Page 1 :
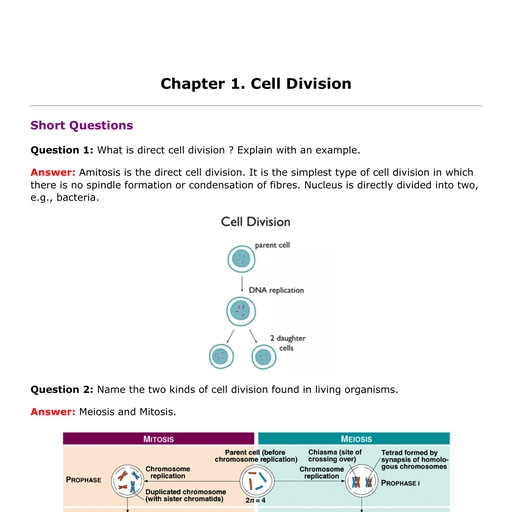
Question Bank, The Periodic Table, 1., , Why was there a necessity for classification of elements? Give at least two, reasons?, , Ans. (i) The classification may lead to correlate the properties of elements with, some fundamental property that is the characteristic of all elements., (ii) The classification may further reveal the relationship between different, elements., 2. In which way were the elements classified by early chemists? State two, reasons for rejecting the classification named by you., Ans. The early chemists classified elements into metals and non-metals, based, on the set of physical and chemical properties., Reasons for rejection :, (i) This classification hardly serves any purpose, as all the elements are, divided into two major groups., (ii) There is no justification for the more active metals or the more active, non-metals or the elements (metalloids) which exhibit the properties of, metals as well as non-metals., 3. What do you understand by the triad of elements? Name at least two triads., Ans. Dobereiner’s law of triads : A group of three elements having similar, chemical properties arranged in the order of their increasing atomic weights,, Class-IX, , 1, , Question Bank
Page 2 :
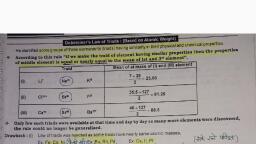
such that the atomic weight of the middle element is almost the arithmetic, mean of the other two elements is called the law of triads., Examples of triads :, (1) Lithium (7.0), sodium (23) and potassium (39), (2) Chlorine (35.5), bromine (80) and iodine (127), 4. (i) State Dobereiner’s law of triads., (ii) P, Q and R are three elements in Dobereiner’s triad. If the atomic weight, of P is 35.5 and R is 127, calculate the atomic weight of Q., Ans.(i) Dobereiner’s law of triads : A group of three elements having similar, chemical properties arranged in the order of their increasing atomic, weights, such that the atomic weight of the middle element is almost the, arithmetic mean of other two elements is called law of triads., (ii) Atomic weight of, Q=, , At. wt. of P + At. wt. of R, 35.5 + 127 162.5, = 81.25, =, =, 2, 2, 2, , 5. Lithium, sodium and potassium were put in the same group on the basis of, their similar properties., (i) What is the similarity in their properties?, (ii) If the atomic weights of lithium and potassium are 7 and 39 respectively,, what is the atomic weight of sodium?, Ans. (i) Li, Na and K are very reactive alkali metals, which react with water, with the formation of an alkali and hydrogen gas., Class-IX, , 2, , Question Bank
Page 3 :
(ii) Atomic weight of Sodium =, , At. wt. of Li + At. wt. of K, 2, =, , 7 + 39 46, = 23, =, 2, 2, , 6. From the list of elements given below, make three triads and name the, family of each triad., List : Cl, Li, Ca, Br, Na, Sr, I, K and Ba., Ans.(i) Alkali metals triad, , :, , Li, , Na, , K, , (ii) Alkaline earth metals triad, , :, , Ca, , Sr, , Ba, , (iii) Halogens triad, , :, , Cl, , Br, , I, , 7. (i) Name an alkali metal other than lithium, sodium and potassium., (ii)Name an alkaline earth metal other than calcium, strontium and barium., (iii)Name one halogen other than chlorine, bromine and iodine., (iv)Name a non-metal having properties similar to carbon., (v)Name a rare gas other than neon, krypton and xenon., Ans.(i) Rubidium, (iv) Silicon, , (ii) Magnesium, , (iii) Fluorine, , (v) Argon, , 8. What is the achievement of Dobereiner’s law of triads?, Ans. The law recognised the relation between atomic weight of an element and, its chemical properties for the first time., , Class-IX, , 3, , Question Bank
Page 4 :
