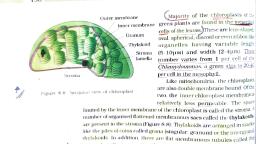
Page 1 :
5.4. DROUGHT, Since time immemorial, mankind has lived under the threat of natural disasters. Amongst various, , hazards of nature, drought is the most disastrous. In the past, India had been a frequent victim, pf disastrous droughts, which resulted in famine deaths of large members of human and livestock., Drought, thus, is a precursor of famine and undoubtedly man's worst natural enemy. Technological, developments and natural efforts are in progress to ameliorate the impacts of drought and being, , about sustainability to agricultural productivity in the country., Low rainfall or failure of monsoon rains is a recurring feature in India. This has been responsible, for droughts and famines. The word drought, generally, denotes scarcity of water in a region., , Though arjdity and drought are due to insufficient water, arjdity is a permanent climatic feature, and is the culmination of a number of long term processes However drought is a temporary
Page 2 :
short period due to deficient precipitation for vegetation, river flow, and human consumption Drought is due to anomaly ií atmospheric circulation, , Condition that occurs for, water, , supply, , a, , resulting either, Droughtis a climatic anomaly, characterised by deficit supply, combination all the factors., from subnormal rainfa!l, uneven distribution, higher water need or a, Droughts lead to problems like widespread crop failure, unreplenished groundwater resources,, in, shortage of drinking water, reduced fodder availability etc., of moisture, , depletion, , lakes/reservoirs,, , 5.4.1. DEFINITION OF DROUGHT, There is no universally accepted definition of drought. Early workers defined drought as prolonged, period without rainfall According to Ramdas (1960), drought is a situation when the actual, , seasonal rainfall is deficient by more than twice the mean deviation American Meteorological, as a period of abnormally dry weather, sufficiently prolonged for lack, defined, , drought, , Society, , of water to, In, , cause a, , severe, , general, drought, , hydrological, , means, , different, , imbalance in the, , things, , area, , to different, , affected., , people, , To a, , meteorologist it is the, , absence of rain while to the agriculturjst it is the deficiency of soilmoisture. in the crop root zone, , to support optimum crop growth and productivity. To the hydrologist it is the lowering of water, levels in lakes, reservoirs ete, while for the city management it may mean the shortage o, 10r, drinking water availability, Thus, it is unrealistic to expect a universal definition of drought, , allfields of activity., , Prolonged deficiency of soil moisture adversely, , affect crop, , growth indicating incidence or, , agriculture droughIt is the result of imbalance between soil moisture and evapotranspiration, , needs of an area pver a fairly long period, the yields., , as, , to cause, , damage, , to, , standing, , crops and to reduce
Page 3 :
proga, , DROUGHT OR MOISTURE sTRESS, Anlextended period of deficiept rainfall compared to normal rainfall of the region is called, drought Depending op the criteria used, drought is called as meteorological, agriculture or, , hvdrological drough(Meteorological dròught refers to substantial deficit of rainfall relative, , o average of the region. Indian Metcorological Department defines meteorological drought, as a siqyation when there is a 25% decrease in the averagerainfall for a given periodin_a, region Apicultural drought refers to extended dry period in whichlack of raintalresult, n Imsufhcient moisture in the root zone of the soil causing adverse effects on cropg., Hydrological drought is extended dry period leading to marked depletion of surface wáter, , and consequent drying up of reservoirs, lakes, streams, rivers, cessation of spring flows and, fall in groundwater levels), and famines are, Based on extent of rainfall deficit, the terms like dry spell, drought, , 15 days in, used.Dry spell is a rainless periðd more than 10 days in light soils areas and
Page 4 :
PRINCIPLES OF AGRONOMY, , 434, , heavy soil areas. Drought is, , prolonged dry, , spell resulting wilting.or_drying, g of crops, , crops. Svere, famine, formdrought is called, Desertification is land deradation in arid, semiarid and dry humid areas resulting fros, , various factors including climate variation and human activities) LDesertification process, mainl, occurs due to recurrent droughts, over grazing, reduction in, vegetation, soil degradation and, reduction in water resources. The main effect of drought is reduction in, crop growth, reduction, in yield and/or crop failure depending on the, intensity of drought. The other effects, , drought, , o, , shortage, drinking water to livestock., Soil moisture is the most limiting factor in dry farming and dryland farming situations, Understanding of the physiological proceses that occur during moisture stress or drought, are, , acute, , of fodder and, , stress is necessary to, , ameliorate, , the stress, , improvement., , I n biology,, , effects either by management practices or by plant, , stress is the result of action of, , stress indicates the action of lack of, is generally used for, , or excess, , external factor, , of water, , deficitmoisture conditions though, , on, , on, , anorganism) Moisture, , plants. The(term moisture stress, , it is applicable to excess, , moisture, , also. Since moisture deficit is most prevalent under dry farming conditions, the effect of, , moi_ture stress due to deficit is discussed in this chapter, Stress due to excessive moisture, is discussed under irigation., DAvelonmant f, , MictuLPA t r a c
