Page 1 :
2., , Plant tissues, , perform several lite processes such as growtl, respiration, excrction,, .nrfornm, Plants, out by various types of cells arranged in different parts of, thesc limct, photosynthesis, etc. All, soil is pertonned by roots. Exchange of gascs and, lrom, nerals, Absorption of wvater and mi, plant., stomata, Photosynthesis, performed by chloroplasts of leaves., thec p, ofleaves., perfornmed by, anspiration is, by low and various vegclative parts ol the plants. In this lesson we learn more, performed, Reproduction, plant and their functions., arrangement of cells iin various parts of, about the, , Introducti, , Onion pecl (Activity):, Observing cells in, in onion pecl., Aim: observing cells, covcrslip., slide, microscope, glycerine, water,, Apparatus: onion,, Procedure:, an onion peel., I. Take a piece of, it on the slide., 2. Now place, and glycerine on it., 3. Put a drop of water, it with a cover slip., 4. Gently cover, the microscope., it, under, 5. Observe, Observations:, are similar in shape and structure., We observed that all the cells, as a group., 2. Cells are arranged in rows, and cytoplasm., nucleus, wall,, cell, has, 3. Each cell, shape., 4. The cells are in rectangular, , Tell wull, , Nucleus, yulasn, , Tiy-1 Oniún pecl, , ., , Observing cells in Betel leaf (Activity):, leaf., Aim: observing cells in betel, betel leal, cover slip., slide,, microscope,, Apparatus:, Procedure:, , ., , Take a betel leaf., it with a single stroke. So that a thin edge, Tear, 2., be seen at the torn end., microscope., 3. Observe the thin edge under the, , Observations:, , Fi-2 Brel leuf pee, size., All the cells are not similar in shape and, in the small gaps called stomata., 2. They are arranged compactly leaving, guard cells., shaped, bean, 3. Stomata are surrounded by, in, groups., 4. The cells are arranged, size and arrangement of cells depend on their, Inference: The cells are arranged in groups. The shape,, , ., , functions., , Observing cells in Root tip (Activity):, Aim: observing cells in root tip of onion., Apparatus: onion, cover slip, microscope, slide, glycerine,, Tilter paper, transparent bottle., , Procedure:, I., , 2., 3., , 4., 5., 6., , 7., , Take a transparent bottle filled with water., Take an onion bulb and put it on the mouth of the, bottle filled with water., Observe the growth of roots for a few days till they, grow to an inch., Take the onion oul and cut some of the root lips., Take a root tip and place it on the slide., Put a drop of water and glycerine on it., Cover it with a cover slip., , TSN(9491720974), , 2.Plant tissues., , iy-, , Onion root, 9
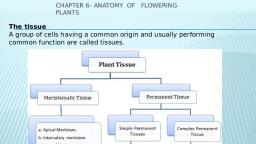
Page 2 :
S., , Drain out cxcess water with filter paper., , 9. Tap the cover slip gently to spread the material cqually., 10. Observe the structure and arrangement, , of cells under microscope., , Observations:, All the cells are not similar in shape and size., diferent rows., 3. Apical meristematie tissue present below the root cap., 1., , 2. They ane arranged in, , Tig- Onion Rnot Tip, , Observing growth in the roots of Onion (Activity):, Aim: observing the growth in roots of onion., Apparatus: onion, transparent bottle, marker, water., , Procedure:, , ., , 2., 3., 4., 5., 6., , Take a transparent bottle filled wvith water., Take an onion bulb and put it on the mouth of the botle filled with water., Observe the growth of roots for a few days till they grow to an inch., Take the onion out and cut some of the root tips., Mark the cut ends of the roots with a marker., Leave the set up aside for at least 4-5 days., , Observations:, 1. By removing the tip of the onion root, the growth of the, root is stopped., 2. Cells are present in groups., , Tissue: the group of cells which have similar structure and perform similar functions are called tissue., Types of plant tissues:, Plant Tissues, Meristematic tissues, , Demal tissues, , Ground tissues, , Apical meistematic tissues, , Parenchyma, , Lateral meristematic tissues, , FCollenchyma, , L Intercalary meristematic tissues, , L