Page 1 :
2. Animal tissue, Introduction: Animals, , have different types of tissues in their, body. Various functions are carried out, by these tissues. Some tissues cover and protect the body., Some tissues help in the movement if their, body parts. Some carry information. In this lesson we, learn more, about the types of animal tissues,, , their arrangement and their functions., , Observing skin tissue in chicken piece (Activity):, Aim: observing skin tissue in chicken piece., Apparatus: microscope, slide, dilute HCI, forceps, cover slip, chicken, piece with skin., Procedure:, Collect a small piece of chicken with skin., , ., , 2. Put it in dilute HCI for two hours., 3. Keep the skin with forceps on the slide., 4. Keep another slide on it and press both the slides gently., 5. Placea cover slip tap on it and observe, undermicroscope., , ., , Observations:, , We observe all the cells are similar. Each cell is, round in, d in shape., 2. They are arranged in layers and tightly, packed., no, There is no intercellular space., 33. There, , ANaio.e, , Observing muscle tissue in chicken picce (Activity):, , Aim: obscrving muscle tissue in chicken., Apparatus: microscope, slide, dilute HCI, forceps, covcr slip., chicken muscle, vinegar., , Procedure:, , ., , Take a piece of muscle of chicken., 2. Put in dilute ICl or vinegar and leave it for, two hours., 3. Collect the piece of muscle on a slide with, forceps., 4. Press gently with another slide. put few drops of water and place a, cover slip onit., , Observe, , 5., , it, , under microscope., , Observations:, I. Muscle cells are long and arranged in layers one above the other., , Observing bone tissue in chicken bone (Activity):, Aim: observe the tissues in chicken bone., Apparatus: microscope, slide, dilute HC1, forceps. cover slip, chicken bone., Procedure:, . Collect a chicken bone and keep it in dilute HCl overnight., 2. The bone becomes soft., 3. Keepa small of part of it on slide by using forceps., 4. Press gently with another slide put few drops of water on it., 5. Place a cover slip on it., 6. Observe it under microscope., Observations: we can observe star shaped cells in it., , Observing blood tissue (Activity), Aim: observe the blood tissue., Apparatus: microscope, slide, syringe, cover slip, blood sample., , Procedure:, , ., , Take a sterilized syringe needle., , 2. Collect one drop of blood from finger dip by pricking with, syringe needle., T.S.N, , (9491720974), , 3. Animal tissue, , 17
Page 2 :
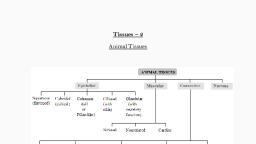
., , Take a slide keep the finger on it to collect blood., 4. Put another slide on it gently press both sides., 5. Observe it under microscope., Observations: we can observe round shaped blood cells in i., , tissues in, There are 4 major types of, 2.Conncctive, 2.Connective tissue, 3.Musculat tissuc, 4.Nervous tissue., , yp, , the animals-, , 1., , £pithelial tissue,, , tieueS, , Anlmal Tlseue, Nervous Tissue, , Muscular Tissuc, , Connective lissue, , Lpitheliol Tissue, , StriatedMusclas, squamous Epthelum, , Arcolor Tissue, , Stratified Sguanaus, Epthelum, , Atlipose Tissue, , Cubaldal Fpithelium, , 8cine Tissue, , Glandular Cpithe lium., , Cartilage, , Columnar Epithe lium, , Non Striated, , musclPs, , Cardiac Muscles, , igoment, , Tendon, Bloud Tissue, , 1., , Epithclial tissue:, body. Especially, tubules., , It is covering and protecting tissue. It is present inside, , in the, , or outside of animal, , skin, lining of mouth, lining blood vessels, lung alveoli and kidney, , Arcal Sufaxc, , laut, , 21ctmon:, , Squanious Epithelium, , helium, , blumnar, , Epithelium, , Squamous epithelium is a type ofepithelial tissue. It is present in oesophagus, lining of, mouth, lining blood vessels, lung alveoli where transportation of substances occurs through, permeable membrane., , Stratified Squamous epithelium present, , in skin arranged in the form of layers. It, protects, our body from cold and heat. Nails and hair grow from skin. The scales of fishes. reptiles, and feathers of birds