Page 1 :
BIOHACK NOTES, , ORGANISMS AND, , POPULATIONS, • Based on active recall and spaced repetition, • Target 360/360 in NEET Biology & 100/100 in Boards!
Page 2 :
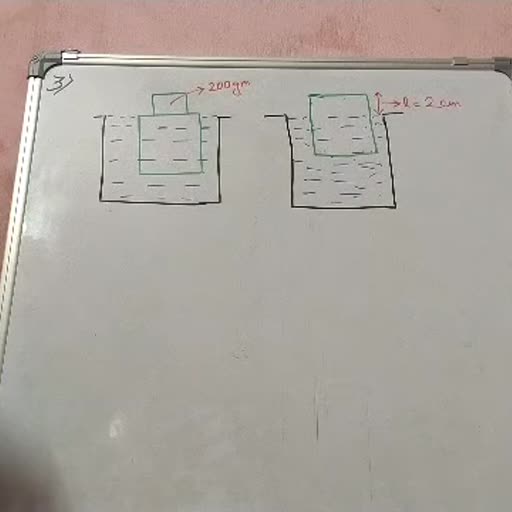
• INTRODUCTION, , 1. ________ is revered as the Father of Ecology in India. (NEET), 2. Arrange the various level of biological organisation in ascending order - (9), 3. Ecology is concerned with which 5 levels of biological organisation ?, • ORGANISM AND ITS ENVIRONMENT, , 4. Ecology at organismic level is essentially __________, 5. Precipitation includes both rain and snow. T/F, 6. Our intestine is a unique habitat for hundreds/thousands of species of microbes., 7. Name the abiotic factors that result in formation of different habitats (4) 8. What is a niche? (NEET), 9. Most ecologically relevant environmental factor is 10. Mangoes cannot grow in tropical/temperate countries like ______ and ______, 11. Snow leopards are not found in ______ forests., 12. Tuna fish are rarely caught beyond tropical/temperate latitudes., 13. Snow leopards are found near _______ and ________, 14. Organisms which can thrive on wide range temp. called 15. Restricted to narrow temp. range called 16. < ___ salt is present in inland water., 17. ___-___ salt is in the sea., 18. > ____ salt is in hypersaline lagoons., A, , B, D, E, F, , C, , DigaQ. 1
Page 3 :
DigaQ. 2, , A, , B, , C, , D, , 19. Organisms tolerating wide range of salinities 20. Tolerating only narrow range of salinities 21. _____ and _____ are adapted to photosynthesise optimally under very low light., 22. Soil composition, grain size and aggregation determine the _______ and ________ of the soils., 23. Sediment characteristics often determine the type of ______ animals that can thrive there., 24. Success of mammals is because - (1), 25. 99 % of animals are regulators/conformers., 26. Nearly all plants cannot maintain a constant internal environment. T/F, 27. Thermoregulation is energetically expensive for small/large animals., 28. Small animals find it very hard to live in colder areas. T/F, 29. Every winter, thousands of migratory birds come from ______ to ________ (NEET), 30. Ex. of hibernation - (1), 31. Ex. of aestivation - (2), 32. Stage of suspended development is called _______ and is seen in _______, 33. ____ in North/South American deserts can meet his water requirements through fat oxidation. (NEET), 34. Kangaroo rat however cannot concentrate its urine. T/F, 35. In ______, photosynthetic function is taken by flattened stems., 36. Define Allen's Rule., 37. Thick layer of fat in seal is called ______, DigaQ. 3, 38. Rohtang Pass is near Manali and Leh. T/F (NEET), 39. Symptoms of altitude sickness are - (3) (NEET), A, 40. Body acclimate to low oxygen at high altitude, B, by - (3) (NEET), 41. Ex.of animal having behavioural response to change, C, (abiotic) in environment is - (1) (NEET), 42. ________ bask in the sun, and move to shade, according to change in body temperature.