Page 5 :
DROUGHT, Drought is, , a precursor, , of -, , Famine, feature, , Aridity is a permanent climatic, short period because of insufficient, , whiereas, drought, , rainfall to, , is, , temporary condition, , occur, , rs for a, , vegetation., , seasonal rainfall is deficient, Drought is a situation when the actual, mean deviation,, , by more than twicee tha, , Drought Classification, Based, 1., , 2, 3., , 4., , on, , duration and nature, , Permanent, , drought: It, , in a whole, , year., , occurs, , in, , a, , desert climate where, , agriculture is possible only by irrigation, , season and dry seasons, drought : It occurs in arid and semi-arid regions where rainy, are well defined., occurs in humu, It, rainfall., especially, of, failure, abnormal, the, It, is, Contingent drought :, and sub-humid regions and usually affects small areas, , Seasonal, , rainfall is insune, when there is frequent rain in a region. When, It occurs in humid regro, to meet ET loSs, the result is borderline water deficiency., Invisible, , drought: It, , occurs
Page 6 :
DRYLAND, Based o n u s e r, , Aoricultural drought: It resulted from an imbalance between available soil moisture and, evapotranspiration of a crop. This insufficient soil moisture in crop root zone does not, support, , optimum growth, , and, , development. It is also known, , as, , soil drought., , Agriculture (1976), agriculture drought is defined as a, 50% of LTA (long-term, period of 4 successive weekS with a rainfall deficiency of more than, , According to National, , Commission, , on, , weeks during another season., average) during crop season (mid-May to mid-October) or 6, winds, by, dry, hot,, low, accompanied, to, due, is, It, humidity, atmospheric, Atmospheriç drought:, even, , under, , adequate soil, , Hydrological drought :, , moisture., , It resulted when, , depletion of surface water and, , consequent, , drying of, , the reservoir, tanks, ponds, etc. it occurs when meteorological drought prolongs, , rainfall deficiency is, situation, is, a, the, it, when, IMD,, Meteorological drought: According, sub-station. It is categorized as moderate drought, of, a, meteorological, LTA, of, the, o r more, deficiency is higher, rainfall deficiency is between 26 to 50%) and severe drought (if rainfall, to, , than 50%), ICcal, , 0, co, Season., , drought Sufficient, , water, , is there but could, , not, , be stored, , or, , harvested due to, in Megnalaya, , Cherapunjee, infrastructural facilities or poor economic investments, e.g.,, from extreme drought during, Une highest rainfall in the world but suffers, , the winter, , t h e soil
Page 7 :
5.4.2. CLASSIFICATION OF, , DROUGHT, , be classified based on duration and nature of users. In both the classifications,, the cause and, demarcation between the two is not well defined and many a time overlapping of, effect of one on the other is seen. Droughts are classified into four kinds., , Drought, , can, , Permanent Drought, This is, , characteristic, , drought and agriculture is, , climate where sparse vegetation growing, possible only by irrigation during entire crop season,, , of the desert, , 1s, , adapted, , to, , Seasonal Drought, , This is found in climates with well defined rainy and dry seasons Most of the arid and, , semiarid zones )fall in this category. Duration of the crop varieties and planting dates should be, such that the growing season should fall within rainy season., , Contingent Drought, This involves an abnormal failure ofrainfall It may occur almost any where especially in, most parts of humid or subhumid climates It is u[ually brief, irregular and generally affects only, a small areà., , Invisiblé Drought, This(can occur even when there is frequent rain in an area When rainfall is inadequateto, meet the evapotranspiration losses, the result is borderline water deficiency in soil resulting in
Page 8 :
DRYLAND AGRICULTURE, less than, , 277, , optimum yield. This, , occurs, , usually in humid regions., , Droughts are also classified based on their relevance to thé users., , Meteorological Drought, n, , India, the definition for meteorological drought adopted by IMDis a situation when the, , dehciency, , of rainfall at, , meteorological sub-division level is 25 per cent or more of the long(LTA) of that subdivision for a given period( Drought is considered moderate; if, the deficiency is, between 26 and 50 per cent and severe if it is more than 50 per cent.), in our, countrya year is considered to be a drought year in case the area affected by, moderate and severe drought, either, individually or together, is 20 to 40 per cent of the total, area of the, country and seasonal