Page 2 :
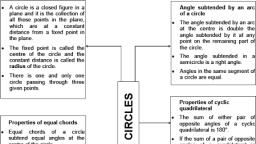
MATHS CIRCLES, , Circles, 1. A circle is a collection (set) of all those points in a plane, each one of which is at a constant distance, from a fixed point in the plane., The fixed point is called the centre and the constant distance is called the radius of the circle., 2. All the points lying inside a circle are called its interior points and all those points which lie outside, the circle are called its exterior points., 3. The collection (set) of all interior points of a circle is called the interior of the circle while the, collection of all exterior points of a circle is called the exterior of the circle., , 4. A line can meet a circle at the most in two points. A line segment joining two points on a circle is called, the chord of the circle., 5. A chord passing through the center of the circle is called a diameter of the circle. A diameter of circle, is its longest chord., 6. A line which meets a circle in two points is called a secant of the circle., , 7. A polygon is a closed figure made up of three or more line segments., 8. A polygon is called a regular polygon, if it has all its sides equal and has all its angles equal., , www.topperlearning.com, , 2
Page 3 :
MATHS CIRCLES, , 9. A (continuous) part of a circle is called an arc of the circle. The arc of a circle is denoted by the symbol, ‘, ’., An arc less than one-half of the whole arc of a circle is called a minor arc of the circle, and an arc, greater than one-half of the whole arc of a circle is called a major arc of the circle., , 10. The whole arc of a circle is called the circumference of the circle., , 11. One-half of the whole arc of a circle is called a semi-circle of the circle., , 12. Any angle whose vertex is centre of the circle is called a central angle., 13. The degree measure of a minor arc is the measure of the central angle subtended by the arc., 14. The degree measure of a circle is 360°. The degree measure of a semi-circle is 180°, www.topperlearning.com, , 3
Page 4 :
MATHS CIRCLES, , 15. The degree measure of a major arc is (360° - θ°), where θ° is the degree measure of the, corresponding minor arc., 16. Two circles are said to be congruent if and only if either of them can be superposed on the other so, as to cover it exactly., 17. Two arcs of a circle (or of congruent circles) are congruent if either of them can be superposed on, the other so as to cover it exactly., 18. The part of the plane region enclosed by an arc of a circle and its two bounding radii is called a sector, of a circle., If the central angle of a sector is more than 180° , then the sector is called a major sector and if the, central angle is less than 180° , then the sector is called a minor sector., , 19. A chord of a circle divides it into two parts. Each part is called a segment., 20. The part containing the minor arc is called the minor segment, and the part containing the major arc, is called the major segment., , 21. Equal chords of a circle subtend equal angles at the centre., 22. If the angles subtend by the chords of a circle at the centre are equal, then the chords are equal., 23. In a circle, perpendicular from the center to a chord bisects the chord., 24. The line drawn through the centre of a circle to bisect a chord is perpendicular to the chord., , www.topperlearning.com, , 4
Page 5 :
MATHS CIRCLES, , 25. An infinite number of circles can be drawn through a given point, say P., , 26. An infinite number of circles can be drawn through two given points, say A and B., , 27. One and only one circle can be drawn through three non-collinear points., 28. Perpendicular bisectors of two chords of a circle, intersect each other at the centre of the circle., , 29. The length of the perpendicular from a point to a line is the distance of the line from the point., 30. The chords corresponding to congruent arcs are equal., 31. Equal chords of a circle (or of congruent circles) are equidistant from the centre (or centres)., 32. Chords equidistant from the centre of a circle are equal in length., 33. The angle subtended by an arc at the centre is double the angle subtended by it at any point on the, remaining part of the circle., 34. If a line segment joining two points subtends equal angles at two other points lying on the same side of, the line segment, the four points are concyclic, i.e., lie on the same circle., 35. Angles in the same segment of a circle are equal., , www.topperlearning.com, , 5
Page 6 :
MATHS CIRCLES, , 36. An angle in a semi-circle is a right angle., 37. The arc of a circle subtending a right angle at any point of the circle in its alternate segment is a semicircle., 38. A quadrilateral, all the four vertices of which lie on a circle is called a cyclic quadrilateral. The four, vertices A, B, C and D are said to be concyclic points., , 39. The opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilateral are supplementary., 40. If the sum of any pair of opposite angles of a quadrilateral is 180°, then the quadrilateral is cyclic., 41. Any exterior angle of a cyclic quadrilateral is equal to the interior opposite angle., , www.topperlearning.com, , 6