Page 1 :
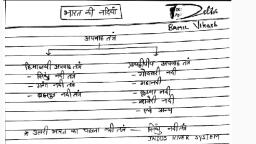
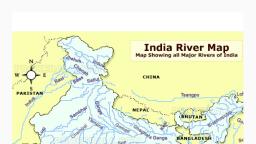
The Indus River System, , The Indus arises from the northern slopes of the Kailash range in Tibet near Lake, Mansarovar, , •, , It has a large number of tributaries in both India and Pakistan and has a total, length of about 2897 km from the source to the point near Karachi where it, falls into the Arabian Sea out of which approx 700km lies in India, , y, d, u, t, s, ., s, s, e, l, e, r, i, t, , •, , It enters the Indian Territory in Jammu and Kashmir by forming a picturesque, gorge, , •, , In the Kashmir region, it joins with many tributaries – the Zaskar, the, Shyok, the Nubra and the Hunza, , •, •, , It flows between the Ladakh Range and the Zaskar Range at Leh, It crosses the Himalayas through a 5181 m deep gorge near Attock, which is, lying north of Nanga Parbat, , The major tributaries of the Indus River in India are Jhelum, Ravi, Chenab,, Beas, and Sutlej., The Indus river is one of the world's largest river basins. It is also known as Sindhu. The, river lows through China(Tibet region), India and Pakistan. In Tibet, it is known as Singi, Khambai or Lion's mouth. The Indus Valley Civilization was born around this river., , ., , , ., , , ., , , ., , , ., , , ., , , f, , @tireless.study
Page 3 :
Primary Tributaries of the Indus rive, The Rav, , y, d, u, t, s, ., s, s, e, l, e, r, i, t, , • The Ravi river originates near the Rohtang Pass in Kullu hills in, the state of Himachal Pradesh., , • The river flows through Chamba valley., • The river drains away the area lying between southeastern part, of Pir Panjal and the Dhauladhar ranges., , • It enters Punjab Plains near Madhopur and later enters, Pakistan below Amritsar, , • It debouches into the Chenab a little above Rangpur in, Pakistani Punjab, , • It merges into Chenab river near Sarai Sandhu in the Punjab, region of Pakistan., , , , , , , , r, , , , , , ., , , ., , , i, , , @tireless.study
Page 4 :
The Jhelum, , At Muzaffarabad, the river takes a sharp hairpin bend southward, , Thereafter, it forms the India-Pakistan boundary for 170 km and emerges at the Potwar, Plateau near Mirpur, After flowing through the spurs of the Salt Range it debouches (emerge from a confined, space into a wide, open area) on the plains near the city of Jhelum, It joins the Chenab at Trimmu, , The river is navigable for about 160 km out of a total length of 724 km, It merges into Chenab in Pakistan., , ., , , ., , , ., , , @tireless.study, ., , , •, •, •, , The river forms steep-sided narrow gorge through Pir Panjal Range below Baramula, , , , , •, , The Jhelum river rises from the Sheshnag Lake near Verinag at the foot of Pir Panjal, range., , , , , •, •, •, , y, d, u, t, s, ., s, s, e, l, e, r, i, t, , At Baramulla the river enters a gorge in the hills., , ., , , •, •, , It flows northwards into Wular Lake (north-western part of Kashmir Valley). From Wular, Lake, it changes its course southwards., , ., , , •, , The Jhelum has its source in a spring at Verinag in the south-eastern part of the, Kashmir Valley., , , , , •
Page 5 :
The Chenab, , Near Kistwar, it cuts a deep gorge, , It enters the plain area near Akhnur in Jammu and Kashmir, From here it through the plains of Pakistani Punjab to reach, Panchnad where it joins the Satluj after receiving the waters of, Jhelum and Ravi rivers., , @tireless.study, ., , , •, •, •, , The united stream Chandrabhaga flows in the north-west direction, through the Pangi valley, parallel to the Pir Panjal range, , ., , , •, , y, d, u, t, s, ., s, s, e, l, e, r, i, t, , Two small streams on opposite sides of the pass, namely Chandra, and Bhaga, form its headwaters at an altitude of 4,900 m, , ., , , •, , The Chenab originates from near the Bara Lacha Pass in the LahulSpiti part of the Zaskar Range., , ., , , •
Page 6 :
