Page 1 :
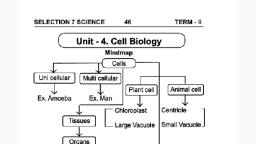
1., , Cell Its structure and functions, -, , Introduction: All organisms are made up of cells. Cell is the structural and functional unit of, organisms. Each and every part of the organism is made up of cells. All metabolic activities are carried, out at cell level. That is why cell is called as structural and functional unit of organisms. Cclls arc in, different sizes and shapes. Thcir size and shape depends up on their functions. Onion cells are, rectangular,check cells are circular and bonc cells are in star shape. The nerve cells are about 100, centimcters long and the cgg of ostrich is round and has 18 centimeters diametre., Uni cellular and Multi cellular Organisms: The oraganisms which have one cell in their body are, called uni cellular organisms. Ex: Amoeba, paramoecium. The organisms which have number of cells, are called multi cellular organisms. Ex: mammals, Aves, Pisces etc.., Cell organelles: The smal structures which are present in the cell are called cell organelles. Ex:, nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, ribosomes, Iysosomes, endo plasimic reticulum, golgi apprutus,, vacuoles., , Typical cell: All the cell organelles are not exsist in every cell but to study its complete structure and, fuctions we designed a cell with all cell organelles is called typical cell., Typical Plant cell and Animal cell:, Mitochondria, , Endpl>snatctulum, Nucl, , Mitxhonuns, , Nuecicus, , ntrane, flgi, , or7a ata, , cdaal, hloroplast, , (iolgapruranus, , Ekplasmicreticulhoa, , Ti2, , Pasn:cnt, iy-, , brle ul Plant, , Tiyicol uiul, , Pavranrtnne, celt, , cell, , Plant cells have a thick cell wall, large vacuoles and number of plastids. But animal cells have none of, these. Animal cells have Centrioles but plant cells have no Centrioles always., Cell membrane/Plasma membrane: The cell membrane is the outer most of the cell. It is called as, It, plasma membrane. We can observe this structure only through an electron micro scope. is flexible, It, It, cell., the, size, the cytoplasm, and, encloses, of, and is made up of lipids and proteins. defines the shape, a, cell, a, has, very specilic, and protects from the external environnent. The interval environnment of, composition of various substances which maintain a balance. The cell membrane maintains this, it, it, balance. The exchange of substances occurs through cell membrane and is very selective. Hence is, known as selective permeable membrane., Pim, Observing the Cell membranc/plasma membrane (activity):, n.mbrue, Aim: Observing the cell membrane, Apparatus: Rheo leaf, slide, cover slip, microscope, salt waler., Procedure:, Slunwka, 1. Take a Rheo leaf and tear it., yuplm, Take a thin transparent peel on slide and put a drop of water on it., (rll m mhrat, Iig-th, microscope., the, under, Cover the pecl with cover slip and observe, or, it, 5, 4. Now put, 2 drops of salt solution on the membrane and leave for to 10 minutes., 5. Again observe it under microscope., Observations: when we put salt solution over the peel, the water present inside the cells come out and, shrinks the cytoplasm. Then the cell membrane is separated from the cell wall and observed very clear., , ., , I, , maI
Page 2 :
Cell wall: lt is a unique feature of plant ecll. In plant cells there is any extra layer outside the cell, membrane is called as cell wall. It is mainly made up of cellulose. It is tough but flexible porous layer, It involves in continues exchange, of infomation from one cell to other cells. It exerts an inward wal, pressure to resist the outward pressure., , Nucleus: It was discovered by 1Robert Brown in the yenr 1831., Schleiden one the proponents of cell theory called it as cytoblast, It is the largest and inmportant, cell organelle. It regulates and, controls all eell finctions and detenines the charncteristics, of the organism. It consists of genctic infomnation., lt is called as the cel's control room. It involves in cell, division., Nuclear membrane encloses the nucleus and is very similar, to the cell membranc., , Ciemetic, , Materiat, , Nuclear, , nembrang, , Nclert, Nuclear, pore, , Nucle, , Tig-, , Plasm, , Nurle n, , Prokaryotic eells-Eukaryotic cells: The cells which have well defined nucleus with a membrane are, called cukaryotic cells. Ex: all plant and aninmal eells. The cells that do not have, membrane are called prokaryotie eells. Ex: bacteria., , a, , nucleus, , Witlh, , Observing the Nucleus (lab activity):, , Aim: To observe the nucleus in check cells., Material: Tooth pic/ice cream spoon/ spatula, slide, cover slip. watch glass. needle, blotting paper, o, Methylene blue. normal saline, glycerine, microscope., , Procedure:, 1., , Wash, , hands and scrape the intcrnal lining of the check with ice cream spoon., 2. Place the scrape in a watch glass containing a, very small quantity if normal saline., 3. Then place the material on a glass slide., 4. Put a drop of Methylene