Page 1 :
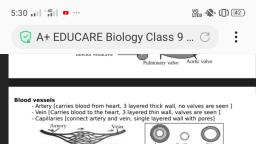
Class 9 Biology, , 3. Simple Nutrients into Cells, , Transport of material is carried out by the circulatory system (blood & lymph)., Transport in plants is carried out through vascular tissues (Xylem & Phloem)., * Example for an anticoagulant ? - EDTA (Ethylene Diamine Tetra Acetic acid)., When we add EDTA like anticoagulant to blood, the fluid part and cells separate., Human Blood, 55% Plasma (pale yellow coloured fluid), [90-92% water, 7-8% proteins (Albumin, Globulin, Fibrinogen), and other substances like fat, sugar, salts, hormones, urea etc.], 45% Blood cells, [Red blood corpuscles(RBC), White blood corpuscles (WBC),, Platelets], •, , Functions of plasma proteins ?, Albumin, :- Regulates blood pressure., Globulin, :- Helps in immunity., Fibrinogen :- Role in the coagulation (clotting) of blood., , RBC, , WBC, , Blood vessels, - Artery [carries blood from heart, 3 layered thick and elastic wall,, blood flows with speed and pressure], - Vein [Carries blood towards the heart, 3 layered thin wall, valves are seen, inside, blood flows with low speed and pressure], - Capillaries [connect artery and vein together, single layered wall with minute, pores, valves are absent, blood flows with low speed and pressure], , Artery, , Capillary, , Vein, , Human Heart, Position - placed in the thoracic cavity, behind sternum, in between the lungs., Size, - approximately about one's fist., Envelope – pericardium, a double membrane with pericardial fluid filled inside., Chambers – 4 (upper left atrium & right atrium and lower left & right ventricles), Arteries - pulmonary artery (deoxygenated blood), aorta (oxygenated blood)., Veins, - pulmonary vein (oxygenated), inferior-superior venacavas (deoxygtd.), Valves between chambers - Tricuspid valve (right) and Bicuspid valve (left)., Valves at the beginning of arteries - Aortic valve and pulmonary valve.
Page 2 :
Pace maker ? : The Sino Atrial Node (SA node), seen at the anterior part of atrium is, known as pacemaker, which initiates and regulates the heartbeat., Double circulation of blood: Our blood circulation is so called because of having,, * Pulmonary circulation (blood circulation between heart and lungs) RV, LA, * Systemic circulation (circulation between heart and various parts) LV, RA, ie, Same quantity of blood passes twice through the chambers of heart., Right, Atrium, , Lu, ng, s, , Left, Atrium, , Right, Ventricle, , LA, LV, , RA, RV, , Left, Ventricle, , [Remember, Those vessels that carry blood to atria, are veins and those vessels that carry blood from the, ventricles are arteries], Rasheed Odakkal, 9846626323, GVHSS Kondotty, odakkalblog, , * CO2 rich blood from body parts reaches into RA through Inferior-superior Venacavae,, while O2 rich blood from lungs reaches into LA through pulmonary veins., * When atria contract, blood reach into ventricles through valves (Tricuspid-Bicuspid)., * When ventricles contract, CO2 rich blood goes to the lungs through pulmonary artery, and at the same time O2 rich blood goes to the other body parts through aorta., Portal circulation ?, Circulation of blood from one organ to another organ, before reaching heart,, through the portal veins., Portal veins begin from one organ as capillaries and end in another organ as capillaries., [eg:- Hepatic portal system ie, From Intestine, Liver, Heart], Capillaries in the intestine, Heart, •, , Hepatic portal vein, Venacava, , Capillaries in the liver, , Hepatic vein, , Liver, , Why do nutrients reach the liver ?, To store glucose as glycogen, to release energy from fatty acids, to produce, cholesterol and to destroy pathogens if present., , Heart beat ? - One heart beat consists one contraction (systole) and relaxation, (diastole) of heart chambers., Normal heart beat is 72 per minute.., [0.8 seconds in between two consecutive beats], Blood Pressure, • The instrument used to measure blood pressure ?, Sphygmomanometer , Digital BP apparatus etc., •, , [ Normal BP is 120/80 mm.Hg, which means, the high pressure or systolic pressure is 120 mm.Hg, and the low pressure or diastolic pressure is 80 mm.Hg ], , Sphygmomanometer, , Digital BP, apparatus
