Page 1 :
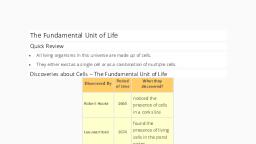
Q1.Who discovered cells, and how?, Answer.Robert Hooke, an English scientist, discovered cells in 1665. While examining a tiny, slice of cork under his self-designed microscope, he saw a honeycomb-like structure., Q2. Lysosomes are called suicide bags., Answer. Lysosomes contain powerful digestive enzymes made by RER that can digest all, organic matter. When a cell becomes damaged or turns old, the lysosomes burst and, release their contents, and the cell gets digested. Hence, they are also called 'Suicidal, Bags'., Q3. Cell is called the structural and functional unit of life., Answer. Every organism is made up of the same building blocks called the cells. They, perform all functions necessary for an organism's survival. Hence, they are called the, structural and functional unit of life., Q4. Mitochondria are called the powerhouse of the cell., Answer. Mitochondria oxidises the carbohydrates and fats derived from food with the help of, enzymes. Energy is released during this process. This energy is used by mitochondria for, the production of ATP. These molecules provide the energy for the cell to carry out its, various functions. Hence, mitochondria are called the powerhouse of the cell, Q5. What will happen if we put a plant and animal cell in:, (a) hypotonic solution:-Plant cells swell up when kept in hypotonic solution because plant, cells absorb large amounts of water. The vacuole gets completely filled with water and the, cytoplasm presses against the cell wall. But it does not burst due to the presence of the cell, wall. The cell wall can withstand dilute hypotonic media and thus it prevents bursting of cells., Therefore, plant cells withstand changes in environmental concentration much better than, animal cells which burst in such conditions., (b) hypertonic solution:-Both the animal and the plant cell will undergo plasmolysis. This, means that water will move out of the cells and as a result they will shrink. The shrinking of, the cell will result in the breaking down of plasma membrane, (c) isotonic solution:- Both the animal and the plant cell will remain unaffected due to no, net movement of water. This will occur because of balance of osmolarity in the cell and the, solution, Q6. What would happen if the plasma membrane ruptures or breaks down?, Answer. The rupture or breakdown of a cell's plasma membrane signals that the cell has, been injured, and in this case, the damaged cell's lysosomes may burst, causing the, digestive enzymes inside those lysosomes to eat their own cell. The cell will die as a result, of this., Q7. What would happen to the life of a cell if there was no Golgi apparatus?, Answer. The preservation, modification, and packaging of products in particles are all tasks, of the Golgi apparatus. All types of storage, modification, packaging and dispatch of, materials within and beyond the cell would be impossible if there was no Golgi apparatus for, the cell., Q8.Where do the lipids and proteins constituting the cell membrane get synthesised?, Answer.There are two types of endoplasmic reticulum:, (i). The smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) is in charge of producing the lipids that make, up the cell membrane., (ii). The ribosomes are housed in the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER), which is, responsible for the production of proteins that make up the cell membrane., Q9. How does an Amoeba obtain its food?, Answer. Amoeba feeds on planktonic bacteria that float in water. It grows artificial feet, or, pseudopodia, to encircle the meal and then catches it in a sac-like structure called the food, vacuole, within which food digestion occurs., Q10. What is osmosis?, Answer. The passage of water (solvent) through a semipermeable membrane from a, location of high-water concentration to a region of low water concentration is known as, osmosis. It can only happen in a liquid medium; it cannot happen in solids or gases. Plant, roots, for example, absorb water from the earth.
Page 2 :
Q11. Cytoplasm: The cytoplasm is the fluid content inside the plasma membrane. It also, contains many specialised cell organelles. Each of these organelles performs a specific, function for the cell., Q12. Cell Organelles: Every cell has a membrane around it to keep its content separate, from the external environment. The different components of a cell perform different functions, and these components are called cell organelles., Q13. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) (Channels, Network for transport): The ER is a large, network of membrane-bound tubes and sheets. It looks like long tubules or round or oblong, bags., There are two types of ER-Rough endoplasmic reticulum [RER] and smooth, endoplasmic reticulum [SER]. RER has particles called ribosomes attached to its surface., The ribosomes are the sites of protein manufacture., The SER helps in the manufacture of fat molecules, or lipids, important for cell function., Some of these proteins and lipids help in building the cell membrane. This process is known, as membrane biogenesis. Some other proteins and lipids function as enzymes and, hormones., The one function of ER is to serve as channels for the transport of materials between, various regions of the cytoplasm or between the cytoplasm and the nucleus. The ER also, functions as a cytoplasmic framework providing a surface for some of the biochemical, activities of the cell., Q14. Golgi Apparatus (Packaging): The golgi apparatus, first described by Camillo Golgi,, consists of a system of membrane-bound vesicles arranged approximately, parallel to each, other in stacks called cisterns., The material synthesised near the ER is packaged and dispatched to various targets, inside and outside the cell through the Golgi apparatus. It's functions include the storage,, modification and packages of products in vesicles. In some cases complex sugar may be, made from simple sugar in the Golgi apparatus. It is also involved in the formation of, lysosomes., Q15. Lysosomes [Suicide bags] (Cleanliness of cell): Lysosomes are a kind of waste, dispatch and disposal system of the cell. Lysosomes help to keep the cell clean by digesting, any foreign material as well as worn-out cell organelles. Foreign materials entering the cells, such as bacteria or food, as well as old organelles, end up in the lysosome, which break, them up into small pieces. They are able to do this because they contain powerful digestive, enzymes capable of breaking down all organic material. Under abnormal conditions, when, the cell gets damaged, lysosomes may burst and the enzymes digest their own cell., Therefore they are also known as “suicide bags”, Q16. Mitochondria (Powerhouse, Energy provider): Mitochondria are known as, powerhouses of the cell. The energy required for various chemical activities needed for life is, released by mitochondria in the form of ATP [Adenosine Triphosphate] molecules. ATP is, known as the energy currency of the cell. Mitochondria have two membrane coverings, instead of just one. The outer membrane is very porous while the inner membrane is deeply, folded. They are able to make some of their own protein., Q17. Plastids: Plastids are present only in plant cells. There are two types of plastids:, chromoplasts and leucoplasts. Chromoplasts are the coloured plastids present in leaves,, flowers and fruits. Plastids containing the pigment chlorophyll are known as chloroplasts., They are important for photosynthesis in plants. Chloroplasts also contain various yellow, or orange pigments in addition to chlorophyll. Leucoplasts are found primarily in organelles, in which materials such as starch, oils and protein granules are stored. The internal, organisation of the plastids consists of numerous membrane layers embedded in a material, called stroma. Plastids are similar to mitochondria in external structure. Plastids have their, own DNA and ribosomes., Q18. Vacuoles (Storage): Vacuoles are storage sacs for solid or liquid contents. Vacuoles, are small-sized in animal cells while plant cells have very large vacuoles [50% to 90% cell, volume].
