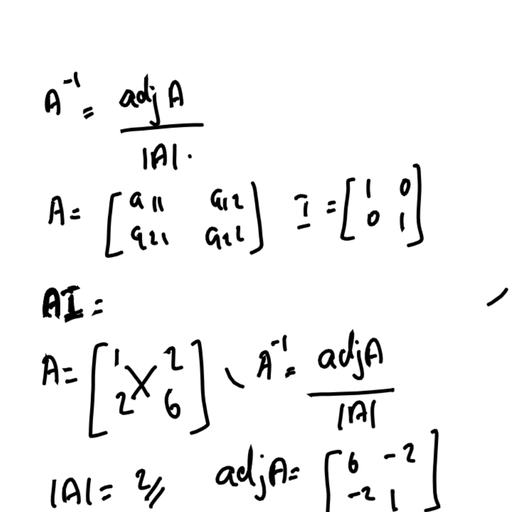Page 1 :
BSc. ComputerScience (Academic Year 2019-200nwards), SEMESTER III, XXXXA11- Python Programming, Course Number: 14, Contact Hours per Week: 4T, Number of Credits: 4, Number of Contact Hours: 64, Course Evaluation: Internal – 20 Marks + External – 80 Marks, Outcome of the Course:, Understand various statements, data types and functions in Python, Develop programs in Python programming language, Understand the basics of Object oriented programming using Python, Objectives of the Course:, To learn basics of Python programming, To learn decision making, looping andi, • Understand Object Oriented Pfogramming using Python, functions in Python, Prerequisites:, • Knowledge of C language., Course Outline, UNIT I [16T], Introduction to python, features, IDLE python interpreter Writing and executing python scripts,, comments, identifiers, keywords, variableslaA type, operators, operator precedence and, associativity, statements, expressions, user inputs, type function, eval function, print function., UNIT II [16T], Boolean expressions, Simple if statement, if-elif-else statement, compound boolean expressions,, nesting, multi way decisions. Loops: The while statement, range functions, the for statement, nested, loops, break and continue statements, infinite loops., UNIT III [16T], Functions, built-in functions, mathematical functions, date time functions, random numbers, writing, user defined functions, composition of functions, parameter and arguments, default parameters,, function calls, return statement, using global variables, recursion., 31 | Page Board of Studies UG | Computer Science& Applications University of Calicut, Page 32 of 122, Scanned by CamScanner
Page 2 :
BSc. ComputerScience (Academic Year 2019-200nwards), UNIT IV [16T], String and string operations, List- creating list, accessing, updating and deleting elements from a, list, basic list operations. Tuple- creating and accessing tuples in python, basic tuple operations., Dictionary, built in methods to access, update and delete dictionary values. Set and basic operations, on a set., References:, 1. E. Balaguruswamy, Introduction to Computing and Problem Solving Using Python, 2. Richard L. Halterman, Learning To Program With Python, 3. Martin C. Brown, Python: The Complete Reference., UNIVERSITY, 32 | Page Board of Studies UG Computer Science& Applications University of Calicut, Page 33 of 122, Scanned by CamScanner, OF CALICU
Page 3 :
BSc. ComputerScience (Academic Year 2019-200nwards), XXXXA12 Sensors and Transducers, Course Number: 15, Contact Hours per Week: 4T, Number of Credits: 4, Number of Contact Hours: 64 Hrs., Course Evaluation: Internal – 20 Marks + External – 80 Marks, Course Outcome, The students will be able to, • Explain resistance, inductance and capacitance transducers., • Perceive the concepts of temperature and pressure transducers., • Perceive the concepts level transducers such as and flow transducers, • Explain Electromagnetic transducers and fadiation sensors, • Explain force and torque transducendand sound transducers, Course Outline, Unit I [16 T], Transducers: Definition, Principle of sensing &, of transducers. Basic requirement of transdycers., Classification, Characteristics, Resistance Transducer: Basic principle Potentiometer -Loading effects, Resistance strain, gauge- Types., Inductance Transducer: - Basic principle – Linear variable differential transformer RVDT-, types. Capacitance Transducer: Basic principle- transducers using change in area of plates -, distance between plates- variation of dielectric constants -Types, Unit II [16 T], Thermal sensors: Resistance change type: RTD - materials, construction, types, working, principle, Thermistor - materials, construction, types, working principle, Thermo emf sensors:, Thermocouple – Principle and types, Radiation sensors: Principle and types., Pressure Transducers: basic principle- different types of manometers-u tube manometer-well, type manometers., 39 | Page Board of Studies UG Computer Science& Applications | University of Calicut, Page 40 of 122, Scanned by CamScanner
