Page 1 :
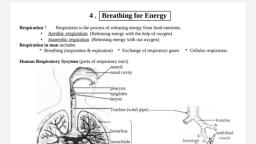
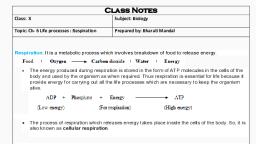
Question Bank, Respiration in plants, 1. Define the following :, (i) Respiration (ii) Breathing (iii) Fermentation, Ans. (i) Respiration : It is the process of breakdown of food, materials to produce energy., (ii) Breathing : It is a mechanism by which organisms obtain, oxygen from the environment and release carbon dioxide., (iii) Fermentation : The process by which micro-organisms, obtain their energy by anaerobic respiration is called, fermentation., 2. List any four differences between respiration and combustion., Ans. Comparison between Respiration and Combustion, 1., 2., 3., 4., , Respiration, Occurs in living organisms., Enzymes take part., Energy is released step by step (in, many steps)., Occurs at body temperature., , Combustion, 1. Occurs in non-living objects., 2. No enzymes involved., 3. Energy is released at once in one, step., 4. Occurs at high temperature., , 3. Write about the process of respiration in a simplified form., Ans. Respiration is a much more complex process. It is a, biochemical process and includes (i) breathing — the, exchange of gases (O2 and CO2), and (ii) oxidation of food in, order to release energy., In this process, carbon dioxide and water are produced as byproducts. The process of respiration can be summarized as, follows :, Food + Oxygen –→ Carbon dioxide + Water + Energy, , Biology Class-IX, , 1, , Question Bank
Page 2 :
4. What are the main types of respiration? Write about them., Ans. Respiration is of two types (i) aerobic respiration (ii), anaerobic respiration., (i) Respiration in the presence of oxygen is known as aerobic, (or oxybiotic) respiration and the organisms which, undergo aerobic respiration are called aerobes., (ii) Less common type of respiration which occurs in the, absence of oxygen is known as anaerobic (or anoxybiotic), respiration, and the organisms are called anaerobes., Certain bacteria are complete anaerobes., 5. With the help of a reaction, write down how respiration occurs, in yeast., Ans. Respiration occuring in yeast is anaerobic respiration, i.e., it, occurs in absence of oxygen. It may also be called, fermentation. Here glucose is metabolised to form carbon, dioxide, ethyl alcohol and energy., Yeast, → 2CO2 + 2C2H5OH + Energy, C6H12O6 ⎯⎯⎯, 6. Write down in brief about, the mechanism of respiration., Ans. Respiration occurs in two stages., The first stage is known as, glycolysis and produces pyruvic, acid (in the form of pyruvate), from glucose. The second stage, is called Kreb’s cycle in which, pyruvic acid is further broken, down. The degradation of food, material upto pyruvic acid formation, is same in both aerobic and anaerobic, respiration, while the further degradation, of pyruvic acid differs in the two types of respiration., , Biology Class-IX, , 2, , Question Bank
Page 3 :
7. Write any two differences between glycolysis and Kreb’s, cycle., Ans., Glycolysis, (i) Glycolysis occurs in the cell, cytoplasm., (ii) Incomplete breakdown of, glucose occurs forming pyruvate., , Kreb’s cycle, (i) Kreb’s cycle takes place inside, mitochondria., (ii) Complete breakdown of glucose, Occurs, forming CO2, H2O and energy., , 8. Differentiate between aerobic and anaerobic respiration., Ans. Comparison between Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration, Aerobic Respiration, 1. It occurs in the presence of oxygen., 2. Glucose, the respiratory substrate, is, oxidized completely into CO2 and, H2O., Glyocolysis, → Pyruvate, Glucose ⎯⎯⎯⎯, Kreb's cycle, →, Pyruvate ⎯⎯⎯⎯, +O, 2, , CO2 + H2O + Energy, , Anaerobic Respiration, 1. It occurs in the absence of oxygen., 2. The respiratory substrate is incompletely, oxidized into CO2 and ethyl alcohol (in, alcoholic fermentation), or lactic acid (in lactic acid fermentation)., Glyocolysis, Glucose ⎯⎯⎯⎯, → Pyruvate, Fermentation, Pyruvate ⎯⎯⎯⎯→, O, 2, , Ethyl alcohol + CO2 + Energy, 3. The energy released is more., 3. The energy released is less., 4. While the first step (glycolysis) takes, 4. Both the first step (glycolysis) and the, place in the cytoplasm, the second step, second step, i.e., conversion of