Page 3 :
Q19. Plasma membrane is made up of which two components?, Answer. Plasma membrane is made up of lipids and proteins., Q20. What is a hypotonic solution?, Answer. A solution having solute concentration lower than that of the cell sap is called, hypotonic solution (Cell sap is a fluid found in the vacuoles), Q21. What is a hypertonic solution?, Answer. A solution having solute concentration higher than that of the cell sap is called, hypertonic solution., Q22. What is an isotonic solution?, Answer. A solution having solute concentration same as that of the cell sap is called isotonic, solution., Q23. Cell wall is made up of which component?, Answer. Cell wall is made up of cellulose., Q24. Give an example of a unicellular organism., Answer. Amoeba, Bacteria, Paramecium. (Any one), Q25. Role Of Glial Cells1.Renders physical strength to neurons 2.Nutrition supply and required oxygen for neurons, 3.Protection for neurons and cooling (insulator between neurons) 4.Eliminates dead neurons, 5.Destroys pathogens 6.Repairs neurons after brain injury, Q26. Cell size may range from a few micrometres to a metre. Support this statement, with the help of examples., Answer. Many cells are visible only under a microscope., Example: Mycoplasma is the smallest cell and longest cell in the human body is a nerve cell, or neuron., Q27. What is plasmolysis? What happens to a plasmolysed cell when it is placed in, water?, Answer. Shrinkage of protoplast from the cell wall in presence of hypertonic solution due to, exosmosis is known as plasmolysis. When a plasmolysed cell is placed in water, the, concentration of water in the outside medium is more than the concentration in the cell,, Hence, water moves inside the cell leading to its swelling, Q28. What is plasma membrane? What are its functions?, Answer. Plasma membrane, also called a cell membrane, is the outer covering of a cell that, separates its contents from the surrounding medium. It is made up of lipids and proteins, and, provides a mechanical barrier to protect the inner contents of the cell. It encloses the, nucleus and cytoplasm of the cell, Q29. What do you mean by a nucleoid?, Answer. In prokaryotes and lower organisms like bacteria, the nuclear region of the cell may, be poorly defined because of the absence of a nuclear membrane. Such an undefined and, incipient nucleic region containing only naked nucleic acids without any membrane covering, them is called a nucleoid., Q30. Which structure present in the nuclear region of a living cell bears genes?
Page 4 :
Answer. Chromosomes is the structure present in the nuclear region of a living cell which, bear gene, Q31. Why is the cell called the structural and functional unit of life?, Answer. Because shape and size of cells are related to specific functions they perform. Cells, constitute various components of plants and animals., Q32. Name the factor which decides the movement of water across the plasma, membrane., Answer. Amount of substance dissolved in water or solute concentration., Q33. Where are chromosomes present in the cell? What is their chemical, composition?, Answer. Chromosomes are present in the nucleus of a cell. Their chemical composition is of, DNA, RNA and proteins:, Q34. How many pairs of chromosomes are present in humans?, Answer. We have 23 pairs of chromosomes., Q35. What are the consequences of the, following conditions?, (i) A cell having higher water concentration than the surrounding medium., Answer. When a call possesses higher water concentration than the surrounding medium, then exosmosis occurs in the cell due to difference in concentration and cell shrinks., (ii) A cell having lower water concentration than the surrounding medium., Answer. When a cell has lower water concentration than the surrounding medium then, endosmosis occurs that results in the swelling of the cell., (iii) A cell having equal water concentration to its surrounding medium., Answer. A cell having equal water concentration to its surrounding medium will not show any, changes., Q36. Name the materials of which the cell membrane and cell wall are composed of., Answer. Cell wall is composed of cellulose and cell membrane is composed of lipids and, proteins:, Q37. Explain the terms:, (a) Endocytosis:- The flexibility of the cell membrane enables the cell to engulf food and, other materials from its external environment. Such a process is known as endocytosis., (b) Plasmolysis:- When a living plant cell loses water through osmosis, there is shrinkage or, contraction of the contents of the cell away from the cell wall. This phenomenon is known as, plasmolysis., Q38. What will happen if the organisation of a cell is damaged due to certain physical, or chemical reasons?, Answer. When the organisation of a cell gets damaged, lysosomes will burst and their, enzymes will eat up their own cell organelles. Therefore, lysosomes are also known as the, suicidal bags of the cell.