Page 1 :
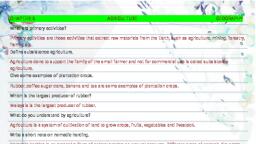
FUTURE BHUBANESWAR SCHOOL, Class VIII_Subject_Geography, Chapter 4 - Agriculture, , , , AGRICULTURE:PRIMARY ACTIVITY, THREE TYPES OF ECONOMIC ACTIVITIES, , , , , , , , , , , , , , PRIMARY SECONDARY TERTIARY, , , , , , , , , , , , Extraction and Processing of Supports primary and, production of “| the resources | => secondary sector, natural resources, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , E.g: Plant-Fruits —_— Finished product- Jam, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , TYPES OF FARMING, I, SUBSISTENCE COMMERCIAL, FARMING FARMING, INTENSIVE PRIMITIVE COMMERCIAL MIXED | |PLANTATIONS, SUBSISTENCE SUBSISTENCE GRAIN FARMING, t FARMING, I 1, SHIFTING NOMADIC, , CULTIVATION) | CULTIVATION, , , , , , , , , , , , , , Classification of different types of culture related to farming., , , , , , FARMING, , [AGRICULTURE] [SERICULTURE] [PISCICULTURE] [VITICULTURE] [HORTICULTURE, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , 1. What is agriculture?, Ans: Agriculture is a primary activity. It is the science and art of cultivation on the soil, raising, crops and rearing of livestock., , 2. Mention the factors influencing agriculture., , Ans: Factors influencing agriculture include:, , a) Climatic Conditions: Temperature and the amount of rainfall a place gets arethe, important determining factors. Certain crops need hot and wet climates to grow (like rice),, while certain crops grow in drier cooler climates (like wheat). Hence, temperature and, rainfall are important for the growth of plants.
Page 2 :
b) Nature of Soil: Soil provides food and nutrients to the plants. The kind of soil found in a, place affects the kind of crops grown there. Clayey soil retains water, which is suitable, for crops like rice and cotton. Fertile alluvial soil is ideal for agriculture and supports, most kind of crops. River banks which have deposits of alluvial soil are the most heavily, cultivated areas around the world. Sandy soils which allow water to seep through rapidly, are more suited to grow crops like groundnut and millets., , c) Relief: Flat land like plains, valleys, flat top of plateaus and deltas are bettersuited for, agriculture than mountainous terrain. Hilly areas are more suited for cattle rearing, and for, crops which need well drained soils like tea and coffee., , d) Economic Factors: Transport, loans for farmers, market are essential constituents of, economic factors., , e) Other Factors: Availability of irrigational facilities, size of land holdingsand nearness, of land also affects the nature of agriculture., , 3. What is shifting cultivation? What are its disadvantages?, , Ans: Shifting cultivation is the form of agriculture in which a plot of land is cleared by felling, , of trees and burning them. The ashes are then mixed with soil and crops are grown. After, sometimes the land is abandoned and the farmers move to a different place., , It has several disadvantages. It involves deforestation, pollutes the air, contributes towards global, warming, natural habitat of wildlife is destroyed., , 4. What is plantation agriculture?, , Ans: Plantation agriculture is a type of commercial farming where only a single crop like tea,, coffee, sugarcane, cashew, rubber, banana or cotton is grown. Large amount of labour and, capital is required. The produce may be processed in the farm or nearby factories., , 5. Name the fibre crops and mention the climatic conditions required fortheir growth., Ans: The major fibre crops are jute, flax and cotton grown in India and other parts of the world., Climatic conditions required for their growth are:, e Jute and flax require high temperature, heavy rainfall and humid climate. They grow, , well in fertile alluvial soil of the flood plains., ¢ Cotton needs high temperature, light rainfall, bright sunshine and 210 frost free days., , Black soil and alluvial soil are best for their growth., , 6. What are the characteristics of commercial farming?, Ans: It is a type of farming in which cultivation is practised for the purpose of sale. Following are, the characteristics of commercial farming., a) The cultivated area and the amount of capital are very large., b) Most of the farming practices involve machines., c) Commercial farming includes commercial grain farming, mixed farmingand, plantation agriculture., , 7. What are the physical conditions required for cultivation of rice?, Ans: The physical conditions required for rice cultivation are high temperature, high humidity, and rainfall. Alluvial soil and clayey soil, which can retain water, are the best for rice.
