Page 1 :
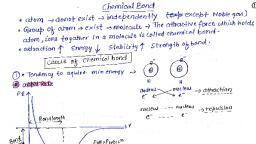
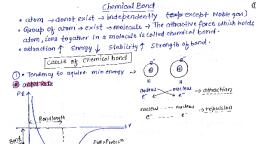
Sop hh NEET/JEE/CET Dr.Mahadev Shegavi a, aol ae, , Chapter-4, HE BOND AND CUI TRUCTUR, , , , The attractive force which holds. various constituents such as atoms, ions and molecules,, together in different chemical species is called a chemical bond., , Many theories were put forward to understand and explain chemical bonds., , 1, Kossel — Lewis approach, be VESEPR theory, , Be VBT, , 4. MOT, , Kossel ~ Lewis approach:, , With the exception of first-member; helium which has only two electrons in it's, valence shell the test of the elements have 8 electrons., , In 1916, kossel.and Lewis stated independently that the stability of noble gases is due to the, presence of 8 electrons in their valence shell or due to the presence of complete octet., , Lewis postulated that atoms achieve the stable octet when they are linked by chemical bonds., , For example, octet is achieved in NaCl by the transfer one electron by Na and gain of one, electron by Cl, In case-of Clo, Fp ete, the octet'is gained by sharing a pair of electrons., , Lewis symbols:, , In the formation of a:moleculer only the outer shell electrons take part in chemical, combinationand are known.as valence electrons., , Lewis introduced simple notations to represent valence electrons :in an atom. These notations, are called Lewis.symbols. For example, the Lewis symbols of, , s e o o- oe oo, Lie; ¢Be ; «Be, “Cle, *N* . $09 . gFe, s F « = , e, , Significance of Lewis symbols:, , The number of dots around the symbol represents the number of valence electrons., , The number of valence electrons helps us to-calculate the valency or group valence of the, element., , The group valence of the element is generally equal to either the number of dots in the Lewis, symbol or [8 — (number of dots)]}
Page 3 :
So» hh NEET/JEE/CET Dr.Mahadev Shegavi a, aol ae, , Octet Rule:, , Atoms can combine either by transfer of valence electrons from one atom to another or by, sharing of valence electrons in order to have 8 electrons or octet itt their valence electrons., , Covalent Bond:, Langamir (1919) refried Lewis postulations by introducing the term covalent bond., , “The bond’ formed between two or more. atoms by mutual contribution and sharing of, electrons is called covalent bond”,, , The atoms taking part in the covalent bond, formation may share one, two or three, electron pairs-depending upon their requirement and this leads to the formation of single (-);, double @) or triple (=)bond respectively., , Homoatomic molecules:, , Ex He + +H ——» HiH o H~H, , Ex: 3c. + 2lz—> Giri: or Cl-Ci, , =) @) — GP « 0-0, (iwi) + —> (GR) N=eN, , Heteroatromic molecules:, , — ©: @-@—@ap, CH), . Methane: a(x) + —— Ch E09, 3. Carbon dioxide: (8+ Ge) +82) oan 0=C=0
Page 5 :
NEET/JEE/CET Dr.Mahadev Shegavi a, iar), , , , Formal charge:, , Formal charge of Total number Total number of Total number, an atom in a = of valence electrons}—4 nonbonding electrons }— yy of bonding electrog, Lewis structure in free atom (lone pair) (Shared), , Formal charge is an apparent charge on the atom in a molecule and not it’s real charge., , Formal charge help in the selection of the lowest energy structure from a number of possible, Lewis structures. Generally the lowest energy structure in the one with the smallest formal, charges on the atoms., , Limitations of the octet rule:, 1. Incomplete octet of the central atom, , In some compounds, the number of electrons surrounding the central atom is less than 8., Ex:- LiCl, BeH) and BCI, , cl F, , LiCl HiBetH ci:B:cl F:B:F, 2. Odd-electron molecular:, Octet rule is not ratified for all atoms if the molecule contains odd number of, , electrons, Ex: NO, NO,, , , , N=9, 3.The expanded effect:, , It is a condition when the central atom has more than 8 electron around it., Ex: PFs, SFe, H3SO4 ., , F F, | F F | OF I, a, F—P ae H—O-S—O-H, |“ Ro N I, F oO, F F, , 4. Octet rule is based on the chemical inertness of noble gases. However, some noble gases, combine with oxygen and fluorine to form a number of compounds like XeF>, KrOF2, X.OF2, etc,, , 5. This theory does not account for shape of a molecule., , 6. It does not explain the relative stabilities of different molecules by comparing their, energies., , Jonic bond / Electrovalent bond:, As ionic / electrovalent bond is formed as a result of complete transfer of one or more, electrons from one atom to the others, It is generally formed between atoms belonging to, metals and non-metals., , The metal atom loses one or more electrons to become action while the anion gains one or, , more electrons. The oppositely charged ions are attracted towards. Each other and are held by, electrostatic force of attraction.