Page 1 :
Let’s Recall, , L, , Il., , 196, , Solve the given double puzzle by rearranging the jumbled up words and find out the, final word., , DISPUTES, , JURISDICTION, , APPELLATE, , PLAINTIFF, , SUBORDINATE, , Final word: JUDICIARY, , Fill in the blanks., , 133 2.65 3. District Judge 4. Revenue 5. probate, State whether the following statements are true or false., , 1, False. Disputes involving the violation of Fundamental Rights come under the original, jurisdiction of the Supreme Court of India., , 2, False. Advising the President of India on constitutional matters comes under the, advisory jurisdiction of the Supreme Court of India., , 3. False. Judges of the High Court of a state are appointed by the President in consultation, with the Governor of that state and the Chief Justice of Supreme Court., , 4, False, The age limit for a judge of the stare High Court to stay in office is 62 years., 5. False, The highest District Court to try criminal cases is that of the Sessions Judge., Answer the following questions in brief., , 1. Judiciary is that organ of the government which administers justice and awards, punishments to those who break the laws., , 2. The highest court in India is the Supreme Court. It is located in New Delhi., , 3. The term ‘jurisdiction of a court’ is defined as the domain of responsibility of a legal, body, over which it has the authority to make legal decisions., , 4. The three types of subordinate courts in a district are the Civil Courts, the Criminal, Courts and the Revenue Courts., , 5. ‘The highest civil and criminal courts in a district are those of the District Judge and the, Sessions Judge respectively., , Answer the following questions in detail., , 1, The judiciary plays a crucial role in the functioning of a democracy. It performs the, following functions:, , * Itsettles disputes and punishes the guilty through the application of relevant laws., * It protects the rights of the citizens of India, including their Fundamental Rights., * It interprets the laws in conformity with the Constitution., , * It resolves disputes at different levels, i.e., between citizens; between citizens and the, government; between two or more state governments; between the centre and the, State government., , * It issues writs or formal written orders to the concerned organ of the government, or any other government institution that has violated the rights of the people, thus, ensuring that people enjoy their Fundamental Rights., , * Itcan declare any law passed by the central or the state government as, , i I
Page 2 :
4. The three types of subordinate courts in a district are the Civil Courts, the Criminal, Courts and the Revenue Courts., , 5. The highest civil and criminal courts in a district are those of the District Judge and the, Sessions Judge respectively., , Answer the following questions in detail., , 1, The judiciary plays a crucial role in the functioning of a democracy. It performs the, following functions:, , * It settles disputes and punishes the guilty through the application of relevant laws., * It protects the rights of the citizens of India, including their Fundamental Rights., * It interprets the laws in conformity with the Constitution., , + It resolves disputes at different levels, i.e., between citizens; between citizens and the, government; between two or more state governments; between the centre and the, state government., , * It issues writs or formal written orders to the concerned organ of the government, or any other government institution that has violated the rights of the people, thus, ensuring that people enjoy their Fundamental Rights., , * It can declare any law passed by the central or the state government as, unconstitutional, if it thinks that the law is not in conformity with the Constitution., , 2. It is important for the judiciary to function in an independent and impartial manner, So as to protect and ensure a citizen's rights. The independence and impartiality is, maintained though the following practices:, , * The Indian Constitution advocates separation of powers between the organs of, , government. This ensures that no single person performs both executive and judicial, functions., , * The procedure to remove a judge has been made very demanding. A judge of the, Supreme Court can be impeached only on grounds of proved misbehaviour or, incapacity., , 3. Original jurisdiction: The cases which are heard only by the Supreme Court fall under, its original jurisdiction. These include disputes involving the union government and the, states; and disputes involving the violation of Fundamental Rights., , Appellate jurisdiction: The Supreme Court can issue verdicts on appeals filed against the, judgments of the High Courts. These cases fall under its Appellate jurisdiction. These, include reviewing the judgements of the High Courts and giving its own decisions on, such judgments., , 4. India’s judicial system is like a pyramid with the Supreme Court at the top, followed by, the High Courts in the middle level and the lower or subordinate courts at the base or, lowest level.
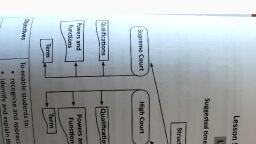
Page 3 :
‘The Supreme Court is located in New Delhi and it is the highest court in India. It is, also called the Apex Court. According co the Indian Constitution, the Supreme Court, is the guardian of the Constitution. All courts in India function under the direction and, control of the Supreme Court of india. If a citizen is not satisfied with the judgement, of a lower court, he/she can appeal to the higher court. Each state in India has a High, Court, which is the highest court in the state. Sometimes, one or more states can be, placed under one High Court, There are courts in the districts of a state as well. These, are subordinate to the High Court of the state. There are three types of subordinate, , courts in a disisict—the Civil Courts, the Criminal Courts and the Revenue Couns., , , , 5. Civil cases are different from criminal cases in the following ways:, , , , , , , , for damage suffered because of someone, 's fault, , , , , , Civil cases Criminal cases, cases relate to disputes regarding property | cases relate to the act or attempt of theft,, or inheritance, or the violation of a kidnapping, murder and other zypes of, contract, or a family issue involving crime, divorce and custody of children, plaintiff may ask a judge for compensation | the guilt or innocence of the accused is, , decided by a judge or a jury based on the, evidence presented during a trial