also grow from this epithelium. These are the modified epithelial cells., Cuboidal epithelium present in the lining of organs, tubules and other parts. It provides, mechanical support. These cells are arranged compactly without inter cellular spaces., Glandular epithelium present in glands, Columnar epithelium present where absorption and secretion occurs especially in small, intestine. Cells are long and compactly arranged without inter cellular spaces., , Observing epithelial tissue in mouth lining (activity):, Aim: observing epithelial tissue in mouth lining., Apparatus: Tooth pic/ice cream spoon/ spatula, slide, cover slip, watch glass, needle, blotting, paper,, 1% Methylene blue, normal salinc, glycerine, microscope., Procedure:, 1. Wash hands and scrape the internal lining of the cheek with ice cream, spoon., T.S.N, , (9491720974), , 3. Animal tissue, , 18
Page 3 :
Place the scrapc in a watch glass containing, a very small quantity if normal saline., Then place the material on a glass slide., Put a drop of Methylene blue and wait, for couple of minutes., Wipe off the extra stain with a blotting, paper., Put a drop of glycerine over it., 7. Place a cover slip and press it gently., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6., , ., , Observations:, , Cells are extremely thin and flat., 2. Cells are compactly arranged without, inter cellular spaces., 2. Connective tissue: The tissue keeps the internal, organs in their specific places. The tissue gives, support and shape to the animals. These tissues also play, a major role in transport if material. They, also help in body defence, body repair and storage fat., , of, , Yellow elastic, fitres, Piragocyte, , Whie ibres, , -Fiorcblast, Osteoeyte**, Adipose tissue", Bone marrow, is, Areolar tissue one of connective tissue which keeps the organs in their specific, places., These cells are called fibroblasts. These cells also help in repair, of the tissues when they are, Areolar, , issue, , injured., , Adipose tissue is present below the skin. These cells are filled with fat globules. The fat acts as, insulator and prevents the escape of heat from body. The old people shiver during winter, because they have no adipose tissue and heat is escaped from their body., Bones form the frame work that support the body and give definite shape to the body. Bone is, made up of calcium phosphate and calcium carbonate. These slats are secreted by cells, called osteocytes which are present in bone marrow., , Atiu, , Cartilagge, , Blood cells, , Cartilage is hard but not as hard as bone., , It is found in the joints of bonds, tip of ribs, tip, of, trachea., and, The embryos of vertibrates, skeleton of sharks also made up of, nose, external ears, , cartilage., , Ligament, , connects bones at the joints and holds them in position. It is made up of collagen, fibres, which are elastic in natire., Tendon is also made up of collagen fibres. It joints the muscles to the bones., Blood has different types of cells and each one has a different function. All the cells in the, blood float freely in the fuid called plasma. Blood is the source to identify our wellness or, illness. There is a highly sophisticated and well developed mechanism to circulate the blood to, the entire body. Our heart pumps nearly 36000 litres of blood in the distance of nearly 20000, kilo metres in the lime period of 24hours. Blood is red in colour because of haemoglobin but, the blood in cockroach is in white and in snail in blue colour. An adult human being has 5 litres, of blood., Plasma consists of 90% of water and several nutrients such as glucose. amino acids., proteins. vitamins and hormones which are required for the body. The excretory products such, , T.S.N, , (9491720974), , 3. Animal tissue, , 19
Page 4 :