9. Why was classification on the basis of the law of triads rejected?, Ans.(i) Quite a large number of elements cannot be grouped into triads., (ii) Classification on the basis of triads left room for chance. It was, possible to group dissimilar elements into triads., 10. What was the similarity observed by Newland, when he arranged the, elements in the order of their increasing atomic weights with the, musical scale?, Ans. Newland observed that the properties of the first and the eighth elements, were similar, much like the first and the eighth note of the octave of the, musical scale., 11. State Newland’s law of octaves. Support your answer with two examples., Ans. (i) Newland’s law of octaves : Elements when arranged in the increasing, order of their atomic weights show resemblance in physical and chemical, properties between the eight and the first element similar to the eighth, note and first note on a musical scale., Examples : (i) The eighth element from lithium is sodium. Similarly,, eighth element from sodium is potassium. Thus, lithium, sodium and, potassium have similar chemical properties., (ii) The eighth element from fluorine is chlorine. Thus, fluorine and chlorine, have similar chemical properties., , Class-IX, , 4, , Question Bank
Page 5 :
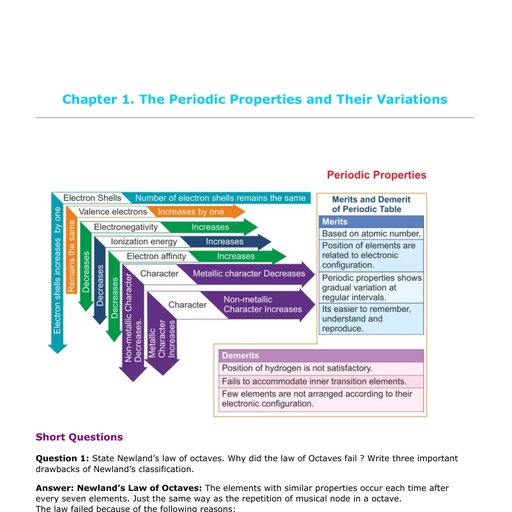
12. Complete the statement given below :, On the basis of Newland’s law of classification of elements, the properties, of sodium and potassium are similar, because potassium is the ________, element, starting from sodium., Ans. On the basis of Newland’s law of classification of elements, the properties, of sodium and potassium are similar, because potassium is the eighth, element, starting from sodium., 13. State two achievements of the law of octaves., Ans.(i) Atomic weights of the elements was recognised as the basis of, classification of elements., (ii) The periodicity as a fundamental property of elements was recognized, for the first time., 14. State two reasons for rejecting the law of octaves., Ans.(i) The law did not extend properly beyond the element calcium., (ii) The law did not provide any specific place for hydrogen., 15. The elements A and B obey the law of octaves. How many elements are, between A and B?, Ans. There are six elements between A and B., 16. (i) What are the basis of classification of elements in Mendeleev’s, periodic table?, (ii) State Mendeleev’s periodic law., , Class-IX, , 5, , Question Bank
Page 6 :
Ans. (i) Basis of Mendeleev’s periodic classification :, (i) Similarities in the chemical properties of the elements., (ii) Increasing order of atomic weights of the elements., (ii) Mendeleev’s periodic law : The physical and chemical properties of all, elements are the periodic function of their atomic weights., 17. State two merits of Mendeleev’s periodic table over previous attempts of, classification of elements., Ans. Merits of Mendeleev’s periodic table :, (i) It is based on the fundamental property of elements i.e. their atomic, weights., (ii) The gaps left in the periodic table helped in the discovery of unknown, elements., 17. Mention two problems which are unresolved in original Mendeleev’s, periodic classification., Ans. (i) Hydrogen is not given a definite position., (ii) The position of the rare earth elements and the actinides cannot be justified, on the basis of the atomic weights., 19. (i) Who prepared the modern periodic table?, (ii) Define (a) Modern periodic law (b) Modern periodic table., Ans. (i) H.G.J. Moseley prepared the modern periodic table in 1913., , Class-IX, , 6, , Question Bank
Page 7 :
(ii) (a) Modern periodic law : It states that the physical and chemical, properties of all elements are the periodic function of their atomic, numbers., (b) Modern periodic table : It is a chart of elements prepared in the, increasing order of their atomic numbers, such that the elements in, any vertical column have similar, but graded chemical properties., 20. With reference to the long form of the periodic table fill in the blank spaces, with appropriate words given within the brackets., (a) Chemical properties of an element are the periodic function of their _____, (atomic weight/atomic number)., (b) The