Page 1 :
Industries, Have you ever given a thought to the fact that the note, book you use for writing has come to you after a long, process of manufacturing. It started its life as part of a, tree. It was cut down and transported to the pulp mill., There the wood of the tree was processed and converted, into wood pulp. The wood pulp was mixed with chemicals, and finally changed into paper by machines. This paper, found its way to the press where ink made from chemicals, was used to print the lines on the pages. The pages were, then bound in the form of a note book, packed and sent to, the market for sale. Finally, it reached your hands., Journey begins..., , ...paper made..., ...recycle..., , Activity, Trace the journey, of your shirt from, a cotton field to, your wardrobe., , Secondary activities or manufacturing change, raw materials into products of more value to people. As, you have seen pulp was changed into paper and paper, into a note book. These represent the two stages of the, manufacturing process., The paper made from pulp and cloth made from, cotton have had value added to them at each stage of the, manufacturing process. In this way the finished product, has more value and utility than the raw material that it, is made from., Industry refers to an economic activity that is, concerned with production of goods, extraction of, minerals or the provision of services. Thus we have iron, and steel industry (production of goods), coal mining, industry (extraction of coal) and tourism industry, (service provider)., , Classification, , of, , Industries, , Industries can be classified on the basis of raw materials,, size and ownership., , 2015-16(19/01/2015)
Page 2 :
Raw Materials: Industries may be agro based, mineral, based, marine based and forest based depending on the, type of raw materials they use. Agro based industries, use plant and animal based products as their raw, materials. Food processing, vegetable oil, cotton textile,, dairy products and leather industries are examples of, agro-based industries. Mineral based industries are, primary industries that use mineral ores as their raw, materials. The products of these industries feed other, industries. Iron made from iron ore is the product of, mineral based industry. This is used as raw material for, the manufacture of a number of other products, such, as heavy machinery, building materials and railway, coaches. Marine based industries use products from the, sea and oceans as raw materials. Industries processing, sea food or manufacturing fish oil are some examples., Forest based industries utilise forest produce as raw, materials. The industries associated with forests are pulp, and paper, pharmaceuticals, furniture and buildings., , Activity, Give some, examples of agro, based industries., , Size: It refers to the amount of capital invested,, number of people employed and the volume of production., Based on size, industries can be classified into small, scale and large scale industries. Cottage or, household industries are a type of small scale, industry where the products are manufactured, by hand, by the artisans. Basket weaving,, pottery and other handicrafts are examples, of cottage industry. Small scale industries, use lesser amount of capital and technology, as compared to large scale industries that, produce large volumes of products. Investment, of capital is higher and the technology used, is superior in large scale industries. Silk, weaving and food processing industries are, small scale industries(Fig 5.1). Production of, Fig 5.1: Stages in food processing of, automobiles and heavy machinery are large, Gorgon nut (makhana), scale industries., Ownership: Industries can be classified into private, sector, state owned or public sector, joint sector and, cooperative sector. Private sector industries are owned, and operated by individuals or a group of individuals., The public sector industries are owned and operated by, the government, such as Hindustan Aeronautics Limited, Industries, , 51, , 2015-16(19/01/2015)
Page 3 :