Page 4 :
• POPULATIONS, , 43. Natural selection operates at organism/population level., 44. _______ cranes are found in Bharatpur wetlands., 45. The tiger census in our _______ and _______ is often based on - (2), 46. Exponential growth is arithmetic/geometric growth., 47. In dN/dt = rN, r is called 48. R value for norway rat 49. R value from flour beetle 50. In 1981, r value for human population in India was 51. Exponential growth curve is __- shaped., 52. Logistic growth curve is __- shaped., 53. Population growing in habitat with limited resources show phases (4) 54. This type of population growth in limited resources is called ______-______ logistic growth., 55. The logistic growth equation is - (NEET), 56. Organisms which breed only once - (2), 57. Large no. of small sized offspring are produced by - (2), DigaQ. 4 - Name the type of pyramid., A, , DigaQ. 5, , B, , C, , P, , Q, , S, , R
Page 5 :
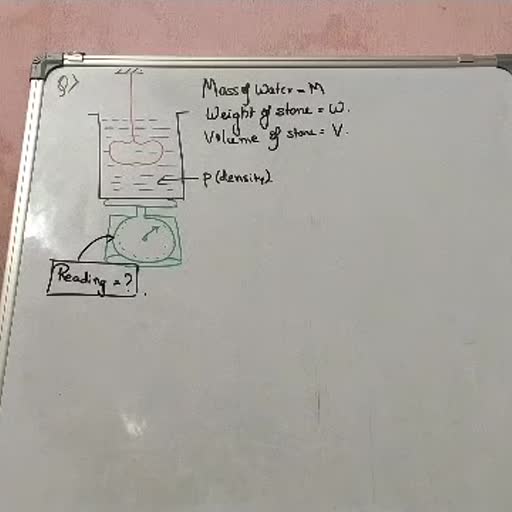
• POPULATION INTERACTIONS, , 58. Both species lose in 59. Ex. of interactions in which one species is benefited and other is not 60. Interacting species live closely together in - (3), 61. Sparrow eating a seed is a predator. T/F (NEET), 62. ______ act as 'conduits' for energy transfer across trophic levels., 63. Predators keep prey population under control. T/F (NEET), 64. ________ was introduced in Australia in early _____ (year) and became invasive., 65. It was brought under control by introducing 66. Predators have no function in maintaining the species diversity in a community. T/F (NEET), 67. In the rocky intertidal community of _______ the starfish _____ is an important predator. (NEET), 68. More than ___ (no.) species of vertebrates/invertebrates disappeared after removing starfish due to, ______ (NEET), 69. Predators are not prudent. T/F, 70. Some frogs are cryptically coloured. T/F, 71. _____ and _____ are cryptically coloured., 72. ______ is highly distasteful to its predator. (NEET), 73. Butterfly acquire this distasteful chemical during its _______ stage by feeding on _______ (NEET), 74. Nearly 25 % of all arthropods are phytophagus. T/F, 75. _____ are the most common morphological means of defense., 76. Ex of plants which have thorns - (2), 77. Calotropis produce highly poisonous ________., 78. Ex. of chemicals produced by plants for defense but extracted commercially - (5) (NEET), 79. Quinine is used to treat 80. Strychnine is an alkaloid. T/F, 81. It is used to kill pests. T/F, 82. According to Darwin, interspecific/intraspecific competition is a potent force in organic evolution., 83. In south american lakes, ______ and ______ compete for their common food, i.e. ________, 84. Resources need to be limited for competition to occur. T/F, 85. Define competition., 86. The ________ in Galapagos Islands became extinct when _____ were introduced.
