Page 1 :
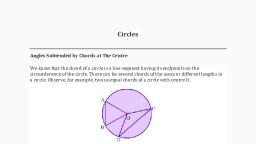
Circles, , Important Points, , 1, Girele The collection of all points in a, fixed distance from a fixed point in th, The following examples of circle are, , Plane wh;, , , , Bangle, , 2. Basic Definition, , hich, plane is are ay, called cin y ’, , 311, , tween two points is called =, jece any two points on them, the PQ is, lie on ee —- lete circle is, The length of the complet, jeter erate of a circle divides af tata bs, iit es i an arc. Each of these two arcs i:, , SF parts, , i aid to be, i ‘Arc) Two circles are §, f myer eer either of them can be superposed, 4 ce actly., ee o reo as corer a quadrilateral ABCD is called, , others, oath uadrilater f it lie on a circle., D, , ‘ cyclic the four vertices 0!, yee" A, , circle be!, , ea incl:, , Common chord The intersection point of two circles is, , - the common chord of the circle., , jsportant Theorems ;, , ;) The perpendicular from the centre of a circle to a chord, bisects the chord and it is vice-versa., , i) Equal chords of a circle (or of congruent circles) are, equidistant from the centre., , + Ittwo chords of a circle are equal, then their corresponding, , acs are congruent and conversely, if two arcs are, {) Chord Suppose, we take any two points on a circle, the ’, , the line segment P@is called the chord of the circle., , mT?, (i) Diameter, , the circle is called a diameter AB of the circle., , . re, The chord which passes througii the, , congruent, then their corresponding chords are equal., ') Congruent ates of a circle subtend equal angles at the centre., \) The angle subtended by an are at the centre is double the, , angle subtended by it any point on the remaining part of, the circle,, , a) i, "Angle in the same Segment of a circle are equal., , ) The ‘4, ‘aaa a of either pair of opposite angles of a cyclic, The nl ateral is 180° and vice-versa., i fae m8 semi-circle is a right angle., a rds of a circle are equal, then their corresponding, , Nieves,’ MOY or semi-circle) are congruent and
 Learn better on this topic
Learn better on this topic



















































 Learn better on this topic
Learn better on this topic