Fig 5.2: Sudha dairy in, Co-operative sector, , and Steel Authority of India Limited. Joint sector, industries are owned and operated by the state, and individuals or a group of individuals. Maruti, Udyog Limited is an example of joint sector, industry. Co-operative sector industries are, owned and operated by the producers or suppliers, of raw materials, workers or both. Anand Milk, Union Limited and Sudha Dairy are a success, stories of a co-operative venture., , Factors Affecting Location, , Fig 5.3: Locational factors for industries, , of, , Industries, , The factors affecting the location, of industries are the availability of, raw material, land, water, labour,, power, capital, transport and market., Industries are situate d where some or, all of these factors are easily available., Sometimes, the government provides, incentives like subsidised power, lower, transport cost and other infrastructure, so that industries may be located in, backward areas. Industrialisation, often leads to development and growth, of towns and cities., , Industrial System, , Activity, Find out the, inputs, outputs, and processes, involved in the, manufacture of a, leather shoe., , An industrial system consists of inputs, processes and, outputs. The inputs are the raw materials, labour and, costs of land, transport, power and other infrastructure., The processes include a wide range of activities that, convert the raw material into finished products. The, outputs are the end product and the income earned, from it. In case of the textile industry the inputs may be, cotton, human labour, factory and transport cost. The, processes include ginning, spinning, weaving, dyeing, and printing. The output is the shirt you wear., , Industrial Regions, Industrial regions emerge when a number of industries, locate close to each other and share the benefits of, their closeness. Major industrial regions of the world, are eastern North America, western and central Europe,, eastern Europe and eastern Asia (Fig 5.4). Major, , 52, , Resources, , and, , Development, , 2015-16(19/01/2015)
Page 4 :
Fig 5.4: World’s Industrial Regions, , industrial regions tend to be located in the temperate, areas, near sea ports and especially near coal fields., India has several industrial regions like MumbaiPune cluster, Bangalore-Tamil Nadu region, Hugli region,, Ahmedabad-Baroda region, Chottanagpur industrial belt,, Vishakhapatnam-Guntur belt, Gurgaon-Delhi-Meerut, region and the Kollam-Thiruvanathapuram industrial, cluster., Industrial Disaster, In industries, accidents/disasters mainly occur due to technical, failure or irresponsible handling of hazardous material., One of the worst industrial disasters of all time occurred, in Bhopal on 3 December 1984 around 00:30 a.m. It was, a technological accident in which highly poisonous Methyl, Isocynate (MIC) gas along with Hydrogen Cyanide and other, reaction products leaked out of the pesticide factory of Union, Carbide. The official death toll was 3,598 in 1989. Thousands,, who survived still suffer from one or many ailments like blindness,, impaired immune system, gastrointestinal disorders etc., Union Carbide Factory, Industries, , 53, , 2015-16(19/01/2015)
Page 5 :
In another incident, on 23 December 2005, due to gas well, blowout in Gao Qiao, Chongging, China, 243 people died, 9,000 were, injured and 64,000 were evacuated. Many people died because they, were unable to run after the explosion. Those who could not escape, in time suffered burns to their eyes, skin and lungs from the gas., , Risk Reduction Measures, 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., , Densely populated residential areas should be separated far, away from the industrial areas., Rescue operation, People staying in the vicinity of industries should be aware of, in Gao Qiao, the storage of toxins or hazardous substances and their possible, effects in case if an accident occurs., Fire warning and fighting system should be improved., Storage capacity of toxic substances should be limited., Pollution dispersion qualities in the industries should be, improved., , Distribution Of Major Industries, Do you know?, Emerging, industries are also, known as ‘Sunrise, Industries’.These, include Information, technology,, Wellness,, Hospitality and, Knowledge., , The world’s major industries are the iron and steel, industry, the textile industry and the information, technology industry. The iron and steel and textile, industry are the older industries while information, technology is an emerging industry., The countries in which iron and steel industry is, located are Germany, USA, China, Japan and Russia., Textile industry is concentrated in India, Hong Kong,, South Korea, Japan and Taiwan. The major hubs of, Information technology industry are the Silicon valley, of Central California and the Bangalore region of India., , Iron and Steel Industry, Glossary, Smelting, It is the process, in which metals, are extracted, from their ores by, heating beyond, the melting point, , 54, , Resources, , and, , Like other industries iron and steel industry too, comprises various inputs, processes and outputs. This, is a feeder industry whose products are used as raw, material for other industries., The inputs for the industry include raw materials, such as iron ore, coal and limestone, along with labour,, capital, site and other infrastructure. The process of, converting iron ore into steel involves many stages., The raw material is put in the blast furnace where it, undergoes smelting (Fig 5.6). It is then refined. The, output obtained is steel which may be used by other, industries as raw material., , Development, , 2015-16(19/01/2015)
