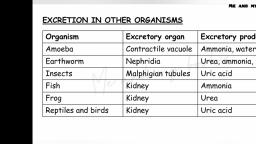
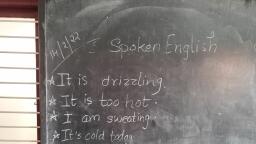Page 1 :
J.au..,_,, , 1, , u•u, , •••• v•--•-•- - v ••u1-• av •-• n.va ■ ••n"9J, , rad all sch•• relllld •ocu111nts carlfully., 1 \..I U\. I V I I.Jo, , A, , Budding, This is a method of asexual reproduction, seen in Hydra, Yeast etc. The buds, formed from the parent body detaches, from it when mature and develop into a, ., new organism., Binary fission, Binary fission is seen in prokaryotes., Existing cell divides to form 2 new cells. In, favorable conditions, bacteria-like, organisms reproduce by binary fission, Spore formation, This type of asexual reproduction is seen, mainly in fungus. Spores are microscopic, cells that can survive unfavourable, conditions and develop into new, organism on the return of favourable, season.
Page 2 :
ll'JU&Ual I, , uau, , ••••••u.•-•- -, , v, , • • - , - • • - - - • ---• • ·---11, , rad all sch•• 19lllecl •ocu11IIIII carlfully., , A, , ~mbryo., Indicators (Text Book Page No:200), Questions 1., Formation of male gametes, Answer:, After the pollination pollen tube grows, towards the ovary. Simultaneously, generative nucleus in the pollen grain, divides at the pollen tube and two, sperms are formed ., , HSSLive.Guru, Questions 2., Formation of embryo, Answer:, One of the sperms fuses with the ovum, and forms the zygote. This process is, called fertilization ., Questions 3., Formation of endosperm and its function
Page 3 :
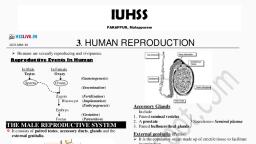
mu.-,, , 1, , u•u ••••v•-•-•- - v ••111-• av •-• n.v• ••n.--,, ■, , rad 111 sch•• rellled •ocu111nts carlfully., , Prostate gland, Secretes a fluid that contains factors, required for the movement and, nourishment of sperms., Penis, Deposits sperms into vagina, Testis, Produces sperms and male hormones., Sperm, Sperm is motile. It has a head, middle, piece and tail. Mitochondria present in, the middle piece provides energy for, movement. In the head, nucleus, containing paternal chromosomes are, present.
Page 4 :
1, , ,, , -J'\.. l ll. ,, , Indicators (Text Book Page No:201), Questions 4., Characteristics of sperms, Answer:, Sperms:- Sperms are motile. It has a, head, middle piece and tail. Mitochondria, present in the middle piece provide, energy for movement. In the head,, nucleus containing paternal, chromosomes is present., Questions 5., Location of testes an,d the production of, sperms, Answer:, , Testis are found in the scrotal sac outside, abdominal cavity. Sperms are produced, in th1e testis.
Page 5 :
mu..,..,, , 1, , u•u •••• .. • . . • - • - -, , .., , ••u1-• •v •-• ....... • ••n--,, , r•d 111 sch•• related tlocu11enb carlfully., A, , (Juestions 6., Importance of glands, Answer:, Sperms reach the penis along with the, fluid produced by accessory glands and, they are secreted to outside. Secretions, provide a medium for the movement of, sperms and nourishment, Female Reproductive System, Ovaries, Oviduct, Uterus, Endometrium,, Vagina, etc., are the parts of female, reproductive system., Ovary - Produces Ovum and female, hormones., Oviduct - Fertilization takes place in, oviduct., Uterus - Foetus completes its, development in uterus., Endometrium - Inner layer of Uterus., Foetus attach the endometrial wall., Vagina - Uterus opens out through, Vagina. Sperms are de osited here.
Page 6 :
l-ftU...UI, , I, , u•u, , 111•v•--•-•- -, , v, , ••u1-•, , av • - • n.va, , ■, , ••n...-,, , rad all sch•• rellled •ocu111nts carlfully., A, , Ovum, Ovum is larger than sperms. They are, non-motile. There are specified, membranes outside the cell membrane, of ovum., Indicators (Text Book Page No:202), Questions 7., Characteristics of ovum, Answer:, Ovum is larger than sperms. They are, non-motile. There are specified, membranes outside the cell membrane, of ovum., Questions 8., Function of ovary, Answer:, Produces ovum and female hormones., Questions 9.
Page 7 :
Size, , Motility, , KSSLM.Qiru, , Morphology, , Answer:, , Characteristics Sperm, , ovum, , Larger, , Size, , Movement, (motility), , Morphology, , Microscopic, , cells, , than, , sperms, , yes, , No, , Parts Ii ke, , Specialized, , head,, , protective, ., , middle, , coverings, , piece and, , Outside, , tail are, , the Cell, , present, , membrane
Page 8 :
Placenta, It is the part that connects embryo with, the endometrium. Oxygen and nutrients, are supplied to the foetus through the, umbilical cord formed from the placenta., Waste materials from the foetus are also, eliminated through placenta., Questions 10., Completing the table (Text Book Page, NO:204), Function, , Umbilical cord, Amnion, , Answer:, , Part, , Function, , Endometrium, , Attachment of Embryo
Page 9 :
Answer:, , Part, , Function, , Endometrium, , Attachment of Embryo, , Uterus, , Complete development, of foetus., Provides oxygen and, , Placenta, , nourishment to the, foetus. Rem- aves, wastes., Connects foetus with, , aves wastes., , mother. Oxygen and, nutrients are carried, through umbilical cord., Amniotic fluids inside, amnion present, , Amnion, , dehydration of focus, and protects from, external shocks
Page 10 :
Menstruation, With the onset of ovulation, there are, certain preparations in the uterus to, facilitate embryonic development., Endometrium becomes thickened, and, more capillary are formed. But if, fertilization does not take place the newly, formed tissues disintegrate and peel off, from the uterine walll. These get, eliminated to outside along with blood, and mu.cus through vagina. This process, is called menstruation., Ferti Iizati on, Fertilization is the process of fusion of, , ovum, that releases from the ovary with, the sperm in the oviduct.
Page 11 :
Questions 3., Formation of endosperm and its function, Answer:, The second sperm fuses with the polar, nucleus in the ovary and forms the, endosperm. Zygote develops into embryo, and endosperrm becomes the stored food, for the growth of embryo., Male Reproductive system, The main parts of male reproductive, system are Vas deferens, prostate gland,, penis, testis etc., Vas deferens, Carries sperms from testis to urinary, tract.
Page 12 :
Pol Ii nation, Ferti Iizati on, Flowers are the sex organs in plants., Pollination is the process of transfer of, pollen grains to the stigma of the flower., After pollination pollen tube grows, towards the ovary. Simultaneously, generative nucleus in the pollen grain, divides at the pollen tube and two, sperms are formed., One of the sperms fuses with the ovum, and forms the zygote. This process is, called fertilization. The second sperm, fuses with the polar nucleus in the ovary, and forms the endosperm. Zygote, develops into embryo and endosperm, becomes the stored food for the growth, of embryo.