Page 1 :
A+ SOCIAL SCIENCE STD - VIII, UNIT: 10, , THE BLANKET OF THE EARTH, 1. What is atmosphere?, , , Atmosphere is the blanket of air surrounding the earth., , 2. Name the atmospheric gases which play a major role in maintaining the earth as a life supporting, planet., , , Oxygen and carbon dioxide, , 3. Plants are significant in regulating the amount of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere., Justify, , , , Through the process of photosynthesis that the plants gather energy for their growth., In this process plants intake carbon dioxide and give out oxygen., , 4. What are the major constituents of atmosphere?, , , Gases, moisture and dust particles, , , , Nitrogen, Oxygen, Argon, Carbon dioxide, Ozone, Neon, Helium, Krypton, Hydrogen,, , , , Nitrogen, , 5. List out the major gases in the atmosphere. Name the most abundant gas among them., Xenon, , 6. What is the importance of oxygen, carbon dioxide and nitrogen in the existence of life forms., , , Plants make use of Carbon dioxide for photosynthesis., , , , Plants make use of nitrogen for their growth through nitrogen fixation., , , , Man and other organisms make use of oxygen for respiration., , 7. Point out the factors that influence the amount of water in the atmosphere., , , Rate of evaporation will be high at places experiencing higher temperature. So the water, , , , The amount of water will be high in the atmosphere close to the surface water sources such as, , content in such places will be high., , oceans, rivers and other water bodies., , 8. What are the main sources of dust particles in the atmosphere?, , , Dust particles brought to the atmosphere by wind., , , , Ash formed by burning of meteors, , , , Dust particles erupted through volcanoes., , 9. Why dust particles are called Condensation nuclei?, , , As the fine dust particles in the atmosphere help in cloud formation they are called as, Condensation nuclei, , 10. What is the significance of dust particles in the atmosphere?, A+ BLOG- www.apluseducare.blogspot.com Whatsapp 9746544422, , Page 1
Page 2 :
A+ SOCIAL SCIENCE STD - VIII, , , Frequent condensation concentrating around the fine dust particles in the atmosphere help in, cloud formation, , 11. Why the mountaineers climbing Mount Everest take oxygen cylinders with them?, , , The gases (oxygen) get rarefied with increasing altitude., , , , Glass panes have the capacity to allow insolation to pass through them and check the, , , , Thus temperature is maintained within the buildings without fall. So feel hot., , 12. Why glass is largely used in the construction of buildings in cold countries?, terrestrial radiation., , 13. How the property of glass is made use of in agricultural sector in cold countries?, , , By preventing the terrestrial radiations the temperature required for the growth of plants is, retained inside such constructions, , 14. What are Green houses?, , , Greenhouses are glass buildings designed for the protection of plants against excessive cold, or heat, , 15. Write a short note on Greenhouse effect., , , Carbon dioxide, methane, ozone etc present in the atmosphere can permit insolation and, , , , These gases and water vapour present in the atmosphere absorb the terrestrial radiation and, , prevents terrestrial radiation., , retain the temperature of the atmosphere. This phenomenon is called Greenhouse effect., , 16. Give three examples of greenhouse gases., , , Carbon dioxide, methane, ozone, , , , The heat emitted from the earth's surface is trapped by the clouds and reflected back to the, , 17. Cloudy days are warmer than days with clear sky. Why?, , earth's surface in the cloudy day. So we feel warm, , 18. Write different sources of greenhouse gases., , , , Volcanic eruptions, decay of biological matter (natural means), Deforestation, burning of fossil fuels etc. (human activities), , 19. How deforestation leads to increase in the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere?, , , Trees remove some of the carbon dioxide from the atmosphere through photosynthesis and, , , , Deforestation reduces the removal component of this cycle, further increasing the carbon, , store that carbon in their tissues and in the soil., dioxide in the air, , 20. What is Global warming?, , , The increase in temperature in the atmosphere due to greenhouse gases referred as Global, warming., , A+ BLOG- www.apluseducare.blogspot.com Whatsapp 9746544422, , Page 2
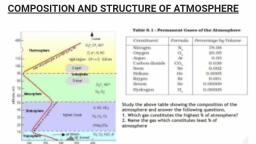
Page 3 :