rainfall deficiency during southwest monsoon season for the, term, , a, , average, , country as a whole is at least 10 per cent or more. When the spatial coverage of drought is more, than 40 per cent, it will, be called as all India severe drought year (IMD Technical Circular No, , 2/2007)), , Atmospheric Drought, It is due, , to, , low air, , humidity frequently accqmpanied by hot dry winds.) It (may occur even, conditions of adequate available soil moisturd. Plants growing under favourable soil moisture, regime are usually susceptible to atmospheric dróught., under, , Hydrological Drought, Meteorological drought,, , surfäce, , water and, , consequent, , how it affects irrigation, , as a, , when, , prolonged,, , results in hydrological, drought with depletion of, drying of reservoirs, tanks etcThis is based on water balance and, whole for bringing crops to, , Agricultural, Drought, is, , maturity., , It, , the result of soil, moisture stress due to imbalance between available soil, moisture and, of a crop) It is, and progressive. Plants can, usually, gradual, therefore, adjust, at least partly, to the increased soil, moisture stress. This situation arises as a, precipitation or its uneven distribution both in space and time. It is also consequence of scant, usually referred as, , evapotranspiration, , drought.), , soil, , When soil moisturë and rainfall are, inadequate during crop growing, crop growth to maturity, which situation, causes extreme, , season to, , crop stress and, , support healthy, , wilting is called, agricultural drought.jlt is defined as a period of four consecutive, weeks, (of severe meteorological, drought) with a rainfall deficiency of more than 50, per cent of the, with, a, , weekly, , rainfall of 5, , when 80 per cent of the, rest, , of the year, , cm or, , country's, , long-term average, or, less during the, period from mid-May to mid-October(LTA), (kharif), total crop is, planted, or six such, consecutive weeks during, , the
Page 9 :
As per IMD studies.all\the drought years are El Nino years where as all the El Nino years are, , notdrought years indicating thereby that various other factors also equally influence the monsoon, over the Indian subcontinent. In this context, the winter circulation over the subcontinent, extended, period of occurrenee of western disturbances (late in the season), strengthening of heat low over, , N-W India in summer and shifts in zonal cells over India are some of the important parameters, , that influence monsoon system over the country., , Criteria of Drought, In India various states and official commission have adapted different criteria for classifying, , droughts., Imigation Commission, while adopting the(IMD classification of Meteorological drought, based on departure of annual rainfall from normal, considered those regions which experienced, drought in 20 per cent of years as drought areas and those arça which experienced drought in, more than 40 per cent of the years as chronic drought areas, , National Commission on Agriculture (1976) considered agricultural drought as an occasion, whetat least four consecutive weeks receive rainfall half of the normal (normal rainfall beng, 5, , mm, , or more) during the crop, , season, , (mid-May, , to, , mid-October), , or, , six such weeks durjng, , other, , period), The criteria adopted in different states also vary depending on the rainfall and crops grown, , n the region. Tamil Nadu considers region receiving less than 900 mm rainfall as drought, affected, while Karnataka considers regions receiving rainfall less than 400 mm during kharif and, less than 30 per cent during crop seaso and 20 per cent deficiency of rainfall during crucial, stages of crop growth as drought affected areas. Rajasthan on the other hand considers an yeap, scarcity year when the productiyity decrease by 50 per cent compared to a good crop year., , Many of the states also follow the Annawary" system wherein the crop conditions are assessed, , through, , visual estimates. The criterion followed, , Production above 75 per cent of normal: Nodrought., Production 50 to 75 per cent of normal :Moderate drought., , Production 25 to 50 per cent of normal Severe drought, Production less than 25 per cent normal: Disastrous drought., , Besides rainfall, various other climatic and soil factors have also been used for drought, , classification. (These include the aridity index (la) anomaly and ratio of actual to potential, evapotranspiration (AE/PE)) Studies at CAZRI categorised drought based on moisture stress, during crop growing seasoD using the following criteria, , rought free period : When cumulative AE curve is above cumulative PE/2 curve., Moderate drought period : When cumulative AE curve lies between cumulative PE/2 and, , PE4 curves., Severe drought period: When cumulative AE curve is below cumulative PE4 curve., , depends on the phonological state of crop growth. Hence, novel method, mpact, of, drought, of classification of agricultural droughts was attempted at CAZRI, considering the values of AE, a, , PE, , during, , different, , phenophases, , of crop, , growth, , as, , indicated in Table, , 5.6.
