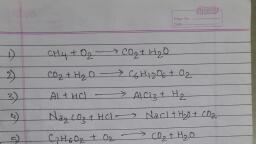Page 1 :
Chemical Reactions and, Equations
Page 2 :
Chemical Reaction, ▪ A process that occurs when matter undergoes change in, composition., ▪ Any process that involves the rearrangement of, structure of the substance to form new substances., ▪ In which one or more substances are converted to one, or more different substances., ▪ The substances which take part in a chemical reaction, are known as reactants., ▪ The new substances formed during a chemical reaction, are known as products., ▪ Reactants and products differ in their physical and, chemical properties., ▪ Law of conservation of Mass and energy holds always, in a chemical reaction., Example:, i. Carbon reacts with oxygen present in air results in, formation of carbon dioxide gas, in the whole process, carbon and oxygen are reactants and carbon dioxide is, product., ii. Water reacts with carbon dioxide results in formation of, carbonic acid, in which water and carbon dioxide are, reactants and carbonic acid is product., iii.What happens if hydrochloric acid reacts with sodium, hydroxide?
Page 3 :
Characteristics of Chemical Reactions, Some of the important characteristics of chemical, reactions are:, • Change of state, Example: When hydrogen gas reacts with oxygen gas, it results in formation of liquid water., • Change in colour, Example: When iron nail is dipped in blue coloured, copper sulphate solution, the blue color changes to, green., • Evolution of gas, Example: When sodium reacts with water, bubbles of, hydrogen gas is seen., • Change in temperature, Example:, i. When water is added to quick lime the vessel, becomes warm due to evolution of heat., ii.When potassium hydroxide is added to ammonium, chloride the vessel becomes cold due to absorption, of heat., • Formation of a precipitate, Example: When silver nitrate solution reacts with, sodium chloride solution it gives precipitate of silver, chloride and sodium nitrate solution.
Page 4 :
Types of Energy Interaction in Chemical, Reaction, In all the chemical reactions, transformation or change in, energy is involved in form of heat. On the basis of change, in energy, all the reactions are divided into two parts:, i. Endothermic reactions, ii.Exothermic reactions., Endothermic reactions : The reaction in which heat is, absorbed i.e., energy is given to the system from the, surroundings., Example:, i. Photosynthesis is an example of an endothermic reaction., In the process of photosynthesis, plants by utilizing the, energy of the sun convert carbon dioxide and water in, glucose and oxygen., ii.Thermal decomposition of calcium carbonate results in, formation of quick lime and carbon dioxide, in this, process energy is used to break the bond between carbon, and oxygen., Exothermic reactions: The reaction in which heat is, evolved i.e., energy is given out from system to the, surroundings., Example: Sodium and chlorine are mixed together to yield, table salt is an example of exothermic reaction. 411 kJ of, energy is produced in this reaction.
Page 5 :
Chemical Equation, ▪ is a short hand representation of a chemical reaction to, occur., ▪ Chemical reactions are typically written one of three ways., There are word equations, skeleton equations and balanced, equations., Word Equations, • are used to describe the reaction in sentence form or in a, literally form., • The "+" means "reacts with", and the arrow means "to, produce"., Example:, magnesium + oxygen -------> magnesium oxide, • Magnesium reacts with oxygen to produce magnesium, oxide.“, • A word equation gives limited information., • It identifies only the reactant and products. It does not give, their formulae, nor does it tell you the masses of reactants, needed or the mass of product produced., Skeleton Equations, • are simply the bare bones of a chemical equation., • are obtained by substituting the chemical formulae into the, word equation., Example:, The skeleton equation for the reaction above is:, Mg +, O2 ---------> MgO
Page 6 :
Balanced Equations, ❑The chemical equations must be written in accordance, with the law of conservation of mass., ❑The law of conservation of mass states that, "The matter, can neither be created nor destroyed”. i.e., In a chemical, reaction, the total mass of reactants is equal to the total, mass of products., ❑A balanced chemical equation is the one in which the, atoms of each element must be equal on both sides of the, equation i.e., both on reactant and product side., ❑The following elements used in diatomic state while, writing a chemical equation; H2, F2, Cl2, Br2, I2, O2, and, N2., ❑All other elements can be treated as if they were, monoatomic (Act like lone atoms)., Example:, Balanced chemical equation for above reaction is given as;, 2Mg + O2 --------> 2MgO
