Page 1 :
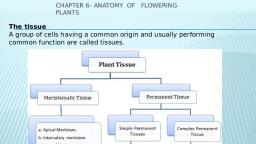
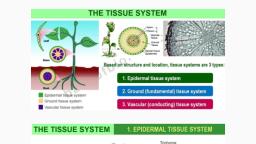
Tissues, , , , , , , , provide division of labour in multicellular organisms., : < in a tissue are arranged and designed so as to give the highest possible efficiency., Due to improved organisation and higher efficiency, multicellular organisms have higher survival, , Most plant cells are dead. These dead cells provide mechanical strength to the plant and need less, maintenance., " Plant tissues are of two types: meristematic and permanent tissues., , , , , , Classification of Plant Tissues, , , , , , Plant Tissues, , Meristematic Permanent, (Cells are capable of cell division) (Mature cells incapable of cell division), , , , , , , , , , Lateral Intercalary Simple-Protective Complex-Conducting, , ot (Below bark, (Internodes and Supporting (Tissue composed of, , ) cambiumindicot of stem) (Tissue composed of more than one type, _ roots and stems) single type of cells) of cells), , 4, , Sclerenchyma Phloem, |. Sieve tube, , Scanned with CamScanner
Page 2 :
—=— oe, , , , , , , , , 6 ts overall, , ‘one-cel thick layer and is covered with the ee, tissue, tus i, , sternatic tissue take Up a perma, , pipe tne :, which cells derived from mer!, , Petonis cated _—_————— ‘og, of cementing substance called the exists between two sclerenchyma, surfaces of many plants bear cutinised hair called, , 2. Sclerenchyma _ 3. Differentiation, , , , , , , 4, Middle lamella 5. Trichomes 1, , rat | 2 Give its importance. ', Peete cover roots of woody plants is known as bark. Bark is made up of, , ‘outer protective covering of stem and, that consists of several layers of compactly arranged dead rectangular cells., , Importance of bark:, | @) It protects plants against water loss and invasion of, () It also protects plants from temperature extremes,, , microorganisms., mechanical injury and from animals., , B, What are the functions of xylem?, 57, (a) The main function of xylem is to transpo, oy of shoots., (b) Xylem also gives mechanical strength to the plant body as walls of tracheids, vessels and sclerenchyma, of xylem are lignified., , & Differentiate parenchyma and collenchyma?, The difference between parenchyma and collenchyma are:, , ame, , Parenchyma | Collenchyma, , fe ae ae, (a) The cell walls are uniformly thickened. (a) The cell walls get extra thickened at places., , rt water and mineral salts from the roots to different parts, , , , , , (b) Parenchyma does not have any permanent | (b) It is a living mechanical ti, ) : cal tissue,, mechanical function except when its cells : af, , , , , , , , , , , , , |___are turgid., © Parenchyma is formed both in the outer | (c) It is i, (c) f mostly restri, § ei ae part orgs Se ly restricted to outer parts of plant, , , , , , ¢ different kinds of meristem depending upon location?, upon location in the body ch the plant, the meristems may be apical, intercalary and latet, are bom at the tips of the stems, roots and their branches., , Is are the left-out portions of the api i, " he apical meristems that get separated, ion of Permanent tissues in-between meristems - the es of., , , , , , , , , , , f vascular bundles in plants?, , 2 ually, , : located along the lateral sides of stems and roots. ours, , , , , , , , Scanned with CamScanner
Page 3 :
3) The large, spnencat ur var cone pe meme ., cells., , 4. Cartilage consists of, epithelium occurs in the lining of renal tubules and ducts of salivary glands., 4. Chondrocyte, , , , 5., Answers: |. Muscle, bone 2. Blood platelets 3. Adipocytes, 5. Cuboidal, Short Answer Type Questions 2-3 marks each, found in connective tissue?, , A. What are the different types of cells, & / The different types of cells found in connective tissue are:, , ae Adipose cells: These cells store fat., Fibroblasts: These cells synthesise the extra cellular matrix and collagen., the destruction and removal of, - se, , Macrophages: They are phagocytic in nature and are involved in, invading bacteria, foreign bodies and damaged cells. Loe, , Scanned with CamScanner
Page 4 :
2 Ee, , hi, , | _@—_ =, , | heparin, histamine and serotonin. ; ca, “Mast cells: They OC oeaeae cytes and plasma cells both producing antibodies,, Immuno. : These inc! lymp! *, the immune response., B. List few functions of lymph., {Functions of lymph are:, (a) Lymph transports oxygen., , , , , , , , nutrients, hormones, etc., to body cells and transports carbon io, , od., other metaboll wastes from the body cells to the blo, ae x loaded with lymphocytes., , (b) It protects the body against infection as it is, (0) It keeps the body cells moist., C. Differentiate between axon and dendrite., , , , , , , , a) It is the short, tapering process of a neuron,, , (a) Itis the long, uniformly thickened fibre-like | (, process of a neuron., , (b) Itis always covered with a medullary sheath.| (b) Medullary sheath is absent., , , , , , , , , , (0) It carries impulses away from the cell body. | (c) It carries impulses towards the cell body. q, , , , , , PAGE 69, , vy). What is a tissue?, A group of cells that are similar in structure and perform a particular function is called a tissue., , 2. What is the utility of tissues in multicellular organisms?, WA (a) Different types of tissues are specialised to perform specific functions., (Y~ (b) Tissues bring about division of labour and increase efficiency., , PAGE 74, , v/: Name types of simple tissues., Three types of simple tissues found in plants are parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma., eae tc meristem found?, Apical meristem is present at the growing tips of roots, stem and stem branch, 3. Which tissue makes up the husk of coconut?, It is formed of sclerenchyma tissue., 4, What are constituents of phloem? f, J Phloem tissue is made uy ¢, , es of plants., 4, , , , Scanned with CamScanner
Page 5 :
‘consists of cell body called the cyton with hair-like parts called dendrites and a long axon., re res of cardiac muscles, ' ., ) Cardiac muscles are cylindrical, branched and uninucleate., They are interconnected by oblique bridges,, , Their ends are flat and Zig-zag, called intercalated discs,, , 4, What are functions of areolar tissue?, , \ Areolar tissue fills the space between the organs, acts as a packing tissue, supports internal organs and, helps in repair of the tissues., , |. Define the term ‘tissue’., Refer to Question | of Page - 69 NCERT IN-TEXT QUESTIONS, , ; 2, How many types of elements together make xylem tissue? Name them., WY Xylem is a compound tissue. It is made up of four types of elements. They are tracheids, vessels, xylem, Parenchyma and xylem fibres., o3 How are simple tissues different from complex tissues in plants?, Vin A simple tissue is a group of cells similar in form, structure and origin, while a complex tissue is formed, , of a group of cells different in form, structure and ongin. Examples of simple tissues are parenchyma,, collenchyma and sclerenchyma and that of Permanent tissue are xylem and phloem., , , , , 4 4. Differentiate between parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma on the basis of their cell wall., \% In the arenchymal cells, cell wall is formed of cellulose but has no pectin or lignin., Ain Pi ro. gi, , In the collenchymal cells, cell wall is pectinised and pitted,, In the sclerenchymal cells, cell wall is lignified and pitted., 5. What are functions of stomata?, ve (@) They are necessary for exchange of gases with atmosphere., V(b) Transpiration also takes place through stomata., , 6. Diagrammatically show the differences between three types of muscle fibres,, , , , , , , , Scanned with CamScanner