Page 1 :
A sentorice that exclaims or expresses some emotion or suviy meee — “Y Direct, sentence. It ends with an exclamatory mark(!). —tc', , Ex. How cold you are! What a foolish girl you are! Sere, , How brightly the sun shines! How fine the weather is! meen, , Ex. |g:, , Phrases : - ‘ shies, , A phrase is a group of words, having no subject and predicate and giving some meaning, but PAR’, not complete sense. ee, , Ex. In a ¢orner, into the air, in the sunshine, in the west. @ : Were, Adiec!, , Clauses: - called, A clause is a group of words, having a subject and a predicate, but yet not having complete 1A, sense. It is only a part of a sentence. a oles the pi, Ex. Tell me what you want. | do not know why he is late. This is the book which | bought apla, , yesterday. We cannot start while it is raining., Clauses are of two kinds. Principal clause and Subordinate clause, ; 2.P, Each of the underlined groups of words has a subject and a predicate. They are sentences but they Ex.), cannot stand alone. For example, the group of words “what you want’ depends for its full meaning on, the sentence:"Tell me”, without which it cannot stand. Such group of words are called clauses. 3. /, , Simple sentence : - A sentence, having only subject and one predicate is called simple Ex. |, , sentence. It expresses one thought. Ex: Abdul Kalam is our president, India is a big country. ine, Compound sentence: - A sentence having two or more clauses of equal rank is called 4. |, Compound Sentence. . it expresses two or more thoughts Ex:-.We went out in the rain and were, , drenched. India is a big country, but it is poor. e, , COMPLEX SENTENCE : A sentence that expresses one independent and one or more dependent vert, thoughts is called complex sentence ex. Though India is a big country, yet it is poor. A man, who is acti, contented, is happy., , , , , , : S.A, The subject : - ~, The thing of which we think is called subject. a, Ex. The boy kicked the ball. In this sentence the boy is the subject. Put a question who or what spe, before the verb kicked. You get the subject. Who kicked.the ball? The boy is the answer. It is the, subject. Subject generally comes first. Subject may be one word. z 8, Ex.: Rama stood first in the class. Rama is the subject one word. —, Subject may be more than, one word. Ay, Ex : Rama, the son of Kishore, the head master, stood first in the class. Ex, Here Rama, the son of Kishore, the Headmaster is the subject. More than one word. Th, The Verb : - ‘ :, What we think about the subject is called the verb. 7., Ex. The boy kicked the ball. Kicked is the doing word. It expresses an action. It is the verb, The S, , , , verb generally comes after the subject., , The verb may be one word. Eg: Sita sang a song. Sang is the verb. One word., The verb may be more than one word. Eg. Sita sang a song melodiously. Sang melodiously is the . &, a . I, , verb. More than one word., se, , A, , The object ; - :, , Ex. The boy kicked the ball. Put a question whom or what before the subject the boy. What did the, boy kick? The ball is the answer. It is the object. Object generally comes after the verb., , Object may _be one word. Eg : | saw sita. Sita is the object. One word., , Object may be more than one word. Eg: | saw sita walking in the fields. Sita walking in the fields is th, object. More than one word. ., , 2 AS, , wen port, Pd Pare ag
Page 2 :
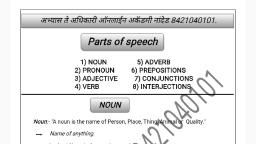
Direct and Indirect object : zs, , , , , , Some verbs take two objects; One relating to a thing is called the Di i sine, v N ; e Dire act;, person is called Indirect object. onameel a —_, , Ex. | gave him (indirect object) a book (direct obj i i 56, . ( , ject). The indirect object him comes before the direct, object a book. The direct object a book comes after the indirect object him., , PARTS OF SPEECH :, , , . Words are divided into eight classes according to the work they do ina sentence. They are Noun,, , Adjective, Pronoun, Verb, Adverb, Preposition, Conjunction, Interjection. These word Classes are, called parts of speech., , 1. A NOUN :- = itis a naming word. It names somebody or something. Ex. Sita took the dog to, , the park. The car makes a lot of noise. Sita name of a person Dog name of an animal, Park name of, aplace. Car name of a thing, noise an idea. : mee, , , , , , 2. PRONOUN == {tis a word used in placé of a noun., Ex.: Rama is absent because he is ill (he in place of Rama). It is a pronoun., , 