stem with its branches and leaves constitute, shoot system, which is generally above ground or, aerial part of the plant., , Flower formation is the transitional phase (change, from vegetative phase to reproductive phase) in the, life cycle of an angiospermic plant., , Forms of angiosperms, , On the basis of habit an angiosperm plant can be, a herb, shrub, tree creepers, twiners, climber and, lianas., , Herbs are small plants with soft and pliable stems., Herbs can be annual (e.g., Buttercup), biennial, (e.g., Henbane) and perennial (e.g., Canna)., Shrubs are woody plants and are branched near, , , , the ground, stem is not much developed into clear, trunk., , Trees are woody plants, which are branched at some, height and thus have much developed trunk., Trees further may be excurrent or conical (having, basal thicker portion and thinner or tapering, portion above), caudex (unbranched stem with, crown of leaves at apex) or deliquescent/, decurrent (sub branches grow after death of apical, bud of stem)., , Trailers are plants which spread on the ground, without rooting at intervals, e.g., Tribulus terrestris,, Euphorbia prostrata., , Creepers are plants spread on the ground, rooting, at intervals, e.g., strawberry., , Twiners are weak-stemmed plants where the stem, coils or twines around an upright support, e.g.,, Ipomoea cairica (Railway creeper), Quisqualis, (Rangoon creeper)., , Climbers are plants that climb up an upright support, by special clinging or clasping structures like, tendrils, roots and hooks., , Woody twiners and climbers are called lianas. They, are found in tropical evergreen forests, e.g., Phanera, (= Bauhinia) vahlii, Hiptage., , Epiphytes are plants which live on other plants for, space only. Angiospermic epiphytes commonly live, on trees, e.g., Vanda, Dendrobium. They often, possess hanging roots with hygroscopic outer, spongy tissue called velamen., , Culms are the plants where stem is having very, clear nodes and internodes (joined stem). Here, nodes are solid and internodes are generally hollow,, e.g., grasses (members of gramineae) and sedges, (members of cypreceae)., , On the basis of life span angiosperm plants can be, annual, biennials or perennials., , Scanned with CamScanner
Page 2 :
Angiosperms, , Annual plants complete their life cycle within, one year, eg. rice, wheat., Such annuals which complete their life within a, brief or short (generally 4-6 weeks) period of time,, are called ephemeral annuals or ephemerals, e.g.,, Argemone (pili katili), Artemisia, Astragalus, etc., Biennials complete their life cycle in two growing, seasons (i.e., complete their vegetative phase in, first season and reproductive phase in second, season). Eg Henbane, raddish., Perennial grow for a number of seasons or for, many years., Perennial plants may be polycarpic i.e., produce, flower and fruit every year, eg. mango or, monocarpic i.e., produce flower and fruit once in, life, e.g., Bambusa bamboos., The century plants flowers after about 100 years, and after flowering dies., Banana (Musa) is one of the largest perennial herbs., On the basis of mode of nutrition angiosperms, may be autotrophic or heterotrophic., Plants which can manufacture their own organic, food from inorganic substances, are called, autotrophic or autophytes., Photoautotrophs or photoautotrophic plants, manufacture their food in presence of chlorophyll, and light from CO, and H,O by the process of, photosynthesis, e.g., most of the green plants., Chemautotrophs or chemosynthetic plants, manufacture their food using chemical energy (not, light energy) without presence of chlorophyll, e.g.,, chemosynthetic bacteria,, The plants which are unable to manufacture their, own food and depend upon other green plants for, food are called heterotrophic or heterotrophs,, Hetrotrophic plants are of three types —, - Saprophytes - obtain nourishment from dead, decaying organic matter, - Parasites — obtain nourishment from other, living organisms, - Carnivorous — predator plants that grow in, nitrogen deficient soil., , Vegetative and floral characters of angiosperms, , Roots are adventitious in monocots and tap root, in dicots., , Stems may be erect, branched or unbranched,, trailers or climbers or twiners., , , , Leaves varies like seed leaves, scale leaves, bract, leaves, floral leaves, prophylls, foliage leaves., Leaves may be simple or compound, lamina may, be dorsiventral or isobilateral,, , Foliage leaves are green, expanded, dorsiventrally, flattened with or without stipule., , Leaf base in monocots are generally sheathing, without stipules., , Flowers may be single or in groups forming, inflorescence., , Inflorescence may be racemose or cymose or, special type., , Flowers may be complete, incomplete, unisexual,, bisexual, sterile or naked., , Complete flower have all the four whorls - calyx,, corolla, androecium and gynoecium while, incomplete flower have one or more of the four, whorl missing., , Bisexual flower have both androecium and, gynoecium while unisexual plant have either, female part (pistillate) or male part (staminate)., Essential whorls of flowers are stamens and, carpels., , Stamens consist of filament, connective and, anther,, , Carpels consist of ovary, style and stigma., Pollen grains are formed within anther., , Ovules are present within ovary., , The development of male gametophyte is completed, within the pollen tube before fertilization,, Double fertilization occurs and endosperm is, triploid., , Seeds always remain within fruit., , Angiosperm seeds may have one, two or many, cotyledons., , A fruit is a mature ovary as seed develop from, ovules after fertilization, the wall of the ovary, thickens to form the fruit., , Fruits protect dormant seeds and aid in their, dispersal,, , Fruits are classified into several types depending, on their developmental origin as — simple fruits, (derived from a single ovary), an aggregate fruit, (results from a single flower with several carpels),, a multiple fruit (develops from an inflorescence)., Seeds may be endospermic or non-endospermic., Germination of seeds may be epigeal or hypogeal., Vascular bundles of root are radial and exarch in, angiosperm., , , , Scanned with CamScanner
Page 3 :
Sy ouVY 2.4 vo Ve, , v, , WtG rapid biology, , Number of vascular bundles in root anatomy are, more than six in monocots and 2-6 in dicots., In stem vascular bundles are conjoint, collateral, or bicollateral open (in dicot) or closed (in, monocots) and endarch,, , Ground tissues are not differentiated into cortex,, endodermis, pericycle and pith in monocots stem, while separated in dicots., , Pith is large in roots of monocots while absent or, very small in dicot., , Secondary growth occur in dicot stem but not in, monocot stem., , Refinements in vascular tissue, especially xylem,, probably played a role in the enormous success of, angiosperms in diverse terrestrial habitats., Like gymnosperms, angiosperms have long, tapered, tracheids that function for support and water, transport., , Angiosperms also have fibres cells, specialized for, support, and vessel elements (in most angiosperms), that develop into xylem vessels for efficient uptake, of water. While evolutionary refinements of the, vascular system contributed to the success of, angiosperms, the reproductive adaptations, associated with flowers and fruits contributed, the most., , One hypothesis for the function of double fertilization, is that it synchronizes the development of food, storage in the seed with development of the embryo., Double fertilization may prevent flowers from, squandering nutrients on infertile ovules., , , , Economic importance of angiosperms, , Agriculture is almost entirely dependent on, angiosperms, either directly or indirectly through, livestock feed., , Of all the families of flowering plants, the Poaceae,, or grass family, is by far the most important, providing, the bulk of all feedstocks (rice, corm maize, wheat,, barley, rye, oats, millet, sugar cane, sorghum)., The fabaceae, of legume family, is in second place., Also of high importance are the Solanaceae, or, nightshade family (potatoes, tomatoes, and pepper,, among others), the Cucurbitaceae, or gourd family, (also including pumpkins and melons), the, Brassicaceae, or mustard plant family (including, rapeseed and cabbage), and the Apiaceae, or parsley, family., , Many of our fruits come from the Rutaceae, or rue, family, and the Rosaceae (rose family, including, apples, pears, cherries, appricots, plums, etc)., , In some parts of the world, certain single species, assume great importance because of their variety, of uses. An example is the coconut (Cocos nucifera), on Pacific atolls. Another example is the olive (Olea, europaea) in the Mediterranean., , Flowering plants also provide economic resources, in the form of wood, paper, fibre (cotton, flax and, hemp, among others), medicines (Digitalis,, camphor), decorative and landscaping plants, and, many other uses., , [For more details on economic importance, refer, chapter Economic Botany.], , The oldest angiosperm fossils are found in rocks in the early cretaceous, about 130 million years ago., By the end of the cretaceous period, 65 million years ago, angiosperms had become the dominant plants, , on Earth., , Scindapsus officinale (family, araceae) is exceptional angiosperm which begins terrestrial life but at, , maturity becomes epiphytic., , Angiosperms with haustoria are parasitic form as Viscum, Loranthus and Cuscuta ete., , Smallest angiosperm is duckweed (Lemna)., Smallest flower belongs to Wolffia microscopia., , Largest flower belongs to Rafflesia arnoldi (1 m in diameter weigh, 15 kg) a fatal root parasite., Smallest parasitic angiosperm is Arceuthobium minutissimum., Leafless inflorescence is depicted by Balanophora dioica., , Largest inflorescence of the world belongs to Puya raimondii (32 ft.) and the second largest is, , Amorphophallus (8 ft)., , Monotrapa and Sarcodes (family pyrolaceae) are total saprophytic angiosperms having mycorthizae., , Dicot without cotyledons is Cuscuta reflexa., , Scanned with CamScanner