blue and wait for couple, of minutes., Wipe off the extra stain with a blotting paper., Put a drop of glycerine over it., 7. Place a cover slip and press it gently., 5., , 6., , Precautions:, 1. Do not scrape the cheek too hard., 2. Scrapped material should be spread uniformly on the slide., 3. Excess stains should be drained off., 4. There should be no air bubbles under the cover slip., , Observations:, , ., , The cells are almost in round shape., 2. We can observe the round dot like structures at the centre of the cell is nucleus., 3. These cells are not similar to the structure of Onion peel cells., Protoplasm Vs Cytoplasm: Protoplasm is the fluid stored inside the cell. For a long a time, it was, believed that the life was stored in this Nluid. Hence it was named as protoplasm which means life, fluid. But when it became clear that the life is not resided in this fluid and it is resided in all organelles., the protoplasm is renamed as cytoplasm. So protoplasm is the fluid content bounded by plasma, membrane. Cytoplasm is basically a medium in which cell organelles float around. The functions of, the cell actually take place in these cell organelles. The fluid inside the nueleus which is surrounded by, nuclear membrane is called as Nuclear fluid or Nucleoplasm. Nucleoplasm is different trom, cytoplasm. Nucleoplasm consists of genetic material., , Mitochondria: Mitochondria are small, cylindrical organelles. They are about 100-150 in cach cell. It, has 2 membranes. The luid filled portion surrounded by inner membrane is called matris. The inner, membrane protrudes into the matrix and forms many folds like structures called cristae. Mitochondra, perforn cellular respiration and produce energy. Because of this Mitochondria are called as power, house of the ecll., TSN (9491720974), , 1. Cell its, , structure and functions
Page 3 :
Observing Mitochondria (netivity):, Ain: Observing Mitochondria in onion peel., Apparatus:, , Slide, nmicroscope, onion,, , Jaus Green-, , 13, , solution., , Proccdure:, , Take a watch glass and pour Janus Green- R solution., Put the onion peel in this solution for half an hour., 3. Keep the pecl on the slide and wash with water., 4. Cover it with a cover slip and observe under mieroscope., 5. We can do this activity with the leaves of Casia tora or cheek cells., Observations: We obscrve green cylindrical grains in the cel., These are the Mitochondria., 1., , Irr, fervrne, , 2., , Outer, , Merntrre, , Plastids: Plastids are prescnt only, , in plants. They are mainly 3 types., They are 1. Chromoplasts (coloured). 2. Chloroplasts, Outcr Merchra, (green colour0. 3. Leucoplasts (colour less). Chloroplasts are of, different shapes like disc. oval etc. In Algac they are in the shape, of ladders. stars and spirals or reticulate. The primary function of, chloroplasts is trap sun light and transform to chemical energy, Ene Mem.keane, in the process of photosynthesis. 50-200 chloroplasts are, present in each leaf cells of plant. Chloroplasts contain grecn, substance called chlorophyll., , Gnum, , Lunn, , Thylakmd, , Fig-9tc, , Observation of chloroplasts in Rheo leaf (activity):, Aim: Observation of chloroplasts in rheo leaf., Apparatus: Slide. microscope, rheo leaf., Procedure:, 1. Take the peel of rheo leaf and keep in water on a slide., 2. Observe it under microscope., Observations: We can observe small green granules called chloroplasts., Observation of chloroplasts in Algae (activity):, Aim: Observation of chloroplasts in algac., Apparatus: Slide. microscope, algae, Procedure:, 1. Collect some algae from pond and separate the thin filaments,, 2. Place few thin filaments on slide and observe them on microscope., Observations: We can observe small green granules called chloroplasts., , Ribosomes: These are granule like structures present in the cytoplasm of the cell. These are made up, of RNA(Ribo Nucleie Acid) and protcins. These are 2 types. Free Ribosomes are scattered in, cytoplasm. attached Ribosomes are on the surface of rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER). Ribosomes, synthesis proteins., network of membranes present, throughout the cytoplasm. It ereates passages within the eytoplasm., Rug, This network of membranes is known as the endoplasmie reticulum., ER is similar to the structure of plasma membrane. ER may have, Ribisomes on their surlace and they are called Rough Endoplasmic, Reticulum (RER). Some do not have Ribisomes on them are called, Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER). RER manufactures proteins, and SER manufactures lipids (fats). The function of ER is transport of, materials especially proteins between eytoplasm to ucleus. lis frame, work providing a surface for some chemical activities. In Vertibrates, liver cells. SER detoxify the many poisons and drugs., , Endoplasmie reticulum (ER): There, , 1, , Coll, , is a, , itc, , ctri, , uro, , nd, , functi, , Enb plasuic Retiuluu, , Eakpl.ou, Rctadan
Page 4 :