3._ADJECTIVE :- Itisa word that adds something to the meaning of a noun or pronoun., Ex. Rama is a good boy. (what kind of boy? A good boy), In this sence good says something about the noun Rama. It is an adjective., , 4. VERB: , , , , , Averb is a doing word. It expresses an action., , Ex. Rama walks quickly. (What does Rama do ? walks is the answer. It is an action word. It is a, , verb. A verb may also expresses being: Ex. He is tired. In this sentence is a being word. It is not an, action word. It is a verb., , , , 5.ADVERB : , An adverb is a word that adds to the meaning of a verb., Ex. Rama speaks English well. : In this sentence the word well adds to the meaning of the verb, speaks. It is an adverb. :, , 6, PREPOSITION : , , , A preposition is a word placed before a noun or a pronoun to show its relation to other words., Ex. The book on the table is mine (the preposition on shows the relation of table to “book”., The commonest prepositions are in, at, on, of, to into, by, for etc. - +, , 7. CONJUNCTION : - ., A conjunction is a joining word. It joins words or group of words. Eg. Rama and Kishare are friends., The conjunction and joins the words Rama and Kishore. :, , , , , , , , 8. INTERJECTION : - oe, , An Interjection is a word that expresses some sudden feeling. Eg: Ah! | have hurt my foot. In this ;, sentence Ah! is a cry of pain. It is an interjection., All parts of speech in one sentence. Study this example. ; , cea, Eg. Alas! the tall Netra and her classmates suddenly met death in an accident. :, 1. Netra, classmates, death, accident = nouns. 2. her = Pronoun 3. met = Verb.; —, 4. suddenly = Adverb 5. tall = Adjective. The, an = Articles (Actually demonstrative adjectives), 6. in-= Preposition 7. and= Conjunction 8. Alas! = Interjection one, , 3
Page 3 :
senameutttnii dts +, , 1..NOUN : KINDS OF NOUNS, , Refer to particular persons (R., , ?an, Book), laces (Mysore, Bangalore) or things (F en, ; ay, ce one oa always written with capital letter at the beginning., , a was a great king. The ship was sunk in the sea., , ama, Kishore), a. Proper nouns >, , MmM>p, , , , Refer to names given in common to all persons (man, women) Places if, , 1., , b. Common nouns: ‘, country) or things (table, chair). ,, eegnized your voice at once. He remembers his school days., , i ‘ir, nouns Refer to the names of a number or collection of persons (mob, team) >¢, , i of ships, herd of cattle) : , / t, Ex. The crowd was very big. Our class consists of thirty pupils., , dA ef nouns : Refer to names of things which we cannot perceive with our senses but,, kof them. 3u, Eg. Kindness, bravery, honesty, boyhood, brotherhood, slavery etc. Another classification 3, , , , , , , , , , , , Ex We all love honesty. ‘Ex. Cleanliness is next to godliness. THE COUNTABLE AND UNCOUNTABLE NOUNS, , 2. The Countable Nouns: Nouhs like cup, bag, table, house, book are countable nouns. Put a_, 2n before ese nouns. a cup, a bag, a table, a house, a book. These have plurals Jike cups, bag, iabies, houses, books. Do not put a or an before countable plural nouns. Don’t say a cups,a bags e70, , , , , , , , b. Uncceuntable nouns : Nouns like milk, sugar, gold, water, paper are uncountable nouns. {, not put a or an before uncountable nouns. Don’t say a milk, a sugar etc., , Note: Some uncountable nouns become countable. For example paper is uncountable..If you say:!, sper, it becomes countable. . 5 é ‘ _, example ; Bread is uncountable. If you say a loaf of bread, it becomes countabie., , , , , , E, , a, The Noun : Number Q e, There are two numbers in English- The singular and the plural. he, , Boy — Boys, Class — Classes, Negro- Negroes, Photo-Photos. he, , The Noun ‘ Gender, , a.) Masculine gender: refers to male persons or things. Eg: Son, uncle, nephew, Gentleme~, Cock, boy, bul! etc., , * by) Feminine gender : refers to female persons or things. Eg : Daughter, Aunt, Niece, Lady, H4., girl, cowetc, ~ oe, , c.) Common gender _: refers to either male or female: Eg. Parent, Person, Student, Baby, Child, Friend etc., , a) Neuter gender: Refers to neither male nor female (thing without life) eg: tree, book,.chair, P2 ., table. ; i, ‘ |
Page 4 :