2. Use a tooth pick to mix the blood, and anti serum. Do it for each of the circles using a fresh, tooth pick every time., 3. Muscular tissue: Muscles are responsible for the movement limbs and internal organs., of, Muscles, which present in blood vessels control the blood flow by regulating, their diameter. The cells of the, muscle tissue are called muscle fibres. Contractile protein stimulates, the muscle contractions and, relaxations. When the body is exposed to cold, it shivers. During shivering, muscle contractions, and relaxations produce heat. Muscles are 3types-1.straited, muscles, 2.non striated muscles,, , 3.cardiac muscles., , Intercalated dists, , AS, , Mitochondria, , Cross, , Nucli, , -Plasma, Membranc, , striation, , Cros s smiations, , *Myofbrils, , Sawkna, , Nucleus, Sarcoplasnm, , Damaged issue, Myocytes, , Striated muveles, , Non-striared muscles, , Cardiac muscles, is in our conscious., , Striated muscles are voluntary muscles. Their movement, , The muscles, have light and dark bands or striations. These cells are long. cylindrical, unbranched and, having many nuclei. Ex: muscles in our hands and legs., Non Striated muscles / Smooth muscles are involuntary muscles. Their movement is not, in our conscious. These cells are long with pointed ends and having a single nucleus. Ex:, muscles in alimentary canal, blood vessels and in the iris., Cardiac muscles are present in heart. The cells are long branched and have nuclei. These, muscles have striations. Though it has striations, it is an involuntary muscle., 4. Nervous tissue: Nerve cells are very specialized cells that respond, to internal and external stimuli and for transmitting information., They do not have the ability of regeneration. There are 3 parts in, nerve cel- 1.Cell body/Cyton, 2.Axon, 3.Dendrites. Cell body, , Dendnte, -Scna (Cll body), , has a large nucleus. The cytoplasm contains granular structures, called Nissal's granules. There are some projections arising from, cell body are called Dendrites. One projection of the cyton is very, long and is ealled Axon. Some axons are covered with myelin, sheath. The gaps present at regular intervals on myelin sheath are, called Ranvier nodes., , Nuclaus, , Myelin sheath, , TEXTUAL QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS, 1., , What do you understand by the term tissue? (A.S-1), Tissue is a group of cells, similary in structure and functions., Ex G Nerve tissue, epithelial tissue., , 2. What is the specific function of the cardiac muscle? (A.S-I), Cardiac muscles are present in the heart. The muscles pump the blood to the body parts., , 3. Differentiate between striated, unstriated muscles on the basis of their, in the body? (A.S-I), , T.S.N (9491720974), , 3. Animal tissue, , shape and site/location, , 21
Page 5 :
S., , Striated Muscle, , No., , Cells are long, cylindrical, and unbranched., These are located in limbs, 2., and attached to skelton, , S., , No., 1., , Unstriated Muscle, Cells are long with pointed ends., , These are located in alimentary canal, blood vessels, Iris of the eye, in uterus and in the bronchi of lungs., , 4. Name of the following: (A.S-), A) Tissue that forms inner lining of our mouth., , Squamouse epithelium, B) Tissue that connects muscle to bone in, , humans., , Tendon, C) Tissue that transports food in animals., Blood tissue., D) Tissue that stores fat in our body., Adipose tissue., E) Conncctive tissue present in the brain., Nervous tissue., 5. Identify the types of tissuce in the following - Linings, , of kidney tubule. (A.S-D, Linings of the organs, Skin, Bone, Internal lining of kidney tubule, , 6., , of the organs, skin, bone, internal lining, , Epithelial tissue, Stratified squamous epithelium (epithelial tissue), Connective tissue, Cuboidal epithelial tissue., , If you touch at elbow, you get a shock like feeling. Why?, , (A.S-i), , In human beings ulnar nerve runs from the shoulder to the hand., 2. The ulnar nerve comes close to the surface near the clbow, and it is not protected by muscle,, 1., , fat or other soft tissues., 3. This makes ulnar nerve more receptive for any small stimuli., 4. That is the reason for getting a shock like feeling if we touch at elbow., 7., , Why, , tlhe, , blood is called a connective tissue?, , (A.S-I), , Connective