Page 1 :
Use of Vernier Callipers, , 6-8, , 24-41-2019, , , , , , Use of Micrometer screw gauge., , 9-11 18-10-2019, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , Use of Spherometer. 11 - 13 |]5-10-26]4, Parallelogram law of vectors 13-15, Coefficient of Static friction. 16 - 18 |Q4~l0- 20)4 ASX, 6 | Travelling microscope 7 19 - 20, 7 | Focal length of convex lens by displacement method. | 21 - 22 |, 8 | Refractive index of liquid by concave mirror 23)\- 24, 9 | Refractive index of Prism. 24-27, 10 Determination of magnetic moment of short bar 28 - 30, magnet. (dipole) using a deflection magnetometer. |, 11 | Thermistor / 31-33, 12 | Diode characteristics. 34 - 37 |[0-|2-2019 au, , , , ‘LIST OF ACTIVITIES, , , , , , Refractive index of convex lens., , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , i (using spherometer and auto collimation method) | 38-39, , 2 | Law of moments 40, , 3 | Rolling friction 41-42, , 4 | Coefficient of restitution. 43-44 /2)-)o-op14 Sus, 5 | ‘J’ by electric method. 45 - 46, , 6 | Refractive index of glass by total internal reflection. 47-48, , 7 | Study of resistor using colour code 49 - 50 29-09-2019 Swe, 8 | Study of potential divider cireuit. 51252 |), , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , Complete minimum 10 experiments and 6 Activities in academic year, , Scanned, , with CamScanner
Page 2 :
Section - | : Experiments, USE OF VERNIER CALLIPERS, , d hollow cylinder by using vernier callipers., , , , , , , , , , Aim : To determine the volume of solid sphere an, Apparatus : Vernier Calipers, given solid sphere, hollow cylinder., , Diagram :, , , , Depth Measuing gauge, Main scale(cm), , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , — Vernier scale, Vernier Callipers, , , , , , Sphere, | Lower, Jaws —, Formulae : 1. Least count: Least count of the vernier calliper is defined as the smallest length., , Which can be measured accuraterly by the vernier callipers., , i : Value of one division on the main scale ay, 2. Least count of vernier callipers= —§ ————_______ —, Number of divisions on the vernier scale, , , , Aah:, 3. Volume of solid sphere = 3 Tr Where r = radius of sphere, , 4. Inner Volume of Hollow Cylinder = 7R*h, Where R = Innerradiusofcylinder h = height of the cylinder, , Procedure : 1) Note the smallest division on main scale of the vernier callipers and the total number of, divisions on its vernier scale. using these values. Find the least count of vernier calipers calculate, it’s zero error and find zero error correction. 2) To measure the diameter of sphere. Adjust the, distance between two Lower Jaws of vernier calliper such that the given sphere just passes, through the two jaws. Note down the main scale reading. To find vernier scale division see, which division on vernier scale coincides with one of the division on main scale. Multiplying the, least count by the coincident division on vernier scale you get the vernier scale reading. Total, , reading is obtained by adding the main scale reading to vernier scale reading, 3) Final corrected, , reading is obtained by substracting the zero error from the total reading. Which gives the diameter, , . ofthe given sphere. 4) Take three readings by orienting the sphere in different directions, find, , mean diameter and hence, volume of sphere. 5) To determine inner diameter of hollow cylinder,, , Insert upper jaws inside hollow cylinder and note Main scale and vernier scale reading. Using, , related formula, total reading is calculated. and hence inner radius is determained. By using, , yernier callipers also determine the height of hollow cylinder and hence, volume ofhollow cylinder., , , , Observations : Determination of Least Count of Vernier Callipers and Zero error., 1. The value of smallest (one) division on Main Scale =X = Q.l....cm., 2. Total number of divisions on the Vernier Scale =N =...1. div., , cm., , , , ., Leastcount (L. C.) of Vernier Calipers, Handbook of Physics Practicals : Std. XI i, , a, , Scanned with CamScanner
Page 3 :
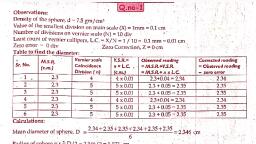
Observation Tables : 1) For Measurement of radius ‘R’ of the sphere, , , , Dimensions | Obs.| Main scale} Coincident | Vernier scale Total | Corrected) Mean, , Object | of spherical] No.] reading |divs. number Reading Reading | Diameter] Diameter, Body (a)em | onV.S. | (b=nxL.C)| (P=at+by TZ d, (n) div. em cm em cm, , , , 1 | 0.6 6 €X0.01 50.06] 0.66, Spherd Diameter| 2 | ©O-& 6 EX001=0,06| 0.66 D Gi6e, : (en ore 6 6X0.0) = 0.06] 0.66, , -. radius of sphere =r=D/2 =0,:22. em., , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , 2) For Measurement of inner diameter ‘d’ and height (depth) ‘h’ of the hollow cylinder, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , Dimensions] Obs.| Main scale| Coincident | Vernier scale Total |Corrected) Mean, Object of No.| reading |divs. number] Reading Reading} Reading | Reading, Cylinder (a) em on V.S. (b=nxLC) | (T=a+by Tt Z, (n) div. em cm em em, ae 1 1.6 < Xo. kee, Diameter 2 iS, Hollow 3 aS, j Cylinder| 1 S-7 5.01= 0,091 6.79, V Height = 7m 2, Tare ) ) 7, } @eptt), 3, I hs ‘ Pall me ( o.852cm, i = yadius of hallow cyline 0.8 rv, , 4 a, Calculations : 1) for Volume of solid sphere V = 5 mr 2) for Volume ofhollow cylinder V’ = TRh, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , 3 2, Bi xan * 0.5? a=log4= 0.6021 a=log n= 3.142, Be jog a- 104° = =, fog 2/4 i b=log n= 3.142 b=logR=, Jego.02° "> c=logr= { c=2logR=, E g.C a ea Stee, 4 G,496945.555 d= Sloge logh, 6,125 0+1-0524) e=at+bt+d= ere =, At A nk, 7 oy | Es nn oe V’=antiloge= sa eseeee cm*, 09-1507, emcie V=oTR*h, Ve=antilog g= |) sssnnnnee cm? Sa) xC0,862)2 x6.19, a Hue (2% 7.9304) 40-8312, = OVS See }O R, = 11892 Anite $)+ 0.283), 3 SiS.46 Ma, GX) <. volume of sphere = V Q-).404cem' a volumecenaney cylinder=V" \att6om?, ba Handbook of Physics Practicals : Std. XI 4 7, , Scanned with CamScanner