Page 7 :
Steps to Balance a Chemical Equation, To show how to balance the equation, the following, equation is used, Fe + H2O → Fe3O4 + H2, ➢Step 1: First of all, draw the boxes around each formula, as shown below-, , ➢Step 2: Find out the number of atoms of each element., ➢For Example, on reactant side, 1 for Fe, 2 H, and 1 O, and on product side we have, 3 for Fe, 4 for O and 2 for, H., ➢Step 3: Start to balance the equation with the compound, having maximum number of atoms. While balancing, does not alter the formula of the compound., ➢Step 4: One by one balance each element on reactant, and product side., , ➢Step 5: After balancing number of atoms on both the, side of the equation, finally check the correctness of the, balanced equation., , ➢Step 6: then write the symbols of the physical state of, reactants and products as shown below3Fe(s) + 4 H2O (g) → Fe3O4 (s) + 4H2 (g)
Page 8 :
Types of Chemical Reactions, The chemical reactions are of following types, i. Combination Reaction, ii. Decomposition Reaction, iii. Displacement Reaction, , iv. Double Displacement Reaction, Some Typical Reactions, , ▪ Precipitation Reaction, ▪ Combustion Reaction, , ▪ Redox Reaction, ▪ Neutralization Reaction
Page 9 :
Combination Reaction:, ▪ is also known as synthesis reaction., ▪ is a reaction in which two or more substances (elements, and/or compounds) combine to form a single new, substance., ▪ The general form of a combination reaction is;, A+ B → AB, Example:, i. Solid sodium metal reacts with chlorine gas to produce, solid sodium chloride., 2Na(s) + Cl2(g) → 2NaCl (s), ii. Carbon reacts with oxygen in air to produce carbon, dioxide gas., C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g), Decomposition Reaction:, ✓ is a reaction in which a substance (compound) breaks, down into two or more simpler substances(elements or, compounds)., ✓ The general form of a decomposition reaction is;, AB → A+ B, Example:, i. Solid sodium metal reacts with chlorine gas to produce, solid sodium chloride., CaCO3(s) → CaO(s) + CO2(g), ii. Carbon reacts with oxygen from air to produce carbon, dioxide gas., 2HgO(s) → 2Hg(l) + O2(g)
Page 10 :
Single-Displacement Reaction:, • is also known as single-replacement reaction., • is a reaction in which one element replaces a similar, element in a compound, i.e., Metal replaces metal and nonmetal replaces non-metal., • The general form of a decomposition reaction is;, A + BC → AC + B, where A and B are metals and C is a, non-metal., X + YZ → XY + Z, where X and Z are non-metals and Y is, a metal., Example:, i. Mg(s) + Cu(NO3)2 (aq) → Mg(NO3)2 (aq) + Cu (s), Double-Displacement Reaction:, • is also known as Double-replacement or Metathesis, reaction., • is a reaction in which the positive and negative ions of two, ionic compounds exchange their places to form two new, compounds., • generally occur between substances in aqueous solution., • in these reaction, one of the product is usually a solid, precipitate, a gas, or a molecular compound such as water., • The general form of a decomposition reaction is;, AB + CD → AD + CB, where A and C are positively, charged ions (cations) and B and D are negatively charged, ions (anions)., Example:, i. NaCl(aq) + AgNO3 (aq) → Na(NO3) (aq) + AgCl (s)
Page 11 :
Some More Typical Reactions, , Precipitate Reactions:, are double displacement reactions in which one of the, compounds formed is insoluble. This insoluble compound is, called precipitate and it settles at the bottom., Redox Reactions:, ▪ are also known as Reduction-Oxidation Reaction., ▪ reaction in which both reduction and oxidation takes place, simultaneously is called redox reaction., ▪ are reactions in which transfer of electrons occurs between, the two species., ▪ Oxidation is defined as addition of oxygen or removal of, hydrogen., ▪ Reduction is defined as removal of oxygen or addition of, hydrogen., ▪ Oxidizing agent is the one which gains the electrons and is, reduced in a chemical reaction., ▪ Reducing agent is oxidized in a chemical reaction and it, loses the electrons., ▪ Fluorine is the strongest oxidizing agent., ▪ Lithium is strongest reducing agent., Neutralization Reactions:, oare double-displacement reaction., oare reactions between acid and base which produce salt and, water as products of reaction., Combustion Reactions:, ✓are reactions in which a substance reacts with oxygen gas,, releasing energy in the form of light and heat., ✓Combustion reactions must involve oxygen gas as one of, reactant., ✓are reactions in which products are oxides of element, present in reacting species.
