Page 1 :
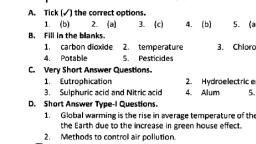
Chapter 18: Pollution, A., , Tick, 1., , B., , Fill, , ()the, (6), in the, , correct, 2., , of Air and Water, , options., , 3., , (a), , 4., , (c), , 1., , carbon dioxide, , 2., , temperature, , 4., , Potable, , 5., , Pesticides, , CVeryShort Answer, , 3., , D., , Sulphuric, , 2., , Short Answer, 1., , Global, , the, , acid, , and, , (i), , 5., , April,, , warming is the rise in averagetemperature ofthe atmosphere of, due to the increase in green house effect., , Earth, , air pollution., , We, , should use catalytic converters, harmful gases into harmless gases., We should grow more plants and, the, , in, , in, , automobiles which convert, to reduce carbon, , tress, , Sedimentation,loading, filtration, chlorination and storage, Toxic gases, smoke, carbon monoxide, oxides of sulphur and, are the natural sources of air pollution., , 5., , (), , Excessive, , (i), , Dead bodies should not, , use of fertilisers and, , Short Answer Type-ll, 1., , should be, , pesticides, off in, , disposed, , a river or, , nitrogen, , discouraged., , a lake., , Questions., , The main causes of water pollution, , ), , dioxide, , air., , 4., , 3., , 1985, , Questions., , Type-1, , concentration, , E, , energy, , Hydroelectric, , Alum, , Nitric acid, , Methods to control, , (), , carbons, , Chlorofluoro, , Questions., , Eutrophication, 3., , a), , 5., , (b), , blanks., , are:, , :The, , Industrial, , of, industrial, sewage, discharge, untreated, sewage, water bodies is one of the main cause of water, , into, , directly, pollution., , (i) Domestic sewage: Liquid wastes from domestic activities such, as kitchen and toilets are discharged, into rivers through sewage, systems causing water pollution., (ii), , Human activities:, lakes,, , wastes:, , (iv) Agricutural, , of pesticides, these, results, (v), , and, , human beings and animals in or near, , the water bodies., , modern, , In, , fertilisers, , agricufture,, , than, find, , Oil spill: Oil, , we use large, , quantities, , by the plants. Excess of, way to water bodles which, , required, , their, , inorganic, chemicals, in water pollution., , from huge tankers is one of the major cause, which affects the marine plants and animals., , spill, , water pollution, , of, , No, Mr. Mehta should not shift to petrol instead of CNG because, CNG is a cleaner fuel and is good for the environment., , 2., , (a), , 3., , (b) tis right to use catalytic converters in the cars because they convert, the harmful gases into harmless gases., Washing away of fertilisers into water bodies causes increased growth, of algae and other weeds, , E, , of, , Bathing, , rivers, etc. pollutes, , Long Answer Questions., Harmful effects of air, , 1, , () Carbon monoxide, , When inhaled, colourless, , and, , water bodies., , in, , on, , pollution, is, , a very, , health, , poisonous, , can, , in excess,, , it, , odourless, , gas., , kill, , a, , This, , is, , called, , gascomingout from automobles., without, as it is a, person, warning, , Oxides of sulphur (sulphur dioxide and sulphur, respiratory, problems and damage lungs., , (ii), , Oxides of nitrogen, , cause lung, , Fumes coming out of, nose and throat., , chemical, , bloom., , are as followsS:, , i), , (iv), , algal, , trioxide), , cause, , congestion., industries, , cause, , irritation in eyes,
Page 2 :
(v) Particles of lead oxide present, affect the brain of children., (vi) Particles, , 2., , in, , the automobile exhausts can, , of dust in air can cause bronchitis., , (a) The phenomenon due to which the Earth's atmospheretraps solar, radiation because, the presence of gases like carbon dioxide,, of, is called green, water vapour,methane and chlorofiuorocarbons, house effect. Carbon dioxide, methane are the green house gases., , (b) Global warming isthe risein average temperature, ofthe atmosphere, of the Earth due to the increase in greenhouse effect., Harmful effects of global warming are:, 0 Polar caps would melt and water would flow into the sea.Ifthe, level of water in the sea increases, low lying areas near coasts, , would be submerged., limate and rainfall pattern would change., 3. The steps involved in the purification of river or lake water, (i), , () Water from river or, tank., , Here,the, , first pumped into the sedimentation, is, large insoluble impurities settle down atthebottom., , Some light insoluble, , lake, , remain suspended., tank where, (i) Then water is passed to, loading, these suspended, impurities also settle down faster by theaddition ofsome chemicals, impurities, , like alum., (in), , Then, water is passed to filtration tank. Here it passes through, the layers of sand, gravel and charcoal, which filter the remaining, impurities., , (v) Then, , chlorine, , is, , added to the water, which, , present in the water., (v) The water is now fit and safe for drinking8, , kills, , all, , the germs