Page 1 :
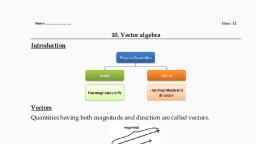
Vector, algebra, A look at vectors...., And it's idea
Page 2 :
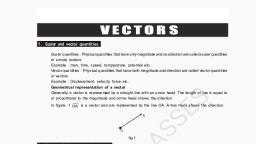
o a quantity that involves only one value (magnitude) which is a real, number ., length, mass, time, distance, speed, area, volume, temperature, work,, money, voltage, density, resistance etc. Are the examples., , Definition : scalar and examples
Page 3 :
• A quantity that has magnitude as well as, direction is called a vector., • Examples: displacement, velocity, acceleration,, force, weight, momentum, electric field intensity, etc., , Vectors and examples
Page 4 :
Directed line and Directed line segment, • Line directed using arrow is, called directed line., • Directed Line has, no boundary . It can move, indefinitely in, both directions. (see fig.1&2, ), , • Line segment directed using, arrow is called directed line, segment., • It has boundary.it has initial, and terminal points., • It has a definite, magnitude and direction., See 3rd pic
Page 5 :
a directed line segment is a vector ., Figure, denoted as AB or simply as r ,, and read as ‘vector AB ’ or ‘vector r'., i will use capital letters to show vectors, and small letters to show magnitude.
Page 6 :
Position vector, • In 2D and 3D,position vector shows the position, Of a point w.r.t origin., Initial point, origin, Terminal point, position of the point, , Z -axis, , P ( x, y, z), , Y- axis, , P (x, y), , Y -axis, , X -axis, X-axis
Page 7 :
Basic type of vectors, 1. zero vector, • A vector whose initial and terminal points coincide, is called a zero vector, (or null vector),, • It is denoted as 0 ., • Visualization: a point itself is a null vector., For example - The vectors AA, BB represent the zero vector where A or B, denote a point., • Magnitude of zero vector is zero.
Page 9 :
• Click to add text
Page 10 :
Unit vector and it's visualization, • Question 1. what do we mean by saying a vector A is in the direction of B?, • Question 2.are other vectors is in the direction of the golden color vector?, Vector a, Ans : vector a and vector d, Vector f, , Vector b, Vector c, Vector d, , Vector e, , Question3: what is the idea of magnitude and, direction as per your answer?, Ans: magnitude: vector b> vector d > vector a, Direction of A,B,D is same.
Page 11 :
Addition of vectors( two), • IDEA :, • MOVE ALONG THE DIRECTION OF, VECTOR ,THEN POSITIVE VECTOR, • MOVE OPPOSITE TO THE, DIRECTION OF VECTOR , THEN, NEGATIVE VECTOR, • DISPLACEMENT = 0, , THE DIRECTION, OF VECTOR IS DECIDED, BY DIRECTION OF ARROW, , TRIANGLE LAW OF VECTOR ADDITION, , C = vector a + vector b, Vector b, , Vector a, Vector b, , Vector a, , PARALLELOGRAM LAW OF VECTOR ADDITION, , Vector a, , Vector b
Page 12 :
Resolution of a vector
Page 14 :
The best thing about vectors is its visualization ., So, what you need to do is IMPROVE your visualization, skills., , Trigonometry help you to, understand world of vectors and, applications better.