Page 6 :
8 tonnes of coal, , +, , 4 tonnes of, iron ore, , +, , 1 tonne of, limestone, , =, , 1 tonne of, steel, , Fig 5.5: Manufacturing of steel, , Steel is tough and it can easily be shaped, cut,, or made into wire. Special alloys of steel can be, made by adding small amounts of other metals, such as aluminium, nickel, and copper. Alloys give, steel unusual hardness, toughness, or ability to, resist rust., Steel is often called the backbone of modern, industry. Almost everything we use is either made, of iron or steel or has been made with tools and, machinery of these metals. Ships, trains, trucks,, and autos are made largely of steel. Even the safety, pins and the needles you use are made from steel., Oil wells are drilled with steel machinery. Steel, pipelines transport oil. Minerals are mined with, steel equipment. Farm machines are mostly steel., Large buildings have steel framework., Before 1800 A.D. iron and steel industry was, located where raw materials, power supply and, 2: The best location, running water were easily, from 1800 to 1950, available. Later the ideal, location for the industry was, near coal fields and close to, canals and railways. After, 1950, iron and steel industry, began to be located on large, areas of flat land near sea, ports. This is because by this, time steel works had become, very large and iron ore had, to be imported from overseas, (Fig 5.7)., In India, iron and steel, industry has developed taking, , Fig. 5.6: From iron ore to steel, in a blast furnace, 1: The best location, before 1800, , 3: The best location, since 1950, , Fig 5.7: The changing location of the iron and, steel industry, , Industries, , 55, , 2015-16(19/01/2015)
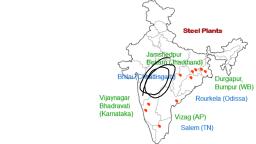
Page 8 :
Sketch, , Fig 5.9: Location of iron and steel industry in Jamshedpur, , Sakchi was chosen to set up the steel plant for, several reasons. This place was only 32 km away from, Kalimati station on the Bengal-Nagpur railway line. It, was close to the iron ore, coal and manganese deposits, as well as to Kolkata, which provided a large market., TISCO, gets coal from Jharia coalfields, and iron ore,, limestone, dolomite and manganese from Odisha and, Chhattisgarh. The Kharkai and Subarnarekha rivers, ensured sufficient water supply. Government initiatives, provided adequate capital for its later development., In Jamshedpur, several other industrial plants were, set up after TISCO. They produce chemicals, locomotive, parts, agricultural equipment, machinery, tinplate,, cable and wire., , Let’s do, With the help of, an atlas identify, some iron and, steel industries in, India and mark, their location on, an outline map of, India., , The development of the iron and steel industry, opened the doors to rapid industrial development in, India. Almost all sectors of the Indian industry depend, heavily on the iron and steel industry for their basic, infrastructure. The Indian iron and steel industry, consists of large integrated steel plants as well as mini, Industries, , 57, , 2015-16(19/01/2015)
Page 9 :
steel mills. It also includes secondary producers, rolling, mills and ancillary industries., , Do you know?, The names of Great, Lakes are Superior,, Huron, Ontario,, Michigan and Erie., Lake Superior is, the largest of these, five lakes. It lies, higher upstream, than others., , Pittsburgh : It is an important steel city of the United, States of America. The steel industry at Pittsburgh, enjoys locational advantages. Some of the raw material, such as coal is available locally, while the iron ore comes, from the iron mines at Minnesota, about 1500 km from, Pittsburgh. Between these mines and Pittsburgh is one, of the world’s best routes for shipping ore cheaply – the, famous Great Lakes waterway. Trains carry the ore, from the Great Lakes to the Pittsburgh area. The Ohio,, the Monogahela and Allegheny rivers provide adequate, water supply., Today, very few of the large steel mills are in Pittsburgh, itself. They are located in the valleys of the Monogahela, and