Page 6 :
Table 1, , 87. Abingdon tortoises however had greater browsing efficiency than goat. T/F, 88. Barnacles are arthropods/molluscs/annelids., 89. Barnacles are insects/crustacea., 90. Superior barnacle was _______ which exclude the smaller barnacle ________, 91. _______ did his field experiments on rocky sea coast of _______ on barnacle., 92. Carnivores are more affected by competition than herbivores and plants. T/F, 93. Two closely related species competing for the same resources cannot co-exist indefinitely and the, competitively inferior one will be eliminated eventually.This statement is called - (NEET), 94. Species evolve mechanism to promote co-existence instead of exclusion. T/F, 95. _______ showed that 5 closely related species of warblers avoided competition due behavioural, differences in ______ activities., 96. Host and parasite tend to coevolve. T/F, 97. Loss of digestive system is seen in parasites. T/F, 98. Adaptations found in parasites are - (4), 99. Ex. of a trematode parasite 100. The intermediate host of liver fluke are - (2), 101. Ex. of ectoparasites are ____ on humans and ____ on dogs., 102. Many marine/freshwater fishes are infested with ecto/endoparasite copepods., 103. Copepods belong to class ______ and phylum _______., 104. Ex. of parasitic plant - (1), 105. Cuscuta don't have leaves and chlorophyll. T/F, 106. Female mosquito is a parasite for humans. T/F, 107. Life cycle of endo/ectoparasites are more complex., 108. Brood parasitism is seen between _____ and _____ (NEET), 109. In this, the crow is a parasite/host., 110. Breeding season is between _____ to ______, 111. Orchids grow as a ______ on a _____ branch., 112. _______ grow on the back of the whale.
Page 7 :
DigaQ. 6, , A, , B, , 113. Ex. of commensalism seen in farmed rural areas is 114. Sea anemone host ______ which get protected due to ______ on sea anemone., 115. Association between fungus and cyanobacteria can be called lichen. T/F, 116. Lichen can form between fungus and non-photosynthesising algae. T/F, 117. Mycorrhiza is between _____ and _____ (NEET), 118. Plants provide _______ to fungi., 119. Fungi help in ________, 120. Fig is pollinated by _____ (NEET), 121. Female wasp use fruit as an _______., 122. Fig even offers some ______ as food for the larvae., 123. Wasp pollinated the fig inflorescence while searching for suitable ________, 124. _______ show bewildering diversity of floral patterns., 125. Orchids are pollinated by - (2), 126. The __________ orchid named ______ employs "sexual deceit"., 127. All orchids offer rewards. T/F, 128. One petal of its flower bears an uncanny resemblance to the female of the bee in ____, ____, ____.
Page 8 :
ORGANISMS AND, , POPULATIONS, , ANSWERS
Page 9 :
• INTRODUCTION, , 1. Ramdeo Misra, 2. macromolecules, cells, tissues, organs, organism,, population, communities, ecosystems and biomes, 3. organism, population, communities, ecosystems and, biomes, • ORGANISM & ITS ENVIRONMENT, , 4. Physiological ecology, 5. T, 6. Hundreds, 7. temperature, water, light and soil, 8. Each organism has defined range of conditions, that it can tolerate, diversity in the resources it, utilises and a distinct functional role in the ecological, system, all these together comprise its niche., 9. Temperature, 10. Temperate, canada and germany, 11. Kerala, 12. Tropical, 13. Himalayan range and central asia, 14. Eurythermals, 15. Stenothermals, 16. 5, 17. 30-35, 18. 