tissue G A loosely spaced tissue mainly carrying different materials to different parts, of the body as well as rendering support, making connection between organs is called connective, tissue., Blood is considered as connective tissue because of the following reasons., 1. Blood connects different organs of our body together by carrying oxygen, nutrients,, hormones and other signaling molecules and removing the waste., It has all he three components of connective tissue i.e., cells, fibers and matrix., Similar to other conncctive tissues, blood is rich in libers like collagen fibers and blood, clotting fibers., 4. Blood originates from the mesodermal layer of the embryo from which all other connective, tissues also originate., , 8.Ifthe platelets are not present in the blood, what happens?, 1., , 2, 3., T.S.N, , Blood platelets, , (A.S-1), , help in blood clotting and prevent blood loss., , If the blood platclets are absent, the blood would not clot at the site of injury and bleeding, , will continue from the wound., Due to excessive loss ol' blood the injured person ultimately dies., , (9491720974), , 3. Animal tissue, , 22
Page 6 :
Ramu felt weak. Ramu's father took him to hospital. The, doctor advised a blood test. The, report says that he does not have the required levels of haemoglobin. How will be its, il, effects?, (A.S-II), , 9., , Haemoglibin helps in the transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide. Low haemoglibin is the, main cause for anaemia., 2. If there is not enough haemoglobin in blood. The, oxygen supply to various parts will be, less, which causes shortness of breath., 3. Low haemoglobin levels leads, to extant heart problems., 4. People with low haemoglobin levels get very tired as their cells do, not get enough Oxygen, to perform their activities., 1., , 10., , Write the procedure to identify your blood group with the help of kit? (A.S-II), Aim: identification of blood groups., Material: blood identiflication kit, wax pencil, disposable needle, cotton, tooth picks, alcohol., Procedure:, 1. Take one porcelain plate,, clean and dry it., 2. With a wax pencil draw 3 circles on the plate., 3. Place one drop of the corresponding antiserum, near the edge but within each of the circles., 4. Choose a left ring finger. Clean it with alcohol in a, cotton ball., 5. Press the finger tip upside down, to hold blood in the finger tip., 6. Quickly let one drop of blood get into cach circle, but not touching anti-sera., 7. Use a tooth pick to mix the blood and anti serum. Do it, for each of the circles using a fresh, tooth pick every time., 8. Watch to see if any of the samples agglutination., , Observations:, I. Determine the blood group by observing where agglutination formed. The table will help, you., Anti-A, Anti-B, Type, Yes, A, No, , No, Yes, No, , Yes, Yes, , AB, O, , No, , 2. If agglutination occurs in anti-RhD serum, the Rh factor is positive. If it does not, the Rh, , factor is negative., , Preeautions:, I. While taking blood samples, don't use same needle for all. It is very dangerous. It spreads, , diseases., , 2., , Usea tooth pick to mix the, , blood and anti serum. Do, , it, , for each of the circles using a fresh, , tooth pick every time., , 11. How blood test is useful to, , diagnose the disease. Explain with daily life situation?(A.S-VII), I. Abnormal red blood cell levels might be a sign of anemia, dehydration, bleeding and other, , disorder, , 2. Abnormal white blood cell levels might be a sign of infection, blood cancer or an immune, , system disorder., 3. Abnormal haemoglobin levels might be a sign of anemia, sickle cell anemia or thalassemia., 4. Abnormal glucose levels in the blood might be a sign of diabetes., 5. Abnormal calcium levels in the blood might suggest kidney problems, bone disease, thyroid, , discase, cancer or malnutrition., 6. Abnormal electrolyte levels might be a sign of dehydralion, kidney disease, liver disease,, heart failure or high B.P., , T.S.N (9491720974), , 3. Animal tissue, , 23