Allegheny rivers above Pittsburgh and along the, Ohio River below it. Finished steel is transported to the, market by both land and water routes., The Pittsburgh area has many factories other than, steel mills. These use steel as their raw material to make, many different products such as railroad equipment,, heavy machinery and rails., , Cotton Textile Industry, Word Origin, The term ‘textile’, is derived from, the Latin word, texere which, means to weave., , Weaving cloth from yarn is an ancient art. Cotton,, wool, silk, jute, flax have been used for making cloth., The textile industry can be divided on the basis of raw, materials used in them. Fibres are the raw material of, textile industry. Fibres can be natural or man-made., Natural fibres are obtained from wool, silk, cotton, linen, and jute. Man made fibres include nylon, polyester,, acrylic and rayon., The cotton textile industry is one of the oldest, industries in the world. Till the industrial revolution in, the 18th century, cotton cloth was made using hand, spinning techniques (wheels) and looms. In 18th century, power looms facilitated the development of cotton textile, industry, first in Britain and later in other parts of the, world. Today India, China, Japan and the USA are, important producers of cotton textiles., , 58, , Resources, , and, , Development, , India has a glorious tradition of producing excellent, quality cotton textiles. Before the British rule, Indian, , 2015-16(19/01/2015)
Page 10 :
Fig 5.10: World : Major cotton textile manufacturing regions, , hand spun and hand woven cloth already had a, wide market. The Muslins of Dhaka, Chintzes of, Masulipatnam, Calicos of Calicut and Gold-wrought, cotton of Burhanpur, Surat and Vadodara were, known worldwide for their quality and design. But the, production of hand woven cotton textile was expensive, and time consuming. Hence, traditional cotton textile, industry could not face the competition from the new, textile mills of the West, which produced cheap and good, quality fabrics through mechanized industrial units., The first successful mechanized textile mill was, established in Mumbai in 1854. The warm, moist, climate, a port for importing machinery, availability, of raw material and skilled labour resulted in rapid, expansion of the industry in the region., , Do you know?, The first textile, mill in the country, was established at, Fort Gloster near, Kolkata in 1818, but it closed down, after some time., , Initially this industry flourished in the states of, Maharashtra and Gujarat because of favourable humid, climate. But today, humidity can be created artificially,, and raw cotton is a pure and not weight losing raw, material, so this industry has spread to other parts, Industries, , 59, , 2015-16(19/01/2015)
Page 11 :
Do you know?, About one-third of, the Indian textile, industry’s total, production is, exported., , Activity, Collect different, types of pieces, of cloth from a, tailor’s shop and, classify them, under cotton, silk,, synthetic and, woollen. Find out, the raw materials, used in their, manufacturing., , Let’s do, On an outline, map of the world, mark the places, which provide raw, material to cotton, textile industry of, Osaka, , 60, , Resources, , and, , Development, , of India. Coimbatore, Kanpur, Chennai, Ahmedabad,, Mumbai, Kolkata, Ludhiana, Puducherry and Panipat, are some of the other important centres., Ahmedabad : It is located in Gujarat on the banks, of the Sabarmati river. The first mill was established, in 1859. It soon became the second largest textile city, of India, after Mumbai. Ahmedabad was therefore often, referred to as the ‘Manchester of India’. Favourable, locational factors were responsible for the development, of the textile industry in Ahmedabad. Ahmedabad is, situated very close to cotton growing area. This ensures, easy availability of raw material. The climate is ideal, for spinning and weaving. The flat terrain and easy, availability of land is suitable for the establishment, of the mills. The densely populated states of Gujarat, and Maharashtra provide both skilled and semi-skilled, labour. Well developed road and railway network permits, easy transportation of textiles to different parts of the, country, thus providing easy access to the market., Mumbai port nearby facilitates import of machinery, and export of cotton textiles., But in the recent years, Ahmedabad textile mills have, been having some problems. Several textile mills have, closed down. This is primarily due to the emergence, of new textile centres in the country as well as