The Bea, , • The Beas river rises from Beas Kund near the Rohtang Pass in the state of, Himachal Pradesh., , y, d, u, t, s, ., s, s, e, l, e, r, i, t, , • The river flows through Kullu Valley., • It forms a gorge at Kati and Largi in the Dhauladhar range., • The river merges into the Satluj river at Harike in the state of Punjab., • Harike wetland is a Ramsar site, a wetland of international importance., • It crosses the Dhaola Dhar range and it takes a south-westerly direction and meets, the Satluj river at Harike in Punjab., , The Satlu, , • The Satluj river rises from the Rakas Lake near the Mansarovar Lake in the Tibet, region., , • In Tibet, the river is known by the name of Langchen Khambab., • The Satluj river flows parallel to the Indus river before entering India at Shipki La., • It is an antecedent river., • The Bhakra Nangal Project is constructed on the Satluj river., , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , j, , , s, , , , , , @tireless.study
Page 7 :
Major River Valley Projects/Dams/Barrages associated with the Indus, syste, , •, , The Indira Gandhi Canal Project- It is one of the largest and the, longest canal project in the world. The Indira Gandhi Canal starts from, the Harike Barrage at Harike(in Punjab), the confluence point of the, rivers Satluj and Beas, to southward till Barmer(in Rajasthan). The canal, has transformed the barren areas of Rajasthan into prosperous, agricultural fields. Besides providing water for agriculture, the canal, supplies drinking water to hundreds of people in far-flung areas, , y, d, u, t, s, ., s, s, e, l, e, r, i, t, , •, , The Bhakra Nangal Project- This multipurpose river valley project was, constructed for supplying electricity to the power-hungry north-western, India and to extend irrigation facilities in the north-western Haryana and, south-western Punjab. Bhakra Dam and Nangal Dam have been, constructed on the river Satluj in the state of Himachal Pradesh. The, water reservoir behind the Bhakra Dam is known as Gobind Sagar, , •, , The Upper Bari Doab Canal- It draws its water from the Ravi river. It, starts from Madhopur near Pathankot(in Punjab). The canal provides, irrigation to the northern districts of Punjab, mainly Pathankot,, Gurdaspur, Amritsar and Tarn Taran., ., , , ., , , m, , , @tireless.study
Page 8 :
•, , The Chamera Dam- The dam has been constructed on the, river Ravi in Chamba district, Himachal Pradesh. The dam, fulfils the hydroelectric needs of the region, The Dul Hasti Dam- The dam has been constructed on the, river Chenab in the state of Jammu and Kashmir., @tireless.study, ., , , •, , The Thein Dam- The dam has been constructed on the river, Ravi near Pathankot in the state of Punjab. It is also known as, Ranjit Sagar Dam. It is the largest hydroelectric project of, Punjab, , ., , , •, , y, d, u, t, s, ., s, s, e, l, e, r, i, t, , The Pong Dam-The dam has been constructed on the river, Beas in the state of Himachal Pradesh. The water reservoir, created by the dam, Maharana Pratap Sagar is a Ramsar, wetland site, , ., , , •, , The Sirhind Canal- It draws its water from the Satluj river. It, starts at Rupnagar/Ropar(in Punjab). The canal provides, irrigation in Ludhiana, Ferozepur, Sangrur, Bathinda and Patiala, districts of Punjab, , ., , , •
Page 9 :
•, , y, d, u, t, s, ., s, s, e, l, e, r, i, t, , The Tulbul Project- The project has been commissioned on the river, Jhelum in the state of Jammu and Kashmir. Wular Barrage on the, Wular Lake(a Ramsar wetland site) is constructed, The Uri Dam- The dam has been constructed on the river Jhelum in, the state of Jammu and Kashmir., , @tireless.study, ., , , •, , The Baglihar Dam- The dam has been constructed on the river, Chenab near Batote in the state of Jammu and Kashmir, , ., , , •, , The Salal Dam- The dam has been constructed on the river Chenab, at Dhyangarh in the state of Jammu and Kashmir, , ., , , •
Page 10 :
y, d, u, t, s, ., s, s, e, l, e, r, i, t, , According to this treaty, India can utilize only 20 per cent of its, total discharge of water., @tireless.study
Page 12 :
Q. Consider the following statement(s) is/are related to, the Indus River System:, I., , y, d, u, t, s, ., s, s, e, l, e, r, i, t, , It is known as Singi Khamban or the Lion’s mouth in, Tibet, , II. It originates from a glacier near Bokhar Chu in the, Kailash Mountain range., Which of the above statement(s) is/are correc, A. Only, B. Only I, , C. Both I and I, , D. Neither I nor II, , t, , , , , , I, , , I, , , I, , , ., , , @tireless.study
Page 13 :
Q. Which of the following is not the tributaries of the Indus Rive, A. Shyo, B. Gilgi, C. Zaska, D. Luni, , y, d, u, t, s, ., s, s, e, l, e, r, i, t, r, , , r, , , k, , , t, , , @tireless.study