Page 3 :
8. Distinguish between:, a) Food Crops and Cash Crops, Food Crops, (i) Crops which are grown for the, consumption or subsistence., (ii) Food crops provide food for, people of the country., , (iii) They primarily satisfy the need of, people and surplus is exported., , (iv) Wheat, rice, barley, etc., , b) Primary and Tertiary Activities, Primary Activities, , (i) Activities concerned with collecting, or making available materials, provided by nature are called, primary activities., , (ii) Primary activities mostly require, human capital for its production., , (iii) Mining, farming, fishing are the, of primary activities., , c) Subsistence farming and Intensive Farming, , Subsistence Farming, (i) Farming practices in which crops are, for local consumption is, called subsistence farming., , (ii) In this type of farming, farms are small, , mainly food crops are grown, such as rice and wheat., , (iii) All types of manures like household, waste water, animal droppings,, green manure and a little of chemical, fertilisers, are applied to get more, production., , Cash Crops, , (i) Crops are grown for commercial, purposes or for selling., , (ii) Cash crops support the country the, economically and bring foreign, exchange., , (iii) They are produced for export the, purposes and as raw materials, for local industries., , (iv) Cotton, jute, coffee, tea,, sugarcane, etc., , Tertiary Activities, (i) Activities which provide service, to sectors like primary and secondary, sectors are called tertiary activities., , (ii) They are assorted for running, modern industries efficiently in, a big way., (iii) Banking, transport, trade, examples, advertising, etc are examples of, tertiary activities., , Intensive Farming, , (i) Farming practices which involves grown, , great use of man power in a small, patch of land is called intensive, farming., , (ii) Intensive farming has also small and, , land holding but is practised in a, densely populated areas., , (iii) Intensive farming implies, introduction of machinery,, increased use of chemical fertilisers,, high yielding variety(HYV) seeds,, pesticides, insecticides for more, production.
Page 4 :
d) Subsistence Farming and Commercial Farming, , Subsistence Farming Commercial Farming, i) Farming practices in which crops are i) Farming practices in which goods, cultivated for local consumption. produced are mainly for the market, for sale., ii) Farms are small and food crops are ii) Farms are larger and cash crops are cultivated, such as rice and wheat. cultivated such as cotton, sugarcane, jute., iii) Old tools and implements are iii) Modern and scientific implements are, used by the farmers. used and there are proper irrigation, facilities., , 9. Tick the correct answer., i) Horticulture means growing fruits and vegetables., ii) Golden fibre refers to jute., iii) Leading producers of coffee: - Brazil, 10. Give reasons., i. In India agriculture is a primary activity., Ans: In India agriculture is a primary activity because:, ¢ Agriculture is the source of basic necessity of food grains., e Agriculture includes growing of crops, fruits, vegetables, flowers and rearing of, livestock., ¢ Two-thirds of India’s population is engaged in this activity directly or indirectly., © It is also a primary activity for people in rural areas and India has very high rural, population., e A good amount of national income comes from agriculture., , ii) Different crops are grown in different regions., , Ans: Different crops are grown in different regions because growing crops depend upon the, geographical conditions, demand of produce, labour and level of technology. Nature of, topography, types of soil, climatic conditions also play an important role in selection of crops to, be grown in a particular area., , 11. Activity, , a) On an outline map of the world, locate the region which practise, , i) Intensive Agriculture, , ii) Horticulture, , iii) Dairy farming, , iv) Cotton and jute producing countries, , v) Sugarcane and sugar beet producing areas, , vi) Rice and wheat producing areas, , vii) Tea and coffee producing areas, , b) Collect seeds of wheat, rice, jowar, bajra, ragi, maize, oilseeds and pulses. Discuss, the geographical conditions necessary for growth of each crop., , c) Find out the difference between the farms in USA and India.