Page 10 :
Physiological drought: A condition where crops are unable to absorb water from the soil, even when water is available, due to the osmotic pressure of soil solution owing to increased, salt concentration as in saline and alkaline soils,, , The dry spell is the rainless period of 10 days (light soil) to 15 days (heavy soils) whereas,, drought is prolonged dry spell., , when leaf water potential reaches at -1.0 to -1.2 M Pa, Primary photochemical and electron transport process affects at -0.8 7 M Pa leaf water potential., , Stomata closing, , in, , soybean, , occur, , Photosynthetic rate is affected by leaf water potential of -1.6 M Pa., The gaseous exchange through plant leaves is governed by boundary layer, stomatal and, mesophyll resistance. However, the decrease in the rate of photosynthesisis mainly due to, stomatal resistance., Range of stomata resistance - 50-100 m/s, , 0 to 400 m/s., Resistance offered by mesophyll cell -100-1000 m/s, Boundary layer, , C4 plants, Drought, , utilize, , resistance ranges from, , CO,, , even, , at low concentration., , decreases the size of the cell and intercellular spaces and thicker the cell wall., enhances accumulation of proline (an amino acid)., , stress, , Drought, Under drought condition, the production of growth promoting hormones (e.g., cytokinin, gibberellic, and, acid and IAA) decreases, and growth regulating hormones (e.g., abscisic acid, ethylene, , betaine) increases.Moisture stress, , tu?, , delay maturity, , but, , as, , per rule, if moisture stress, , after, crop duration increases and when it occurs, , occurs, , before flowering, the, , flowering, the duration decreases.
Page 11 :
464 mm, , moususssy, , s3333u, , AGRONOMY, , FAC, ACTS, , for cOMPETITIONS, , xu.o.sss3333, , EI Nino-Southern Oscillation, , irregularly periodical variation in wis, much of the tron, Pacitie Ocean, ariecting, , (ENSO) : It is, , an, , tropics, , the tropical eastern, as La Nina, and the cooling phase, as El Nino, known, is, a band of warnm, Subtropics. The warming phase, associated wih, ENSO and is, the, of, v, BI Nino: It is the warm phase, Sea surface, , temperatures, , and, and, , over, , equatorial, , ean, , Pacific., , central and east-central, associated with cooler than averam, ENSO and is, the, of, phase, La Nina : It is the cooling, Pacific Ocean, central and eastern tropical, Surtace temperatures in the, development and intensity of El Nins, ino, It indicates the, Southern Oscillation Index (So), water, , that, , develops in the, , verage sea, , :, , or, , the pressure differences betwe, ween, using, calculated, SOl, is, The, Pacific, Ocean., the, in, La Nina events, above7, indicates BNino and, Australia. (The SOI value below 7 often, Darwin., Tahiti and, , Nina episodes., , Drought criteria, , otf country, , affected, , by, , moderate and severe, , According to IMD, when the, Drought, the seasonal rainfall, of the area of the country and, or together) is 20 to 40%, (individually, drought, in the country as a whole, knoyn as drought, monsoon is at least 10% or more, SW, deficiency during, known as a severe drought year., year, , year. If the affected, , area, , :, , area, , is, , more, , than, , 40%, it is, , Drought area:, , occurs in 20% of the year (13 dbAs), Drought area : Area in which drought, So dod, occurs in >40% ofthe year (, Severe drought area : Area in which drought, receives rainfall less than, as drought affected when, In Tamil Nadu, the region is considered, , 900 mm., , affected when receives rainfall less than, In Karnataka, the region is considered as drought, season and 20% deficiency of rainfall, 400 mm in kharifjand le_s than 30% during crop, , during crucial crop growth stàges, In Rajasthan, if productivity decreases by, scarcity year., Annawary system- In this crop production, , 50%, , are, , compared, , assessed, , to, , a, , through, , good crop year,, visual, , known, , as, , symptoms, , : Production above 75% of normal, , No drought, Moderate drought, Severe drought, , : Production 25-50% of normal, , Disastrous drought, , : Production <25% of normal, , : Production 50-75% of normal, , Drought criteria based on moisture stress during crop growth (CAZRI, Jodhpur), /Drought free period, , :AET> PET/2, , : PET/2> AET> PET/4, , Moderate drought period, Severe drought period, , :PET/4 AET, , Aridity index (AI), as-, , as a numerical indicator of the ldegree of drynes_ ofthe climate at a given location, expresseu, Al, , No. of rainy, , days xMean precipitation/day, , Mean temperature +10, AI, , AET, PET, , or
Page 12 :
465, DRYLAND AGRICULTURE, , Departure of aridity, , Drought classification, , index, , from normal, , <0.5, , Moderate, Large, , 0.5-1.0, , Severe, , 1.0-2.0, >2.0, , Disastrous, , Drought area 25% probability of rainfall departure, , from normal, , Chronic drought 40% probability of rainfall departure from normal (40% from normal), , Crop growing, Arid, , Semi-arid, Humid, , period, , ern, , tem, , : 7 4 days, , :75 119 days, :119 days