Sclerenchya, , Chlorenchyna, , Acrenchyma, , Vhscular tissues, , Nylem, Phloem, , Storage Tissue, , There are 4 basic types if tissues in the plants. They areTissues that bring about overall growth and repair are called Meristematic tissues., Tissues that form outer coverings are called as Dermal tissues., Tissues that form the bulk of the plant body, helping in packing othe tissues are called as Ground, tissues., Tissues that help in transport of materials are called as Vascular tissues., 1. Meristematic tissue: these are present in root tip and shoot tip. These are small and, compactly, arranged without inter cellular spaces. They have prominent nucleus and abundant cytoplasm. The cells, continuously divide and form new cells. Meristematic tissues are 3 typesMeristematic tissue at the growing tip that bring about, growth in length are called as Apical maeristematie tissues., These are present at the tip of the shoot and root., uwtitem, ical, Tissues present around the edges and giving rise to growtlh in, al meritein, at, the girth of' stem are called Lateral marestematic tissues., These are present at the lateral side of the root and shoot tips., iualar, Tissues present where branching takes place and where leaf and, flower stalk grows are called I ntercalary meristemnatie, (cambiun) tissues., , TSN(9491720974), , 2.Plant tissues., , 0
Page 3 :
Preparation and observing Dicot stem slide (Activity):, , Meristeatic, , Aim: preparation and observing dicot stem slide., Apparatus: blade, slide, cover slip, glycerine, blotting paper,, microscope, water, dicot stem, salranin solution., , oscular, , tissues, , tisne, , Procedure:, Ground tisue, , I. Collect any dicot stem., 2. Prepare section cuttings from the stem with a sharp, blade and keep them in the peiridish., 3. Take a thin section with brush and put on the slide., 4. Pour one drop of water and glycerine on the section., 5. Stain with safranin and cover with cover slip., 6. Observe the section under microscope., , Dermal iss ue, , Fig-7 Dicot stem (TS), , Observations:, , Tisvues, , cells are not similar in shape and structure., 2. Meristematic tissue, vascular tissue, dermal tissue and ground tissue are present., 1., , All, , thec, , 2. Dermal tissuc: dermal tissue present over the entire surfacc of the plant body. Usually the tissue, consist a single layer. In the big trces the tissue forms scveral layers above the epidermis called bark. The, walls are very thick. In desert plants it may be even more thick and waxy. The tissue protects the plants, from loss of water, mechanical damage and invasion by discase causing organisms. Stomata and rool, hairs ure dermal tissues that perform gaseous exchange. Iranspiration as well as absorption of water and, minerals. The cells store food material. excretory substances and secretory substances. Gum secreted, from the dermal tissue of gum trees. Photosynthesis also carried out by some of the dermal tissues. These, tissues are divided into 3 types. They are epidermis (outer most layer), mesodermis (the middle layer), and endodermis (the inner most layer)., i, , Observing Stomata/ Dermal tissue (Activity):, Aim: Observing stomata in Rheo or Betel plant., Apparatus: Rheo plant or betel plant, slide, microscope, cover slip., , Procedure:, , Take a fresh leaf of Rheo or betel plant., 2. Tear it in single stroke. so that a thin whitish edge can be seen at the torn end., 3. Slowly remove it and observe that peel under the microscope., , Observations:, , Small pores are seen in the epidemis of the leaf., 2. They are enclosed by two kidney shaped cells called guard cells., I., , Cuzd Ceil, , Maau, , C, Fndaral, , Apawe, , lacr, , Cals, , tunpat., , Fi-, , 3., , I'cel of, , h hen leuf -, , Deruul, , tissu, , These are very large with prominent, Ground tissue: The cells form the bulk of the plant body., , the plant. Some of the ground tissues, nucleus. The tissue stores food and providing physical support to, are Parenchyma, Collenchyma,, help in photosynthesis. There are mainly 3 types of ground tissues. They, and Sclerenchyma.
