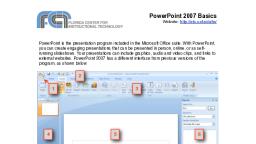
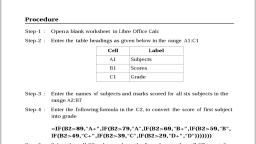
Page 1 :
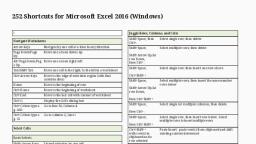
Excel Formulas, Basic math, Function, To add up the total, To add individual items, Subtract, Multiply, Divide, Exponents, Average, Median, Max, Min, , Formula, =SUM(cell range), =Value1 + Value 2, =Value1 - Value 2, =Value1 * Value2, =Value1 / Value2, =Value1 ^ Value2, =AVERAGE(cell range), =MEDIAN(cell range), =MAX(cell range), =MIN(cell range), , Example, =SUM(B2:B9), =B2+C2, =B2-C2, =B2*C2, =B2/C2, =B2^C2, =AVERAGE(B2:B9), =MEDIAN(B2:B9), =MAX(B2:B9), =MIN(B2:B9), , Formula, =PROPER(cell), , Example, =PROPER(A2), , =UPPER(cell), , =UPPER(A2), , =LOWER(cell), , =LOWER(A2), , Formula, =IF(logical test, “result if, the test answer is true”,, “result if the test answer is, false”), =EXACT(Value1, value2), , Example, =IF(B2>69,”Pass”,”Fail”), , Simple formatting tricks, Function, To change a cell to proper, case, To change a cell to upper, case, To change a cell to lower, case, Conditional statements, Function, If statement, , Exact, , =EXACT(B2, C2), , Absolute cell references, When a formula contains an absolute reference, no matter which cell the formula, occupies the cell reference does not change: if you copy or move the formula, it refers, to the same cell as it did in its original location. In an absolute reference, each part of, the reference (the letter that refers to the row and the number that refers to the column), is preceded by a “$” – for example, $A$1 is an absolute reference to cell A1. Wherever, the formula is copied or moved, it always refers to cell A1.
Page 2 :
Pulling things apart, Function, To select a certain number, of characters from the left, To select a certain number, of characters from the right, Find text in a field, , Extract information from, the middle, , Separate a last name, (Example: Smith, Jane), Separate a first name, (Example: Smith, Jane), , Formula, =LEFT(cellwithtext,, number of characters to be, returned), =RIGHT(cellwithtext,, number of characters to be, returned), =SEARCH(“text you want, to find”, where you want to, find it), =MID(cellwithtext, start, position, number of, characters you want, returned), LEFT and SEARCH, functions, MID and SEARCH, functions, , Example, =LEFT(A2, 6), , Formula, =CONCATENATE(text, “ ”,, text), =text & “ “ & text, , Example, =CONCATENATE(A2, “ “,, B2), =A2 & “ “ & B2, , Formula, =YEAR(datefield), =MONTH(datefield), =DAY(datefield), =WEEKDAY(datefield), , Example, =YEAR(A2), =MONTH(A2), =DAY(A2), =WEEKDAY(A2), , =DATE(year, month, day), , =DATE(B2, C2, D2), , =RIGHT(A2, 6), , =SEARCH(“,”, A2), , =MID(A2, 9, 4), , =LEFT(A2, SEARCH(“,”,, A2)‐1), =MID(A2, SEARCH(“,”,, A2)+2, 20), , Putting things together, Function, To combine cells with a, space in-between, To combine cells with a, space in-between (second, option), Dealing with dates, Function, Return the year, Return the month, Return the day, Return the day of the week, (1 = Sunday, 2 = Monday,, 3 = Tuesday, etc.), To create a date from year,, month, and day