serial number of an element in the periodic table is also its _______, (atomic weight/atomic number)., (c) The number of electrons in the valence shell of an atom represents its, ________ (group/period) in the periodic table., (d) The number of electron shells around the nucleus of an atom represents its, __________ (group/period) in the periodic table., (e) __________ (Alkali/Alkaline) and alkaline _______ (earth/halogen) metals, are placed in groups I A and ________ (III A/II A) respectively on the left, hand side of the periodic table., (f) _________ (Metallic/Non-metallic) elements are placed on the right hand, side of the periodic table., , Class-IX, , 7, , Question Bank
Page 8 :
(g) The elements occupying left and right wing vertical columns are called, _________ (transition/normal) elements., (h) Noble _________ (metals/gases) are placed in _________ (7th/zero) group, in the last _________ (column/period) of the periodic table., (i) The ________ (normal/transition) elements are accommodated in the middle, of the periodic table in __________ (two/three) series., (j) The first period has ________ (eight/two) elements and is called a _______, (short/very short) period., (k) The second and the third periods have ________________ (eighteen/eight), elements and are called ________ (long/short) periods., (l) The fourth and the fifth periods have ______ (eight/eighteen) elements and, are called _______ (long/short) periods., (m) The sixth period has _____ (32/18) elements and is called ______ (long/very, long) period., (n) The seventh period is a __________ (long/very long) period, but is, ___________ (complete/incomplete)., (o) ___________ (Actinides/Lanthanides) are elements from atomic number 57, to ______ (71/72) and are placed ______ (outside/inside) the periodic table., (p) Actinides are radioactive elements from atomic number ______ (89/90), to 112., , Class-IX, , 8, , Question Bank
Page 9 :
Ans.(a) atomic number, , (b) atomic number, , (c), , group, , (d) period, , (e) Alkali, earth, II A, , (f) Non-metallic, , (g) normal, , (h) gases, zero, column, , (i) transition, two, , (j) two, very short, , (k) eight, short, , (l) eighteen, long, , (m) 32, very long, , (n) very long, incomplete, , (o) Lanthanides, 71, outside (p) 89., 21. (a) What are transition elements?, (b) Which amongst the following are transition elements? K, Mn, Ca, Cr, Cu,, Cs, Fe, Pt., Ans.(a) The elements in which the valence shell and the shell before the valence, shell (penultimate shell) are incomplete are called transition elements., (b) Mn, Cr, Cu, Fe and Pt are transition elements., 22. Give the name and symbol of the following elements which occupy each of, the following positions in the periodic table :, (a) Period 2, group III A, , (b) Period 2, group VI A, , (c) Period 1, group 1 A, , (d) Period 3, group VII A, , (e) Period 4, group zero, , (f) Period 3, group II A, , Ans. (a) The element in period 2, group III A is : Boron, (b) The element in period 2, group VI A is : Oxygen, (c) The element in period 1, group I A is : Hydrogen, (d) The element in period 3, group VII A is : Chlorine, (e) The element in period 4, group zero is : Krypton, Class-IX, , 9, , Question Bank
Page 10 :
(f) The element in period 3, group II A : Magnesium, 23. Name four alkali metals. To which group do they belong?, Ans. The four alkali metals are : lithium, sodium, potassium and rubidium., They belong to I A group., 24. Name four alkaline earth metals. To which group do they belong?, Ans. The four alkaline earth metals are beryllium, magnesium, calcium and, strontium. They belong to group II A., 25. Name four elements of group VII A. State the common name of this group, of elements., Ans. The four elements of VII A group are : fluorine, chlorine, bromine and, iodine. The common name of VII A group of elements is halogens., 26. Silicon (at no. 14) and phosphorus (at no. 15) belong to the same period, of the periodic table. Write down the electronic configuration of silicon, and phosphorus and name the groups in which these elements occur., Ans.(i) Electronic configuration of silicon (at no. 14) is [(2)K, 8(L), 4(M)]., As silicon has four electrons in its valence shell, therefore, it belongs, to IVA group of the periodic table., (ii) Electronic configuration of phosphorus (at no. 15) is [(2)K, 8(L), 5(M)]., As phosphorus has five electrons in its valence shell, therefore, it belongs, to VA group of the periodic table., , Class-IX, , 10, , Question Bank