Page 4 :
Ne, , co, pa, , Sclerenchyma, , Collenehyma, , Parenchyma, , parenchyma which contains, loosely packed. The, cavities is called, which contains large air, chloroplasts is called chlorenchyma., storage tissue., called, is, food and waste products, Aerenchyma. Parenchyma which stores water,, and, arenchyma cells are soft, thin walledParenchyma, , Storuge Tissue, , .arenchy'ma, , Chlurenchymu, , Collenchyma tissues have thick walled and tightly packed without spaces., Sclerenchyma tissues are thick walled and tightly packed without spaces., minerals as well as food, 4. Vascular tissue (Conductive Tissue): The tissue transports water and, is, typesmaterial in plants. They also give mechanical strength to the plants. Vascular tissue of two, , I.Xylem, 2.Phloem., derm», , sacve, , fibre, , cor ph, , ttaeda, , ylau, phlucn, , ph, , Xylem contains elongated trachied cells, tubular vessels, fibres and parenchyma. Xylein iransports, water and minerals from roots to all parts of the plant. Xylem carries water up to 200 feet in, Eucalyptus trees and up to 330 feet in Red wood trees., Phloem contains long sieve cells, sieve tubes, companion cells, fibres and parenchyma. Phloem, transports food material prepared by photosynthesis to all parts of the plant., , Observing Vascular tissue (Activity):, Aim: Observing vascular tissue in plants., Apparatus: Plant with roots, beaker, red ink., Procedure:, 1. Place the plant in red colour water., 2. Leave it for two hours., 3. Cut a TS of stem and observe it under microscope., , Aiiem, , Piiovn, , ., , Observations:, Red coloured tissues are appeared. These are Xylem, tissues that help in water transportation., 2. The adjacent cells to these are Phloem tissues which, help in food transportation., , TSN(9491720974), , 2.Plant tissues., , die, , i, , S »f sien, , 12
Page 5 :
Nehemiah Grew worked as the sceretary of the royal socicty, London. According him, every, to, plant, consists of two types of parts. One is Pithy and the other is Ligneons (hard) part. He gave the term, parenchyma to pithy part. He studicd histology and wrote a book Anntomy, , of plants., , TEXTUAL QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS, Define the terms a) Tissue, b) Meristematic tissue, c) Dermal tissue? (A.S-1), A. Tissue: Tissue is a group of cells similar in structure and performing similar functions., B. Meristematic tissue: Meristematic tissue is the dividing tissue, present in the growing regions, of the plant., C. Dermal tissue: Tissues that form outer coverings are called as dermal tissues. It gives, protection to plant., , 1., , Write the differences between meristematic tissue and Ground tissue? (A.S-1), , 2., , S., , S., No., , Meristematic tissue, , No., , Tissues that bring about overall, growth and repair are called, meristematic tissues., 2., Cells divide continuously., are living., Cells, 3., cytoplasm is present in the cell, , 1., , 4.Dense, , 2., 3., 4., , Ground tissue, Tissues that form the bulk of the plant body, helping in packing other tissues are called, Ground tissues., Cells do not divide., Cells may be living or dead., Thin cytoplasm is present inthe cell._, , A.S-I), , Write the differences between Apical meristem and Lateral meristem?, , 3., , S., , No., , S., , Apical Meristem, , No., , Apical meristem is found in growing tips of, brings about growth in length of stems and, , It, , Lateral meristems are present around the, , edges in alateral manner, , root, stem and apices of leaves., 2., , Lateral Meristem, , It rise the growth in, , 2., , roots., , diameter of the stem, , and root., , Write the differences between parenchyma and collenchyma? (A.S-I, , 4., , S., , No., , S., , Parenchyma, , No., , thin, and, loosely, walled, packed., They store food. bear chloroplasts and, , The cells of parenchyma are sofi,, , 4., , The cells of collenchyma are thick walled, , and compactlyarranged., 2., , contain larger cavities., Cell wall is primary made up of cellulose., Cells are oval, round and rectangular in, , 3., , Collenchyma, , They give mechanical, , strength in young, tissue of stem., wall has deposition of extracellulose., Cells are elongated, round and spherical in, , 3.Cell, , shape, , 4., , shape., , Write the differencs between sclerenchyma and Parenehyma? A.S-I), , 5., , S., , No., , a, , S. No., , Sclerenchyma, , It is dead tissue., Cells are thick walled., Inter cellular spaces are absent., providesmechanical strength., , 4. It, , TSN(9491720974), , 2., , Parenehyna, It is a living tissuc., , Cells are thin walled, Intercellular spaces are present., , 4tstores food, bears aircavitiesand chloroplasts., , 2.Plant tissues., , 13
Page 6 :
S., , S., No., , Xylem, , 1, , parts ofthe plant., Xylem consists of trachieds,, 2., , vessels, xylem fibres and xylem, , 2., , parenchyma., Only xylem parenchyma is living., , Trachieds, vessels, xylem fibres are, , dead tissues., , Xylem gives mechanical strength to, the plant., Conduction of water by xylem is, unidirectional i.e., from roots to, 6., apical parts ofthe plant., , 7., , It transports food material from the leaves to, growing parts of the plant., , Phloem consists of sieve tubes, sieve cells,, companion cells, phloem fibres and parenchyma., , Sieve tubes, sieve cells, companion cells and, , 3., , phloem parenchyma are living., , 4., , Phloem fibres are dead tissue., , 5, , b., , Phloem does not give mechanical strength to the, , plants., Food material conduction is bidirectional i.e., from, leaves to storage organs or growing points or from, storage