Page 4 :
BSc. ComputerScience (Academic Year2019-200nwards), Unit III [16 T], Level transducer-continuous level measurement-discrete level measurement-mass, capacitive level gauges, Flow Transducers: Bernoulli"s principle and continuity, Orifice plate, nozzle plate, venture, tube, Rotameter, anemometers, electromagnetic flow meter, impeller meter and turbid flow, meter, Unit IV [16 T], Hall effect transducers, Digital transducers, Piezo-electric sensors, eddy current transducers, tacho, generators and stroboscope, Magnetostrictive transducers, Radiation sensors: LDR, Photovoltaic cells, photodiodes, photo emissive cell types, Force and Torque Transducers: Proving ring, hydraulic and pneumatic load cell, dynamometer and, gyroscopes., OF, Sound Transducers: Sound level meter, Mferophone., Text Books, 1. D Patranabis, Sensors and Transducers, PHI, 2nd Edition., 2. E. A. Doebelin, Measuremht Systems. Application, Measurement and, Instrumentation, DhanpatRai and ConpanPrivate Limited., 4. Murthy D.V.S., -Transducers and Instrumentation, 2nd Edition, Prentice Hall, of India Private Limited, New Delhi, 2010., 5. S.Renganathan, –Transducer Engineering, Allied Publishers, 2005, 34 | Page Board of Studies UG Computer Science& Applications University of Calicut, Page 35-of 122, Scanned by CamScanner, CALICUT
Page 5 :
6 Nog and digital signals, Encoding and modulating-, multiplexing, TDM, multiplexing applications: the re, Radio Interface in GSM, BSc. ComputerScience (Academic Year2019-200nwards), SEMESTER IV, XXXXA13- Data Communication and Optical Fibers, Course Number: 19, Contact Hours per Week: 4T, Number of Credits: 4, Number of Contact Hours: 64, Course Evaluation: Internal – 20 Marks + External – 80 Marks, Course Outline, Unit I (16T]:, Introduction- Components, Networks, Protocols and standards, Basic Concepts:, Line, Configuration, Topology Transmission, analog-to-digital conversion, digital, conversion, digital data transmission, DTE-DCE, interface, modems, cable modems. Transmission media: guided media, unguided media, and, transmission impairment., Unit II [16T], Multiplexing: Many to one/ onépo many frequency diision multiplexing, wave division, system, Cellular System, Mobile, Communication-GSM, Mobile Services, GSMs, Unit III [16T], Data link Control: Line Discipline, flow control, error control, Data link Protocols: Asynchronous, Protocols, synchronous protocols, character oriented protocols, bit - oriented protocols, link access, procedures. Local Area Networks: Ethernet, token bus, token ring, FDDI, Comparison, Switching-, circuit switching, packet switching, message switching, integrated services digital networks, (ISDN): services, history, subscriber access to ISDN., Unit IV [16T], Overview of Optical Fiber Communication - Introduction, historical development, general system,, advantages, disadvantages, and applications of optical fiber communication, optical fiber, waveguides, fiber materials, Optical Sources And Detectors- Introduction, LED“s, LASER diodes,, Photo detectors. Ray theory, cylindrical fiber, single mode fiber, cutoff wave length, mode field, diameter., 33 | Page Board of Studies UG | Computer Science& Applications University of Calicut, Page 34 of 122, Scanned by CamScanner