pyruvic, (Kreb's cycle) takes place inside the, acid to lactic acid or ethyl alcohol takes, mitochondrion., place inside the cytoplasm., , 9. Write any three differences between respiration in plants and, animals., Ans. Respiration in plants differ from animals in the three aspects —, 1. The different parts of a plant, like the root, stem and leaf,, perform respiration, separately. This is in contrast to, respiration in animals where it occurs as a unit., 2. There is little transport of gases from one part of the plant, body to the other. In animals, the respiratory gases are, transported to long distances inside the body., Biology Class-IX, , 3, , Question Bank
Page 4 :
10., Ans., , 11., Ans., , 12., Ans., , 3. In plants, respiration occurs at a much slower rate than in, the animals., How does respiration occur in roots?, Respiration in Roots : Roots obtain oxygen from the air, present in between the soil particles by the process of, diffusion. Oxygen diffuses into roots hair and reaches other, cells of the root. Carbon dioxide produced in the cells of the, root produced during respiration moves out from the root hairs, into the soil by the process of diffusion., This gaseous exchange occurs in young roots. The older, portions of the root do not possess root hairs. In these portions,, the gaseous exchange occurs through tiny openings called, lenticels., What does pneumatophore? What is its importance?, The breathing or respiratory root found in the plants growing, in mangroves or saline swamps are called pneumatophore., Each pneumatophore bears breathing pores or lenticels near, the apical region which helps in exchange of gases., How does respiration occur in leaves and stems?, In higher plants, the exchange of gases occurs through the (i), stomata present in the leaves and young stems and (ii) lenticels, present in the bark of woody plants., A lenticel consists of loosely arranged thin walled rounded, cells (complementary cells). The complementary cells enclose, intercellular spaces for exchange of gases., Oxygen moves in through the stomatal pores or lenticels by, simple diffusion into the intercellular spaces. From these, intercellular spaces the oxygen diffuses into the cells., Similarly, CO2 diffuses from the cells into the intercellular, spaces and then through the stomata and lenticels to the, exterior., , Biology Class-IX, , 4, , Question Bank
Page 5 :
13. Write the differences between photosynthesis and respiration., Ans. Differences between photosynthesis and respiration, Photosynthesis, 1. It takes place only in the presence of, light., 2. Only green cells of plants can perform, photosynthesis., 3. It takes place inside chloroplast., 4. It is an anabolic process and builds up, complex compounds (sugars) from, inorganic substances (CO2 and H2O)., 5. It absorbs energy and is an endothermic, process., light, chlorophyll, , 6CO2 + 12H2O ⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯, → C6H12O6 + 6H2O + 6O2, , Respiration, It occurs in all the tissues during both day, and night., This occurs in all the cells of an organism., Aerobic respiration involves mitochondria, and cytoplasm., It is a catabolic process in which complex, compounds (sugars) are broken into, simpler substances (CO2 and H2O)., Energy is given out thus, it is an, exothermic process., C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy, , 14. Match the items in Column A with those in Column B, (a), (b), (c), (d), , Column A, Anaerobic respiration, Muscle, Glycolysis, Mitochondria, , Column B, (i) Kreb's cycle, (ii) Lactic acid, (iii) Alcoholic fermentation, (iv) Cytoplasm, , Ans. (a) — (iii), (b) — (ii), (c) — (iv), (d) — (i), , Biology Class-IX, , 5, , Question Bank
Page 6 :
15. Complete the following statements by choosing the correct, alternative out of those given within brackets., (i) During respiration, temperature _________., (rises considerably/remains low/does not change), (ii) Respiration is controlled by _________., (enzyme/catalyst/heat), (iii) Respiration is a ___________ process., (physical/chemical/biochemical), Ans. (i) Does not change, (ii) Enzyme, (iii) Biochemical, , Biology Class-IX, , 6, , Question Bank