nonupgradation of machines and technology in the mills of, Ahmedabad., Osaka : It is an important textile centre of Japan,, also known as the ‘Manchester of Japan’. The textile, industry developed in Osaka due to several geographical, factors. The extensive plain around Osaka ensured that, land was easily available for the growth of cotton mills., Warm humid climate is well suited to spinning and, weaving. The river Yodo provides sufficient water for, the mills. Labour is easily available. Location of port, facilitates import of raw cotton and for exporting textiles., The textile industry at Osaka depends completely upon, imported raw materials. Cotton is imported from Egypt,, India, China and USA. The finished product is mostly, exported and has a good market due to good quality, and low price. Though it is one of the important textile, cities in the country, of late, the cotton textile industry, of Osaka has been replaced by other industries, such as, , 2015-16(19/01/2015)
Page 12 :
iron and steel, machinery, shipbuilding, automobiles,, electrical equipment and cement., , Information Technology (IT), Imagine how much could be accomplished if companies, could operate on a twenty-four hour workday. Some, software companies in the United States of America and, in Bengaluru, India have joined hands to achieve this., There are many ways in which this form of shift work, across oceans. For example, two software professionals,, Danny in Silicon Valley, California and Smitha in, Bengaluru are working on a joint project. While Smitha, in Bengaluru sleeps, Danny in California is working. At, the end of his workday, he sends a message to, Smitha, updating his progress. When she arrives, at work in Bengaluru, a couple of hours later, she, notices that a message awaits her. She gets to, work on the project straight away. By the end of, her workday she relays the results of her efforts, back to California. By the way they communicate, and work together, it is as if they were sitting in, adjoining offices., The information technology industry deals, Fig 5.11: A View of an IT industry, in the storage, processing and distribution of, information. Today, this industry has become global., This is due to a series of technological, political, and, socio-economic events. The main factors guiding the, location of these industries are resource availability, cost, and infrastructure. The major hubs of the IT industry, Activity, are the Silicon Valley, California and Bengaluru, India., Bangalore has, Bengaluru is located on the Deccan Plateau from, where it gets the name ‘Silicon Plateau’. The city is, known for its mild climate throughout the year. Silicon, Valley, is a part of Santa Clara Valley, located next to, the Rocky Mountains of North America. The area has, temperate climate with the temperatures rarely dropping, below 0 degrees centigrade. The locational advantages, of the Silicon plateau, Bengaluru and Silicon Valley,, California are discussed on the next page. You may, notice the similarities between the two cities., There are other emerging information technology, hubs in metropolitan centres of India such as Mumbai,, , some important, public sector, industries, and research, institutions., Find out the, full forms of the, organisations, listed below., BEL, BHEL, HAL,, NAL, DRDO, ISRO,, ITI , IISc, NCBS, and UAS, , Industries, , 61, , 2015-16(19/01/2015)
Page 13 :
Do you know?, Why do high, technology, industries group, together?, • They can be, located near, main road/, highways for, easy access., • Firms can, benefit from, exchange of, knowledge., • Services and, facilities such, as roads, car, parks and waste, disposal can, be organised, efficiently., , Bengaluru has the largest number of educational, institutions and IT colleges in India., , The city was considered, dust free with low rents, and low cost of living., , The state government of Karnataka was, the first to announce an IT Policy in 1992., The city has the largest and, widest availability of skilled, managers with work experience., , Fig 5.12: Locational advantages, Silicon plateau - Bengaluru, , Close to some of the most advanced scientific, and technological centres in the world, Pleasant climate with an attractive, and a clean environment. Plenty of, space for development and future, expansion., Located close to major roads and airports, , Interesting Fact, Being Bangalored…, means to lose one’s, job to someone, in the city of, Bengaluru. A few, years ago many, IT jobs in the USA, were outsourced, to countries like, India where equally, skilled labour was, available at lower, salaries., , 62, , Resources, , and, , Good access to markets and, skilled work force, , Fig. 5.13: Locational advantages of, Silicon valley - California, , New Delhi, Hyderabad and Chennai. Other cities, such as Gurgaon, Pune, Thiruvanthapuram, Kochi, and Chandigarh are also important centres of the IT, industry. However, Bengaluru has always had a unique, advantage, as a city with highest availability of middle, and top management talent., , Development, , 2015-16(19/01/2015)