Page 13 :
QUIZ, 1. What will happen when a piece of iron metal is placed is copper, sulphate solution?, (a) Physical change, (b) A chemical reaction, (c) Evolution of gas, (d) Heat will be evolve, 2. Respiration is an example of chemical change. The reactants, involved in this are:, (a) Carbon dioxide, (b) Carbon dioxide + water, (c) Glucose, (d) Glucose and oxygen, 3. Which among the following is a balanced chemical equation?, (a) MnO2+4HCl→MnCl2+Cl2+2H2O, (b) Fe+H2O→Fe3O4+H2, (c) Zn+HCl→ZnCl2+H2, (d) 2KClO3→2KCl+H2, 4. What is the corresponding change in colour when iron nail is, dipped in the blue copper sulphate solution?, (a) Red, (b) White, (c) Green, (d) Black
Page 14 :
Oxidation in Daily Life, Corrosion, ▪ Metals are prone to corrosion., ▪ is a slow conversion of metals into some undesirable, compounds., ▪ occurs may be due to reaction with oxygen, gases,, acids etc., ▪ weakens the metal and makes it brittle and reduces, the tensile strength., Example:, When iron reacts with atmospheric oxygen and, moisture, a red layer is formed on the surface of the, iron, this process is known as Rusting., Methods of Preventing Corrosion, i. By coating the metal surface with oil, grease, paint,, varnish, ii. By galvanizing i.e. coating the surface of iron, objects with a thin layer of zinc., iii.By electroplating the metallic surface with less, reactive metal., iv.By alloying the various metals., ## corrosion can sometimes be advantageous., For e.g. Aluminium is a good conductor of electricity, and is used in high tension wires. When it is exposed to, air, it gets coated with a white protective layer of, aluminium oxide ( Al2O3), this layer prevents the, further corrosion of metal by moist air.
Page 15 :
Rancidity, When food containing fats and oils are exposed to the, atmosphere, the oxidation of fat and oil occurs, this is, known as Rancidity., , Methods to Prevent Rancidity, ▪ Store cooking oils from direct sunlight., ▪ Food should be placed at low temperature., ▪ Food should be kept in air tight container to prevent, its oxidation., ▪ By adding antioxidants food can be protected from, rancidity., ▪ Packing material should replace the air with nitrogen., ▪ Minimize the use of salts in fried foods.
Page 16 :
QUIZ, 1. The process of coating iron with zinc is called:, (a) Electroplating, (b) Polishing, (c) Galvanization, (d) Reduction, 2. Rancidity is due to:, (a) Reduction of oils and fats, (b) Oxidation of oils and fats, (c) Displacement of oil and fats, (d) Combination of oils and fats, 3. Identify the substance which is reduced in the given reaction, below?, PbS(s) + 4H2O2(aq) → PbSO4(s )+ 4H2O(l), (a) Hydrogen peroxide, (b) Lead sulphide, (c) Both Lead sulphide and Hydrogen peroxide, (d) Water, 4. Which one of the following is an example of displacement, reaction?, (a) Cl2+2KBr→2KCl+Br2, (b) 2K+I2→2Kl, (c) 2H2S+SO2→2H2O+3S, (d) CaO+H2O→Ca(OH)2