A+ SOCIAL SCIENCE STD - VIII, 21. How Global warming becomes a threat to the life forms of the earth?, , , , , Sea level may rise as a result of melting of polar ice., , Destruction in the coastal ecosystem may lead to the problems such as food crisis, large scale, migration etc, , Leads to the depletion of many species of plants and animals in the ecosystem., , 22. Suggest a few alternatives to resist global warming., , , , Drive fuel-efficient vehicles, Protect trees and forests, , 23. What is Ozone layer? Write its significance, , , , As the ozone gas is concentrated in the upper atmosphere as a layer, it is called Ozone layer., It protects the life forms of the earth by absorbing the harmful ultraviolet rays from the sun., , 24. What is Ozonisation?, , , The single atom oxygen molecules react with ordinary oxygen molecules to form tri atomic, ozone gas. This process is called as Ozonisation., , 25. List out the negative impacts of ultraviolet rays., , , Climate change, , , , Skin cancer, , , , , , , , Blindness, , Premature ageing, , Stunted growth of plants, Crop failure, , Destruction in food chain, , 26. What are the sources of gases such as chlorofluorocarbons, halon etc.?, , , Refrigerators, air conditioners, different types of sprays, fire extinguishers, paints, etc., , , , Gases like chlorofluorocarbons, halon etc rising to the upper atmosphere react with, , , , Chlorine and bromine are capable to decay ozone molecules., , 27. How Ozone hole is formed?, , , , ultraviolet rays from the sun to form chlorine and bromine, , This depletion in the atmospheric ozone layer is called as Ozone hole., , 28. Which day is celebrated as World Ozone Day? Write its importance., , , , 16th September, , To create awareness on the need of conservation of ozone and to control the use of products, leading to ozone depletion, , 29. What is the difference between homo sphere and hetero sphere?, A+ BLOG- www.apluseducare.blogspot.com Whatsapp 9746544422, , Page 3
Page 4 :
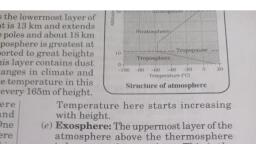
A+ SOCIAL SCIENCE STD - VIII, , , The composition of the atmosphere is somewhat uniform up to about 90 Kilometres from the, , , , Beyond 90 Km from the earth there is no uniformity in the gaseous composition. This part of, , surface of the earth. This part of the atmosphere is called homo sphere., the atmosphere is called as hetero sphere., , 30. Each layer in the atmosphere has its own indigenous characteristics. State the characteristics of each, layer in a tabular format., , , , , , , Troposphere, , Extends up to about , , Extends up to a, , surface of the earth, , Km from the earth, , 90 Km from the, , Lies close to the, , earth., , , , The height of the, , troposphere is more, , , , , this there is, , Km), , temperature with, , climatic, , , , place in this layer, , , , Temperature, decreases, , The zone of, transition-, , tropopause, , , , increase in, , Almost all the, , phenomena take, , stratosphere there is , , altitude. Beyond, , , , altitude., , Presence of ozone, , , , The zone of, transition -, , stratopause, , 50 to 80 Km, earth, , , , Temperature, , decreases with, altitude, , The lowest, , at the mesopause, The meteors on, reaching the, , Thermosphere, , Extends from about, 80 to 600 Km, Considerable, increase in, , temperature with, , , temperature of the, , mesosphere gets, , Allows the free, aircraft., , Extends from about , , atmosphere is felt, , layer, , movement of jet, , Mesosphere, , altitude from the, , Lower parts of the, , temperature with, , regions (about 18, , weather and, , height of about 50, , , , no change in, , in the equatorial, , , , Stratosphere, , altitude., , The lower part of, , the thermosphere is, known as, , , , ionosphere., , Ionosphere helps in, the transmission of, the radio waves, , burnt out due to, , , friction, , The zone of, transition -, , mesopause, , 31. What is Normal Lapse Rate?, , , In the troposphere the temperature decreases at a uniform rate of 1°Celcius for every 165, metres of altitude. This is called Normal Lapse Rate., , 32. What are Transition zones?, , , Transition zones are the parts of the atmosphere separating the major atmospheric layers., , , , In the lower parts of the stratosphere there is no change in temperature with altitude. This, , 33. What is an isothermal zone?, , zone is called isothermal zone, , A+ BLOG- www.apluseducare.blogspot.com Whatsapp 9746544422, , Page 4
Page 5 :
A+ SOCIAL SCIENCE STD - VIII, 34. Put a tick mark ( ✔) in the appropriate columns by identifying the atmospheric layer to which the, given statements are related., , Tropo, , , , Temperature increases with altitude, , , , Temperature decreases with altitude, , , , Climatic phenomena are taking place, , , , Jet air crafts can fly freely, , , , Protects the earth from meteorites, , , , Records the lowest temperature, , , , Ionisation occurs, , , , Reflects radio waves, , sphere, , Strato, , sphere, , ✔, ✔, , Meso, , sphere, ✔, , ✔, , Thero, , sphere, ✔, , ✔, ✔, , ✔, ✔, , 35. Flow chart, , Extended Activities:, , , , Make a poster about the importance of the atmosphere, , Illustrate the structure of the atmosphere in a chart paper., , Prepared by:, , PRIYA B, HST(SS), CSHSS, THRISSUR, , More Resources, Visit https://apluseducare.blogspot.com/, Telegram Group: https://t.me/joinchat/ELv60hbE_g9Hvimlp0s1BA, , A+ BLOG- www.apluseducare.blogspot.com Whatsapp 9746544422, , Page 5