Page 14 :
Exercises, 1. Answer the following questions., (i) What is meant by the term ‘industry’?, (ii) Which are the main factors which influence the location of an industry?, (iii) Which industrty is often referred to as the backbone of modern industry, and why?, (iv) Why cotton textile industry rapidly expanded in Mumbai?, (v) What are the similarities between information technology industry in, Bengaluru and California?, 2. Tick the correct answer., (i) Silicon Valley is located in, (a) Bengaluru, , , (b) California, , , , (c) Ahmedabad, , (ii) Which one of the following industries is known as sunrise industry?, , , (a) Iron and steel indstury, , (b) Cotton textile, (c) Information technology, (iii) Which one of the following is a natural fibre?, (a) nylon, (b) jute, (c) acryclic, 3. Distinguish between the followings., (i) Agro-based and mineral based industry, (ii) Public sector and joint sector industry, 4. Give two examples of the following in the space provided :, (i) Raw Materials: _____________ and _____________________, (ii) End products: _______________ and _________________________, (iii) Tertiary Activities: ________________ and __________, (iv) Agro-based Industries: ____________ and ____________, (v) Cottage Industries: ___________ and ________________, (vi) Co-operatives: ______________________ and _____________, , Industries, , 63, , 2015-16(19/01/2015)
Page 15 :
5. Activity, How to identify a location for establishing an industry —, Divide your class into groups. Each group is a Board of Directors faced with, the problem of choosing a suitable site for an iron and steel plant of Developen, Dweep. A team of technical experts has submitted a report with notes and a map., The team considered access to iron ore, coal, water and limestone, as well as the, main market, sources of labour and port facilities. The team has suggested two, sites, X and Y. The Board of Directors has to take the final decision about where, to locate the steel plant., , 64, , •, , Read the report submitted by the team., , •, , Study the map to find out the distances of the resources from each site., , •, , Give each resource a ‘weight’ from 1 to 10, according to its importance. The, greater the ‘pull’ of the factor on the industry the higher the weight from 1 to 10., , •, , Complete the table on the next page., , •, , The site with the lowest total should be the most satisfactory site., , •, , Remember each group of directors can decide differently., , Resources, , and, , Development, , 2015-16(19/01/2015)
Page 16 :
Report, Factors/Resources affecting the location of a proposed Iron and Steel Plant, on Developen Dweep., • Iron ore: This is a very large deposit of low grade iron ore. Long distance, transportation of the ore would be uneconomic., • Coal: The only coalfield contains rich deposits of high grade coal. Transportation, of the coal is by railway, which is relatively cheap., • Limestone: This is widely available over the island, but the purest deposits are, in the Chuna Mountains., • Water: Both the tributaries of River Neel carry sufficient water to supply a, large iron and steel plant in all seasons. The sea water because of its high salt, content is unsuitable., • Market: It is expected that the chief market for the Plant’s products will be the, engineering works of Rajdhanipur. Transport costs for the products- mainly, small steel bars and light steel plates would be relatively low., • Labour supply: This will have to be recruited mainly from the unskilled workers, in the 3 fishing villages of Hil, Rah and Sing. It is expected that most workers, will commute daily from their present homes., • Port facilities: These are at present minimal. There is a good, deep natural, harbour at port Paschimpur developed to import metal alloys., , Resource, , Distance, from X, , Distance, from Y, , Weighting*, 1-10, , Distance X, weight for, site X, , Distance X, weight for, site Y, , Iron ore, Coal, Limestone, Water, Chief market, Labour supply, Total =, * the larger the pull, the higher the weighting, , Industries, , 65, , 2015-16(19/01/2015)