Page 11 :
27. Oxygen (at no. 8) and sulphur (at no. 16) belong to the same group of the, periodic table. On the basis of their electronic configuration name the, periods in which these elements occur., Ans.(i) Electronic configuration of oxygen (at no. 8) is [2(K), 6(L)]. As oxygen, has two electron shells, therefore, it belongs to the 2nd period of the, periodic table., (ii) Electronic configuration of sulphur (at no. 16) is [2(K), 8(L), 6(M)]., As sulphur has three electron shells, therefore, it belongs to the 3rd period, of the periodic table., 28. Where would you expect to find the element E with atomic number 20 in the, periodic table and why?, Ans. Electronic configuration of element E (at no. 20) is [2(K), 8(L), 8(M), 2(N)]., Now, as E has four electron shells, therefore, it belongs to the 4th period., Also, as E has 2 valence electrons, therefore, it belongs to group IIA. Thus,, on the whole E belongs to the fourth period of group IIA., 29. An element with atomic number 11 is an alkali metal. Into which families will, you place elements with atomic number 10 and 12 respectively., Ans. The electronic configuration of the element (at no. 10) is [2(K), 8(L)]. As this, element has eight electrons in its valence shell, therefore, it belongs to zero, group. The family of elements in the zero group is called noble gases or rare, gases. The electronic configuration of the element (at no. 12) is [2(K), 8(L),, , Class-IX, , 11, , Question Bank
Page 12 :
2(M)]. As the element has 2 electrons in its valence shell, therefore, it, belongs to II A group, which is a family of alkaline earth metals., 30. Which period is (i) shortest (ii) longest (iii) incomplete, in the long form of, the periodic table? How many elements are in (i) and (ii)?, Ans. (i) The first period is the shortest period., (ii) The sixth period is the longest period., (iii) The seventh period is the incomplete period., The first period has only two elements, whereas the sixth period has, 32 elements., 31. The elements A and B have electronic configurations (2, 8, 18, 2) and, (2, 6) respectively., (i) To which period A and B belong?, (ii) To which group A and B belong?, Ans.(i) As A has four electron shells, therefore, it belongs to the 4th period., As B has two electron shells, therefore, it belongs to the 2nd period., (ii) As A has 2 electrons in its valence shell, therefore, it belongs to group II A., As B has 6 electrons in its valence shell, therefore, it belongs to group VI A., 32. The table given below shows the mass number and number of neutrons of four, elements, P, Q, R and S., Elements, Mass number, Number of neutrons, , Class-IX, , P, 12, 6, , 12, , Q, 20, 10, , R, 23, 12, , S, 35, 18, , Question Bank
Page 13 :
(a) Write the atomic number of P, Q, R and S., (b) Write down electronic configuration of P, Q, R and S., (c) To which group P, Q, R and S belong?, (d) To which period P, Q, R and S belong?, (e) Name which amongst P, Q, R and S is (i) alkali metal, (ii) noble gas,, (iii) a halogen, Ans., Elements, (a) Atomic number, (b) Electronic config., (c) Group, (d) Period, , P, (12–6) = 6, 2, 4, 2nd, IV A, , (e) (i) R is an alkali metal, , Q, R, S, (20–10) = 10 (23–12) = 11 (35–18) = 17, 2, 8, 2, 8, 1, 2, 8, 7, 2nd, 3rd, 3rd, Zero, IA, VII A, (ii) Q is a noble gas, , (iii) S is a halogen., , Class-IX, , 13, , Question Bank