Page 1 :
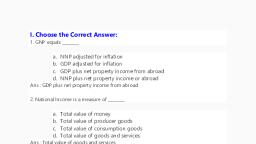
National income, 1. National income, National income indicates the economic condition of a country., A higher national income implies economic progress of a country., The total income received by a country in one year is its national income., It is the amount earned from the production of goods and services in a country during a year., This is received mainly from three sectors:, • Agriculture sector • Industrial sector • Service sector, Adding up the income from these three sectors, we get National Income. When we calculate the, money value of goods and services produced in a country during a particular year, we get, the National Income of the country for that year., 2. What are the objectives of calculating national income?, * National income is helpful in calculating the economic growth of a country, * To compare the economic growth of different countries, • To assess the contribution of different sectors in the economy, • To study the problems faced by the economy, • To help the government in planning and implementing different projects., • To find out the limitations and advantages of economic activities like production, consumption,, and distribution., 3. Important concepts of national income, Gross National Product – GNP, Gross Domestic Product – GDP, Net National Product – NNP, Per capita income, 4. Gross National Product - GNP, Gross National Product is an important concept of national income., It is calculated on the basis of the final goods and services produced in a country., The products that are available for consumption are called the final product., For example, we manufacture shirts using raw materials such as cloth, thread, and buttons. Here, the, shirt is the final product for consumption. The money value of final products is taken into account, for calculating the Gross National Product. While calculating the money value of the shirt, the value, of raw materials such as buttons and clothes are included. Thus, the money value of final goods and, services produced is the gross national product. The GNP of a country is calculated for a particular, financial year. In India, a financial year is from 1 April to 31 March., 5. Gross Domestic Product - GDP, Gross Domestic Product is the most suitable concept of national income to analyse the contribution, of sectors in an economy. The GDP of a country is the total money value of the final goods and, services produced within the domestic territory during a financial year. The income of people, working abroad and the profit of institutions and firms operating abroad will not be included while, calculating the Gross Domestic Product. For example, suppose an Indian firm operates in America., The profit of that institution will be included in the Gross Domestic Product of America but in the, Gross National Product of India. That is to say, while calculating the GDP of India, such income, will be excluded., 6. Net National Product - NNP, Machinery and other things suffer from wear and tear. The cost incurred to remedy this wear and, tear is termed as depreciation charges. The depreciation charges are taken into consideration, while calculating the national income. When we deduct depreciation charges from the Gross, National Product we get the Net National Product. Technically, the Net National Product is, considered as national income., Net National Product =Gross National Product – Depreciation charges, , www.shenischool.in
Page 2 :
7. Per capita income, When we divide the national income by population, we get per capita income. It helps to know the, economic position of a country and to compare it with other countries., Per capita income = National income, Total population, 8. Production and National Income, The economic condition of a country is calculated on the basis of national income. It is necessary to, increase production for economic prosperity. When production increases, the rewards of factors for, production like land, labour, capital, and organisation also increases. The increase in rewards, such as rent, wages, interest, and profit results in increased consumption and investment., Production, income, and expenditure are interrelated., 9. Three methods for estimating national income:, • Product method, • Income method, • Expenditure method, Estimation of national income using any of the above three methods will give the same results., 10. Product method, Under the product method, the national income is calculated by adding up the money value of, goods and services produced by the primary, secondary, and tertiary sectors. It is useful for, assessing the contribution of each of these sectors towards the national income. It is also used to, analyse which sector contributes the most to national income., 11. Income method, Income is the reward received for the factors of production. In income method, national income is, calculated based on rent, wages, interest, and profit, which are the rewards for factors of production., This method is helpful in analysing the contribution of each factor of production to the national, income., 13. Expenditure method, The expenditure method is used to estimate the national income by calculating the expenditure, incurred by individuals, firms and government in a particular year. In Economics, just like, consumption expenditure, investment is also considered as an expenditure. The summation of, consumption expenditure, investment expenditure and government expenditure, gives the, total expenditure., 14. Estimation of national income of India, The Central Statistical Office (CSO) is the official agency that estimates the national income of, India. The estimation is done mainly for the purpose of planning and development activities of the, government. It also helps to understand the nature of the employment sectors and the types of, employment the people are engaged in. In India, we make use of the product, income, and, expenditure methods to estimate the national income., 15. Difficulties in calculating national income of India, The assessment of national income is a tough job that is challenged by practical and idealogical, issues., • Lack of reliable statistical data creates difficulty in estimating national income, • There is a chance of calculating the money value of goods and services more than once (double, counting) while they pass through different stages of production., • Services of housewives is not included in national income., • The production of goods for self consumption is not included in the estimation of national income., Example - vegetable garden at home, • Ignorance and illiteracy of the people create problems in collecting statistical data., • The practical difficulty in assessing the money value of services obstruct the correct estimation of, national income, , www.shenischool.in
Page 3 :
• Consumers seldom maintain records of expenditure incurred by them., 16. Sectoral contribution to India's national income, The sum of income received from the primary, secondary, and tertiary sectors constitutes the, national income of a country., 17. Growth of the Service Sector, The recent trends in the contribution of various sectors to the national income of India show an, increase in the growth of the service sector. The secondary and tertiary sectors have come to, contribute more to the national income than the primary sector. As a part of development, the rise in, the establishment of educational institutions and hospitals along with the advancement in banking,, insurance, and telecommunication have helped the growth of the tertiary sector. With economic, growth, people are more willing to partake in transport and tourism. Development of knowledge, based industries has also helped in the growth of the tertiary sector., 18. Growth of knowledge sector, The knowledge sector is the sector which efficiently uses knowledge and technology to attain, economic growth. Today, modern technology and information & communication possibilities, have grown and developed into knowledge economy. Education, innovation, and Information &, Communication Technology (ICT) form the basis of knowledge economy., In knowledge economy, production and consumption of intellectual capital take place., Intellectual capital is an invisible asset. It is the collective knowledge of all the people in an, enterprise or a society. Today, as a part of the tertiary sector, growth of services based on knowledge, is happening on a large scale. People giving expert advice on shares and taxes, software experts, etc., are a part of this sector. Top business executives, researchers, scientists, expert policy makers,, economic experts, etc. strengthen to this sector. The government also gives priority to the, development of the knowledge sector. Initiatives of Govt. of Kerala like the Info-park and, Technopark are examples. India has achieved immerse progress in information and communication, technology, so much so that today we are a global service provider in the field of software, technology. As a result of this 'knowledge boom', India can enhance the welfare of the people, through an increase in economic growth., 19. Intellectual Capital, The knowledge sector is the sector which efficiently uses knowledge and technology to attain, economic growth. In knowledge economy, production and consumption of intellectual capital take, place. Intellectual capital is an invisible asset. It is the collective knowledge of all the people in an, enterprise or a society., 20. Favourable factors which can help India grow further in knowledge sector, • Human resource including technical experts who are well versed in the English language., • Wide domestic market, • Strong private sector, • Development of science and technology, , PRADEEP B, GHSS PUTHOOR, www.shenischool.in