| 2 PRONOUN:, , A pronoun is a word used in place of a noun., | Eg. Rama is absent because he is ill. (the word he is used in place of R, , i, |, \, |, i, , ama) he is a pronoun., , | KINDS OF PRONOUNS, ‘ity, | 1. Personal pronouns : These pronouns are subdivided into first, second and thitd person. The, | first person refers to the speaker Or speakers (eg. |, We) The ¢:cond person refers to the person or, do oan spoken to (eg. You): The third person refers to persons or things spoken about eg. : ne, she, it, they, —, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , Ww ‘, , \ Subject & | we you he she they., 4 Object: me “us you him her them, , : pee, Subject: Object | . Subject:, , acl | know Rama _| Rama knows me_| He He knows Rama, gsWe | We know Rama Rama knows us [She | She knows Rama, stcyou | You know Rama Rama knows you | They | They know-Rama, DO, , Possessive pronouns : Refer to something belongs to somebody., , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , 4 My [like my job. my Mine It is my money. itis mine. :, We Our We like our jobs. Our | Ours _| It is our money. itis ours. !, You your You like your jobs. | Your _| Yours _| It is your money. A |, He His He likes his job. His His Itis his money. {, She Her. She likes her job. Her Hers Itis her money. 1, They Their They like their jobs. | their_| Theirs | Itis their money. }, 1, , r =, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , 3. Reflexive pronouns : Refer to the action done by the subject turns back upon the subject. |, Self is added to my, your, him, her it. Selves is added to our, your, them. « i, , |, , |, , , , , , Eg. | - Myself | looked at myself. ' |, f He - himself * He cut himself with a knife. ;, She - herself She hurt herself. |, You - yourself Please help yourself (one person)., ‘ You - yourselves Please help yourselves (two or more persons). |, We — - Ourselves : We enjoyed ourselves. {, 5) * They - ’ Themselves They enjoyed themselves,, , \, 4. Emphatic pronouns : Refer to pronouns used for emphasis. |, , 59: 1. I saw the mirror myself. 2. Rama has done the work himself, , 3.. | will do it myself ’ 4, I myself saw him do it. ° ., , i, Demonstrative pronouns : These pronouns are used to point out persons or things., _This and these are used for persons or things that are near the speaker., g. 1. This is a present from my uncle 2. These mangoes are rotten
Page 5 :
manor 7 tt, , 8. Relative pronoun : tt refers to some noun going before. The most common relative, Pronouns are who, whom, which, that. It acts as a pronoun and as a conjunction at the same, , , , time. ‘, Eg. 1. This is the house which belongs to my uncle. 2. Take anything that you like ; a. |, 3. This is the boy who works hard 4. These are the boys whom all praise., at ; b., 7. Distributive PFONOUNS : They refer to persons or things one ata time. a, , Each, either and neither are used only in speaking of two persons or things. Any, no one, none are ~"*, , used in speaking of more than two persons or things., , Eg. 1. The two men hate each other 2. Either of you can go, 3. Neither of the statements is true. 4. We haven't got any money. 4., 5.No one came to visit me while | was in hospital. :, , 6. None of this money is mine. :, , , , , , te, , , , 2 . 2g., 8. Indefinite pronouns: They refer to persons or things in a general way but do not refer to any yy, Person or thing in particular. ‘9:, , , , , , =g:, Eg. 1. Iwill take you there one day. 2. Anyfoolcandothat 3. Some milk was split ,, 4. Do good to others. _ 5. Some are born great. 6. They haven't got any children ¢j, te, 3. ADJECTIVE : KINDS OF ADJECTIVES ~ - i, An adjective is a word used with a noun to add something for its meaning. fa, Eg. It is a nice day today. She isa nice little girl., aie : nt, KINDS OF ADJECTIVES. : be, at 3 rr, a. Descriptive adjectives : Refer to quality of a person or thing., Eg. 1. Sita is a clever girl. 2. He is. an ‘honest man.’ P, 3. It is a big house. 4. These are red apples., pangoens . : . \U, b. Adjectives of quantity : They show how much of a thing is meant. , ar, i 3 os, Eg. 1. Hehas ittle intelligence. 2. Hedidnoteatanyrice. . or, 3.. He has lost all his wealth. 4. He ate some rice. . ee, c. Possessive adjectives : Refer to possession of something by someone. . x, Eg. 1. This ismy pen 2. Karnataka is our state 3. What is your name? 4. It is her dog. A, d. Demonstrative adjectives : They point out something or some person. - }., Eg. 1. That boys intelligent. 2. These mangoes are sour., 3. This book is new. 4. Those flowers are cheap., , , , e. Interrogative adjectives : They are used with nouns to ask questions,, , Eg. Whose book is this ? Which way shall we go? Whose umbrella is this? What kind of thing is it?