Page 4 :
!, !, , , , , , , , , , , , , , Results : 1. Least count of Vernier callipers =, 2. Zero error of vernier callipers..., , , , , , 3. Volume of sphere = V =., , 4. Volume of hollow cylinder = V’=..., Precautions: 1) While taking reading, object is held in jaws at different position., , 2) Use a magnifying glass (convex lens) to read the coinciding division. ifrequired., , 3) Do not press jaws hard, it should just tuch the object., , , , 4) Find zero error before starting the experiment., , , , O14 Sign of Batch Incharge, , , , Slips : 1), , , , Determine the least count of vernier callipers. Find the diameter of the given sphere using vernier callipers. Take 3, independent reading. Calculate the volume of the sphere., , Determine the least count of vernier callipers. Find the inner diameter and depth of the hollow cylinder. Take 3, reading in each case. Calculate the volume of the hollow cylinder., , 2), , , , Bring the two jaws in contact and note the division on the vernier scale which coincides with the zero, division ofmain scale., , , , (a) Ifthe zero division of vernier scale & zero division | Main Scale, fit eee ecincide as hoeninf No Zero Error, ofthe main scale coincide as shown in fig. (a) Vernier See, Then there is now zero error o (a) 10, (b) Ifthe zero of vernier scale laging behind the °, , , , zero of main scale as shown in fig. (b) Main Scale, r Be +ve Zero Error, Then the zero error is positive. 10 Vernier Scale, , 0, Bice . 56 A (b), e.g. If ,.th division of vernier scale coincides with some, , , , , , e.g. Coincident V, D.=3, main scale division then zero error = Z=+ (x x L.C.) Z.E=3 x 0.01=+ 0.03 cm., .. corrected reading T=(a+b)-Z Z =-0.03 cm, (c) Ifthe vernier scale zero division is ahead of main o }, scale zero division as shown in fig. (c) Main Scale, Then the zero error os negative. e.g.If ,.th division of 4 eos are, 3 . Fs 2 ase: ©) 10, vernier scale coincides with some main scale division e.g. Coincident V. D.=7, Then zero error = Z =-[(N-x) x L.C.)] Z.E=- (10-7) x 0.01 em=-0.03 em, corrected reading T=(a+b)+Z Z.=+0.03 cm, , Where N = Total number of divisions on the vernier scale, , , , Whether zero error is +ve or -ve it must be substracted (algebraically) from the total reading to, get the corrected reading ., , Handbook of Physics Practicals : Std. XI, , Scanned with CamScanner
Page 5 :
2. USE OF MICROMETER SCREW GAUGE, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , ? Aim 2 To measure cross sectional area of uniform wire and thickness of metal / glass plate by using, } micrometer screw gauge., i Apparatus : Micrometer screw gauge, wire of uniform diameter, metal / glass plate., | Diagram: Circular Scale, Anvil Main scale, ne Thinibio, Sleeve:, Va Ratchet, Screw with a Reference line, flat end, Spindle, Object, — U-shaped metal frame, Micrometer Screw Gauge, Formulae: 1) Least Count (L.C.) of micromerter screw gauge., , a Pitch of the screw, Total number of division on circular scale, (Pitch is defined as the distane between two consecutive threads.), 2) Diameter of wire / thickness of metal plate = M.S.R. + (C.S.R. x L.C.), 3) Area of cross section of wire (A) = 7?, , Procedure : 1) Determine the L. C. of the micrometer screw gauge and Calculate its zero error. 2) Keep, the given wire between butt and tip of the screw. Rotate the screw so that its tip comes in, contact with the wire. Screw should not be rotaed so as to make it very tight. 3) To measure, the diameter of the wire, note down the Main Scale reading & observe the div. on the Circular, Scale which coincides with the reference line. Multiplying the coincident div. on Circular, Scale by L. C. you get the circular scale reading. 4) Find the corrected reading by substracting, the zero error from the total reading which gives the diameter of the wire. Similarly determine, the thicknesses metal / Glass plate by following the same procedure as above., , Observations : Determination of Least count (L.C.) of Micrometer Screw Gauge, i) Value ofthe smallest division on Main Scale (M.S.)=m =., , , , i) Number of rotations required to advance the screw through, smallest division on M.S.=n=., , ifi) Pitch of the serew= P= aa, 1, , , , iv) Total no. of divisions on circular scale (N)=...0Q.., , , , vy) Least Count (L.C.) of the micrometer screw Gauze = eeoe «m= 0.00) Cm, \Ooo, , vi) Zero error of Micrometor scrow Gauze=Z=+ ..-1... cm., . Handbook of Physies Practicals : Std. XI 2x0 .00) = 40.004 Shy, , Scanned with CamScanner