Ogi, , complex: Camillo Golgi obscrved these strictures in 89, , nese are niade up ofseveral membranes and form, , ns n sac, , nk, , structure. It collects the protcins syntlhesized by RElK berorc, ney are transportcd to other parts of the celI. In some times, nese organelles regenerate and repair the cell membranes., hese are also participated in secretion. That is why these, are large in cells that secrete hormones and enzymes., Ihe components of he, uysOsomes: Lysosomes contain destructive enzymes which can brcak down, components., Ihal is whyih, Cel. Bul these enzymes do not come in contact with the rest of the cell, to, iysosomes,, the, transportcd, arc, do not damage the cell. The materials tlhat nced to be destroycd, Hencelysosomes, material., the, cnzymes, down, break, the lysosomes burst and release the, ymes. The, are called suicidal bags., , T, , Vacuole: The large empty spaces present in the cell are vacuoles. In animals these are snal in sive, while in plants they are very largc. Vacuoles maintain turgur pressure within the cell. Ihey send out, the unwanted material from the cells., Observing Vacuoles (Activity):, Aim: Observing Vacuoles in cactus stem or leaves., Apparatus: Cactus leaf or stem, watch glass, water, safranine, microscope., , Procedure:, 1. Take a leaf or stem of cactus plant., 2. Take thin cross section in a watch glass containing water, 3. Keep it slide and stain it with dilute safranine solution., , 4. Observe it under microscope., , Observations:, I. The large empty spaces are appeared in the cells are Vacuoles., These are fluid filled sac like structures., , 2., , Cell theory: In 1665 Robert Hooke observed little room like structures in oak tree cork. ie named, this structure as cell. In 1838-39, two scientists Schleiden (botanist) and Schwann (zoologist), formulated the cell theory. But the theory cannot explain how the new cells are formed. In !855, Rudolf Carl Virchow first explained that the new cells are formed by the division of the pre- existing, cells. Then the theory was modified as1. All living organisms are composed of cells and their products., 2. All cells arise from pre-existing eclls by cell division., , TEXTUAL QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS, , 1., , Write the differences between plant cell and animal cell?, , S., , No., , Plant Cell, , wall is present., Plastids (clhromoplasts and, 2., chloroplasts)are present, are absent., 3.Cenriolesare, larger in size., Vacuoles, 4, , LI.Cel, , TSN, , (9491720974)_, , 1. Cell its, , (A.S-1), , S., , No., 2, , 3., , 4., , Animal Cell, Cell wall is absent., Plastids are absent except the, protozoan Euglena., Centrioles are present., , Vacuoles are smaller in size., , structure and functions
Page 5 :
Write the differences between prokaryotie and enkaryntie eells?, , 2., , S., , S., , Prokaryotic Cell, , No., , Nuclear membrane, , 3., , Most prokaryotic cells are unicellular., , 4, , It, , 6., , Fukaryotie Celt, , No., , Nuclear membraneis absent., Cell organelles are absent., , ., , contains a single chromosome., , Nucleolus is absent., These are found in bacteria and bluc, green algac., , (AS-), , is present, , Cell organelles are present, Most eukaryntic cells are, multicellular., It contains more than one, , chromoome., Nucleolus is present., 6., , These are present in fungi. plants and, , animals., , 3., , Lysosomes are known as suicidal bags of the cell. Why? (A.S-), 1. Lysosomes contain dcstructive enzymes., 2. The materials that need to be destroyed are transported to the lysosomes., 3. At times the lysosomes burst and the enzymes are released to digest cell., 4. Hence lysosomes are also known as the suicide bags of the cell., , 4., , Why do plant cell posses large sizcd vacuole?, (A.S-I), 1. Plant vacuoles are a water reservoir, an osmoregulator,, a waste reservoir, and control the, turgor of the cell., 2. The central vacuole presses out against the cell wall keeping the cell's shape., 3. Plants can use the internal pressure in cell elongation for controlled growth., 4. The plant's vacuole performs more functions than the animal's vacuole., S. Hence plant cell possess large sized vacuole., , 5., , Cell is the basic unit of Life". Explain the statement? (A.S-I), i. The cell theory states that, cells are the structural and functional units oflife, 2 All organisms are composed of cells and that all cells come from pre-existing cell., 3. All the metabolic activities occur at cell level., 4. That is why the ell is the basic uni/structural and functional unit of life., , 6., , Who and when was "the cell theory" proposed? When did they prepare it? What are the, salient features of it? (A.S-1), M. J. Schleiden and Theodar Schwann was proposed "the cell thecory" in 1838-39., , Features of "the cell theory":, 1., , All living organism are composed of cells and their products., , 2. All cells arise from pre-enisting cell., , 7., , What would happens to the cell if nueleus is removed? (A.S-I), , ., , Nucleus is the most important cell organell. It conurols all the functions of the cell., It contains genetic material which determines the characteristies of the organism., It involves in the process of cell division., 4. If nucleus is removed from the cell, it cannot perform all these functions. It may leads to, the death of the eell., 2., 3., , 8., , TSN, , What happens if plasma membrane ruptures or breaks?, (A.S-I), 1. Plasma membrane protects the cell from external environment., 2. Ii regulates the movement of various substances and maintain their concentration balance., 3. If the plasma membrane is ruptured, its contents leak out. Then the cell will die., , (9491720974, , 1. Cell its, , structure and functions
