Page 1 :
Class LX, X, XI, XII Full Mathematics, Course ( CBSE & RBSE), , Free PDF Notes, Model Paper Available, , join us on YOUTUBE | *, , Maths Wale Guruji, , Kasy way to learn, , Offline Batch :, K. B. 4. B. Sodhpur, Contact : 90513339173
Page 3 :
CHAPTER-1, NUMBER SYSTEMS, , , , KEY POINTS, ttt tt ttt ttt ttt >, 5 4 -3 2-101 2 3 4 5 67 8 9, pis. Sy vccwcunns are natural numbers which are represented by N., Oi) iS) isreeetinc are whole numbers which are represented by W., axuasiene -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, ........... are Integers which are represented, by Zor I., , A number is a rational number if, (a) it can be represented in the form of p/q, where p and q are integers, and q #0., or, (b) its decimal expansion is terminating (e.g. am? 0.4), or, (c) its decimal expansion is non-terminating recurring (repeating), (e.g. 0.1234 = 0.1234234......), , A number is irrational number if, (a) it can not be represented in the form of = , where p and q are, integers and q #0., or, (b) its decimal expansion is non-terminating non-recurring (e.g., 0.1010010001......), All rational and irrational numbers collectively form real numbers., There are infinite rational numbers between any two rational numbers., , There is a unique real number corresponding to every point on the, number line. Also, corresponding to each real number, there is a, unique point on the number line., , Rationalisation of a denominator means to change the Irrational, denominator to rational form., , To rationalise the denominator of, , Va-b Va + b, , where ais a natural number and b is an integer., Va-b, , »We multiply this by
Page 4 :
° Laws of Exponents : Let a > 0 be a real number and m and n are rational, numbers, then, , 1) Wa a"=a™** 2) a” wa"s qi", 3) (a")"=a™ 4) a”. b" =(ab)”, Oo =A) ae 1, 5) a=1 6) a“= a™, ° For positive real number a and b, the following Identities hold, 1) Ja. vb = vab 2) a+ vb =f, , 3) (Ja+Vb)(Va-vo)=a-—b 4) (Ja+ vb) =a+2Vab +b, 5) (a+-vb)(a-vb)= a? -b, All natural numbers, whole numbers and integers are rational, , Prime Numbers : All natural numbers that have exactly two factors, (i.e., 1 and itself) are called prime numbers. e.g., 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17,, 19, 23, ... etc., , Composite Numbers : Those natural numbers which have more than, two factors are known as composite numbers. e.g., 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, ..., , 1 is neither prime nor composite., , Types of Numbers, , , , , , Real Numbers, , |, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , v v, Rational Numbers (2) Irrational Numbers, | : |, , v v, Terminating Non Terminating Non-Terminating, Decimal Expansion Recurring Decimal Non-Recurring, es Expansion Decimal Expansion, q=2"x5 10 E, (2 = 3,33... = 3.3] (J2 = 1.414...), , (F - 0.4)
Page 5 :
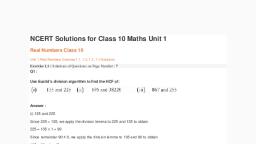
Real Numbers, , , , y, , Rational Numbers, , Eg: [52.0.2], , I, 3, , 6, , y, , Irrational Numbers, , Eg: (\2 \av5n), , , , y, , Integers, (ana, ne, 71,0, Ty 29 xn), , —, , Negative Integers, , y, , Fractions, (2.2.2), 2°3'5, , Whole Numbers (0, 1, 2, 3...), , , , , , , , , , (... -3, -2, -1), , v, , Zero (0) Natural Numbers ( 1, 2, 3, ....), , v v, , Even Numbers Odd Numbers, (2,4, 6, 86.2 11, i he Ly ccs), , y v, , Prime Number Composite Numbers, (2) (4, 6, 8. 10...), v v v, , *, , Ya =, , 4”, , Prime Numbers Composite, (3,827 11 ccc} Numbers, (9,15 x)