100, 19. Euryhaline, 20. Stenohaline, 21. Herbs and shrubs, 22. Percolation and water holding capacity, 23. Benthic, 24. Ability to maintain constant temp., 25. Conformers, 26. T, 27. Small, 28. T, 29. Siberia, , Keolado National Park (Bharatpur), Rajasthan, 30. Bears, 31. Snails and fish, 32. Diapause, zooplankton species, 33. Kangaroo rat, north, 34. F, 35. Opuntia, 36. Mammals from colder climates generally have, shorter ears and limbs to minimise heat loss, 37. Blubber, 38. T, 39. nausea, fatigue and heart palpitations, 40. increasing RBC production, decreasing binding, affinity of hemoglobin and increasing breathing rate, 41. Desert lizards, 42. Desert lizards, • POPULATIONS, , 43. Population, 44. Siberian, 45. Pug marks and fecal pellets, 46. Geometric, 47. Intrinsic rate of natural increase, 48. 0.015, 49. 0.12, 50. 0.0205, 51. J, 52. S, sigmoid, 53. Lag phase, phase of acceleration, phase of, deceleration, asymptote, 54. Verhulst-Pearl, 55. dN/dt = rN[(K-N)/K], 56. Pacific salmon fish, bamboo, 57. Oysters, pelagic fishes
Page 10 :
• POPULATION INTERACTIONS, , 58. Competition, 59. Predation, Parasitism, Commensalism, 60. Predation, Parasitism and Commensalism, 61. T, 62. Predation, 63. T, 64. Prickly pear cactus, 1920, 65. Cactus-feeding predator (moth), 66. F, 67. American pacific ocean, pisaster, 68. 10, invertebrates, interspecific competition, 69. F, 70. T, 71. Frogs and insects, 72. Monarch butterfly, 73. Caterpillar stage, poisonous weed, 74. F, insects would be there instead of arthropods, 75. Thorns, 76. Acacia, Cactus, 77. Cardiac glycosides, 78. nicotine, caffeine, quinine, strychnine, opium, 79. Malaria, 80. T, 81. T, 82. Interspecific competition, 83. Flamingoes and fishes, zooplankton, 84. F, 85. Process in which "r" is decreased due to, presence of other species, 86. Abingdon tortoise, goats, 87. F, 88. Arthropods, 89. Crustacea, 90. Balanus, Chathamalus, 91. Connell, scotland, , 92. F, 93. Gause's 'Competitive Exclusion Principle', 94. T, 95. MacArthur, foraging, 96. T, 97. T, 98. Adaptations found in parasites, I. loss of unnecessary sense organs, II. presence of adhesive organs or suckers to, cling on to the host, III. loss of digestive system, IV. high reproductive capacity, 99. Human liver fluke, 100. Snail and fish, 101. Lice, ticks, 102. Marine, ectoparasite, 103. Crustacea, arthropoda, 104. Cuscuta, 105. T, 106. F, 107. endoparasites, 108. cuckoo(koel) and crow, 109. Parasite, 110. Spring to summer, 111. Epiphyte, mango, 112. Barnacles, 113. Cattle egret and grazing cattle, 114. Clown fish, stinging tentacles, 115. T, 116. F, 117. Fungi and higher plant, 118. Energy-yielding carbohydrates, 119. Absorption of essential nutrients, 120. Wasp
Page 11 :
121. Oviposition (egg-laying), 122. Developing seeds, 123. Egg-laying sites, 124. Orchids, 125. Bees and bumblebees, 126. Mediterranean orchid, ophrys, 127. F, 128. Size, colour and markings, • DigaQs, , DigaQ. 1 – Biome distribution, A – Desert, B – Grassland, C – Tropical forest, D – Temperate forest, E – Coniferous forest, F – Arctic and Alpine tundra, DigaQ. 2 – Major biomes of India, A – Tropical rain forest, B – Deciduous forest, Table 1, , SCAN AND DONATE US SO THAT WE, CAN CREATE MORE SUCH QUALITY, CONTENT FOR YOU!, , C – Desert, D – Sea coast, DigaQ. 3 – Organismic response, A – Conformers, B – Regulators, C – Partial regulators, DigaQ. 4 – Age pyramids for human population, A – Expanding, B – Stable, C – Declining, DigaQ. 5 – Population density, P – Immigration (I), Q – Natality (B), R – Emigration (E), S – Mortality (D), DigaQ. 6 – Mutual relationship between fig tree, and wasp, A – Fig flower is pollinated by wasp, B – Wasp laying eggs in the fig fruit