organs to growingparts of plants., , Write the difference between Epidermis and Bark?, , S., No., , It is the outermost layer of, , 2, , Itandproduces secretions like Gum, Name the following, , :, , Several layered bark tissue is present above the, epidermis of stems and roots,exceptleaves., Itis adead tissue., , Secretions are not produced., , Latex., , 8., , Bark, , No., , roots, stems and leaves., 2. It isa living tissue, 3, , (A.S-1), , S., , Epdermis, , |1., |, , Phloem, , No., , Xylem transports water and, minerals from roots to the apical, , 4., , (A.S-1), , the differences between Xylem and Phloem?, , Write, , (A.S-I), , A) Growing tissue, which cause growth in the length of the plant., Apical Meristem, B) Growing tissue, which cayse growth in the girth (diameter) of the plant., Lateral Meristem., C) Large air cavities in the aquatic plants., Aerenchyma, D) Food material in parenchyama., Storage tissue, E) Pores cessential for gaseous exchange and transpiration., Stomata, , Compare and contrast themeristematietissueand dermaltissue?, , 9., S., , 2., 3., , 4., , S., , Meristematie tissue, , No., , Cells are small havingthin cell wall., They are capable of dividing., |, , Thewalls of the cells are thicker., are not capable ofdividing., , 2.They, , This is present at sho0ot tip, root tip and, where branches arise., , 3., , It helps in the growth, , 4., , TSN(9491720974), , Dermal tissue, , No., , of the plant., , 2.Plant tissues., , It is, , present over the surface of entire, , plant body., It, , protects the plant from water loss, , due to transpiration., , 14
Page 7 :
10., , 11., , 12., , (A.S-I), Xylem is a conductive tissue. Give reasons?, conducts water and mineral salts from the soil to the, apical parts of the plants., away from the root., 2. It transports materials, Conduction ofwater by xylem is unidirectional i.c., from roots to apical, parts, of the plants., , lem, , Epidermis gives protection. Give reason? A.S-D, 1. Epidermis usually consists of a single layer of cells., 2. The walls of the cell are thicker., 3. It protects the plants from losS of water, mechanical damage and invasion by parasitic, and disease causing organisms., Though chlorenchyma, Aerenchyma and storage tissues are Parenchyma in nature. Why do, (A.S-I), they have different (Specific) names?, Chlorenchyma, Acrenchyma and storage tissue are parenchymatious tissues., 2. These three parenchymatious tissues are modified to perform various functions., 3. The parenchyma which contains chloroplasts is called chlorenchyma. It performs, photosynthesis., 4. The parenchyma which contain large air cavities or spaces is called Aerenchyma. It helps, , ., , 5., , 13., , the plant to float., The parenchyma which stores water or food or waste products is called storage tissue., , Describe the functions of Meristem, Xylem and Phloem., , ., , Functions of Meristem:, I. Jt is a dividing meristematic tissue. It divides continuously. The cells formed from, meristems later they differentiated as components of other tissues., 2. It brings about overall growth and repair., 2. Functions of xylem:, 1.It conducts water and mineral salts from the root to apical parts ofthe plant like stems and, leaves., 2. It gives mechanical support to the plant., 3. Functions of phloem: Phloem conducts food material from the photosynthetic parts of thé, plants to other parts., 14., , If you want to know more about tissues in plants, what questions are you going to ask?, (A.S-II), , ., , 2., 3., 4., 5., 15., , Which plant tissue provides both mechanical strength and flexibility?, Which structure protects the plant body against the invasion of disease causing organisms?, What will happen if apical meristem is destroyed or cut?, What is the tissue present in the husk of coconut?, Why plants need different types of tissues?, , Bark cells are impervious to gases and water". What experiment will you perform to prove, this? (A.S-III), I. Dermal tissue forms several layers above the epidermis. It is called bark., 2. If we keep a piece or bark in water and observe afer few hours., 3. The bark did not absorb water as well as air and did not become wet and moist., 4. By the above experiment it was proved that the bark cells are impervious to water and gases., , TSN(9491720974), , 2.Plant tissues., , 15
Page 8 :
16., , Collect information about dermal tissues of plants in what way they help them?(A.S-IV), 1. Dermal tissue usually consists of a single layer of tissues showing variations in the types of, 2., 3., 4., 5., 6., 7., , cells., It forms stomata and root hairs., Stomata helps in the exchange or gases and transpiration., Root hairs absorb soil water into roots., When the plant is injured, Gum is secreted to heal the wound., Dermal tissue in leaves contain chloroplasts and perform photosynthesis, Dermal tissue protects the plants from mechanical damage and invasion by disease causing, organismns., , 17., , While observing internal parts of plants how do you feel about its structure and functions?, (A.S-VI), I. I felt that there are different types of tissues to perform various functions., 2. Demal tissue perform protection, produce secretions and forms root hairs and stomata., 3. Collenchyma and sclerenchyma provides mechanical strength., 4. Xylem conducts water and phloem conducts food material., 5. Hence I felt that tissues are formed by cells and perform various, functions making the plant, , alive., , 18., , Draw and label the diagram of the T.S of stem? (A.S-V), , Xylem, , Palvem, , Fasciar, und!e, Fiy-11 TS of stem