Page 3 :
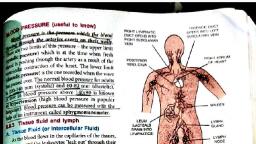
Hypertension : The condition in which the blood pressure increases above the normal rate., Reason- The unhealthy habits, such as excess use of salt and fat, smoking,, lack of exercise etc., Hypotension : The condition in which the blood pressure rate goes below the normal rate., Both the hypertension and hypotension may cause stroke or heart attack., Pulse ?, The wave like movements felt through out the wall of arteries, due to, the contraction and relaxation of heart chambers. (This is also 72 per minute), •, , How do cells get nutrients from blood ?, Cells receive nutrients and O2 from tissue fluid, which is formed from blood., When blood flows through capillaries, the fluid part of blood oozes into, intercellular spaces to form tissue fluid. RBCs, large proteins and platelets, are absent in tissue fluid., Nutrients in blood, Tissue fluid, Cells., , Lymph - The colourless fluid seen inside the lymph vessels., Liquid part of blood oozes out in to the intercellular spaces to form tissue fluid, and when tissue fluid enters the lymph capillaries, the fluid is said to be lymph., The lymphatic system :, Consists of lymph, lymph capillaries, lymph ducts, lymph nodes and spleen., (Lymph nodes are glands function as the centre of lymphocytes production., Spleen is the organ of destruction of germs and inactive RBCs), •, , Functions of lymphatic system ?, Transports nutrients, provides immunity, helps to bring the tissue fluid back to, blood and absorbs and transports fatty acids and glycerol from the intestine., , * How is fatty acid and glycerol reaches cell from the small intestine, through lymph ?, Fatty acids & glycerol are absorbed into lymph lacteals and flow through small and, large lymph ducts until reach into blood in the heart via venacava. When, blood flows, tissue fluid forms and cells get nutrients from it., Health of Heart :, • The factors that affect the health of our heart ?, Change in food habits (excess fatty and salty food), lack of exercise, consumption, of alcohol, smoking etc., •, , How the consumption of excess fatty food adversely affect the health of heart ?, Atherosclerosis, (fat deposition in the arterial wall), Inner diameter of artery reduces, wall becomes, rigid losing its elasticity and may rupture, Blood pressure increases, Formation of thrombus (thrombosis) resulting block, Thrombus in the coronary artery may leads to heart attack, , * September 29 – World Heart Day
Page 4 :
Vascular tissues in plants ?, , Xylem and phloem., , Xylem : Conduction of water and salts from roots, Phloem : Transport of food from leaves, Vascular bundles, Xylem, , Phloem, , * Transports water and minerals from * Carries food from leaves, in the form, roots to various parts of plant., of sucrose, to various parts of plant., * Made of Tracheids and Vessels, * Mainly Sieve tube (having pores to, (both are dead cells), connect cytoplasms) and, Companion cells ., Sieve tube, , Tracheid, , Companion cell, , Vessel, , Rasheed Odakkal 9846626323 GVHSS Kondotty, , •, , What are the forces that help the upward movement of water through the xylem ?, - Root pressure (a pressure exerted in roots due to osmosis), - Cohesion (tendency of water molecules to stick to themselves), - Adhesion (tendency of water molecules to stick with the walls of the vessels), - Transpiration pull in the leaves (a tendency to move water towards the cells, where water is lost by transpiration), •, , Transpiration ?, The expel of water out from leaves, through the stomata, by evaporation., Video class link of this chapter:, PART-1 : https://youtu.be/UWt47aTFBCk, PART-2 : https://youtu.be/x2a4wlOeJuI, PART-3 : https://youtu.be/wRNtBMCizGc, Here, only plant with leaves shows transpiration, , * Different forces that help for the upward movement of water through xylem., In roots : Osmosis and there by root pressure., In stem : Cohesion and adhesion of molecules., In leaves : Osmosis and transpiration pull due to evaporation.