Page 6 :
complex? (A.S-II), , 9., , no Golgi, of cell, if there was, appar, What would happen to the life, perlormed by golgi aratug, activities, most, the, in the cell,, there was no golgi apparatus, will not takes place., golgi apparatus is absent., would not takes place if, substances, various, transferred to lysosom, Package, me, of, 2., in the ribosomes may not, produced, substances, the cel, ultimately, hence, 3. Proteins and other, membrances would not takes place,, 4.If that occurs, repars of cell, dies., are not destroyed they get stored, sent to lysosomes and they, 5. lf the toxic substances are not, in the cell and cell dies., destroyed. I hey get stored in, to lysosomes, they are not, 6. If the toxic substances are not sent, the cell and cell dies., , .If, , 10., , 11., , in laboratory, what, When you observing the nucleus of cheek cell, take? (A.S-II), 1. I do not scrape the cheek too hard., 2. I removed excess stain., 3. Itake care, not to form bubbles under the cover slip., slide., 4. I take care, that scraped material be spread uniformly on the, , precautions do you, , Collect the information about the functions of different cell organells, , in a, , tabular form?, , (A.S-IV), , S.No., , Function, , Cell organelle, , Nucelus, , a, , Nucleus regulates and controls all the functions of cell, anddetermines the characteristics ofthe organism., It serves as channels for the transport of materials, within the cell., 2. It also functions as a cytoplasmic framework providing, a surfacefor various biochemical activities., It packages various substances. Proteins are altered slightly, by golgiapparatus., It participates in intracellular digestion. It destroys the cell, , ., , 2., , 3., , Endoplasmic, reticulumn, , Golgi Apparatus, , 4. |Lysosomes, , |5., , | Mitochondria, Plastids, A.Chloroplasts., B. Chromoplasts, , C. Leucoplasts, , 12., , TSN, , contents., Itproducesenergy through celular respiration., These are responsible for the colour of the plant cells., These trap solar energy and convert this to chemical energy, during photosynthesis., These are responsible for the coloured fruits,, and flowers., These are colourless, stores carbohydrates., oils, proteins., , and, , How do you appreciated about the organization of, cell in the living body?, (A.S-V1), 1. I see five levels of organization of cell in, the living body., 2, The cell is well organized in living body as it, make up tissues. Tissues make, up organs,, organs make up organ system and organ system, make living organisms., 3The cell is the fundamental or basal unit ultimately forming unicellular, and multicellular, organisms., , (9491720974), , 1. Cell its, , structure and functions
Page 7 :
4. Organisation continues beyond organisms to form populations, communities, ccosystems, and to biosphere., , If the organization of cell is destroyed due to physical and ehemical influence, wlhat will, happen? (A.S-VI), , 13., , 1., , 2, , Cell is the smallest unit of lifc, which is capable of carrying all living functions., If the organization of a cll is destroyed due to some physicul or chemical influence, then, the ability of the cell to perfonn all living functions such ns respiration, digestion,, cxcretion, etc., would be affected., , How could you appreciate the funetion of a tiny cell in a large body of an organism?, (A.S-VI), , 14., , ., , The functions of an organism depend on the functions carricd out by its cells., 2. Cells are the building blocks of life., 3. This is the reason why cclls are referred to as the basic structural and functional units, of, life., 4. 1 the cclls present in an organism perform their functions properly the body the, organism also functions properly., 5. It is very appreciable to control a big animal by the smallest cell., , 15. Draw the typical Animal cell, , and label its parts?, , (A.S-V), , Mitochondria, , Nucleus, , Cy1oplasm, -Centnoles, , Golgi, Endoplasmmaeticuun, , 16., , apparatus, , Plasma mmbrane, , Draw the typical plant cell and label its parts?, , (A.S-V), , Endaplasmic seticuhen, , Nicleus, , -Mtochondr:a, , Golzt Jpprarus, , Chloroplast, Cell wal, , Plasna meibiase, , Fig-1 Typiral Piant e, , TSN, , (9491720974), , 1. Cellits structure and functions, , of