Page 1 :
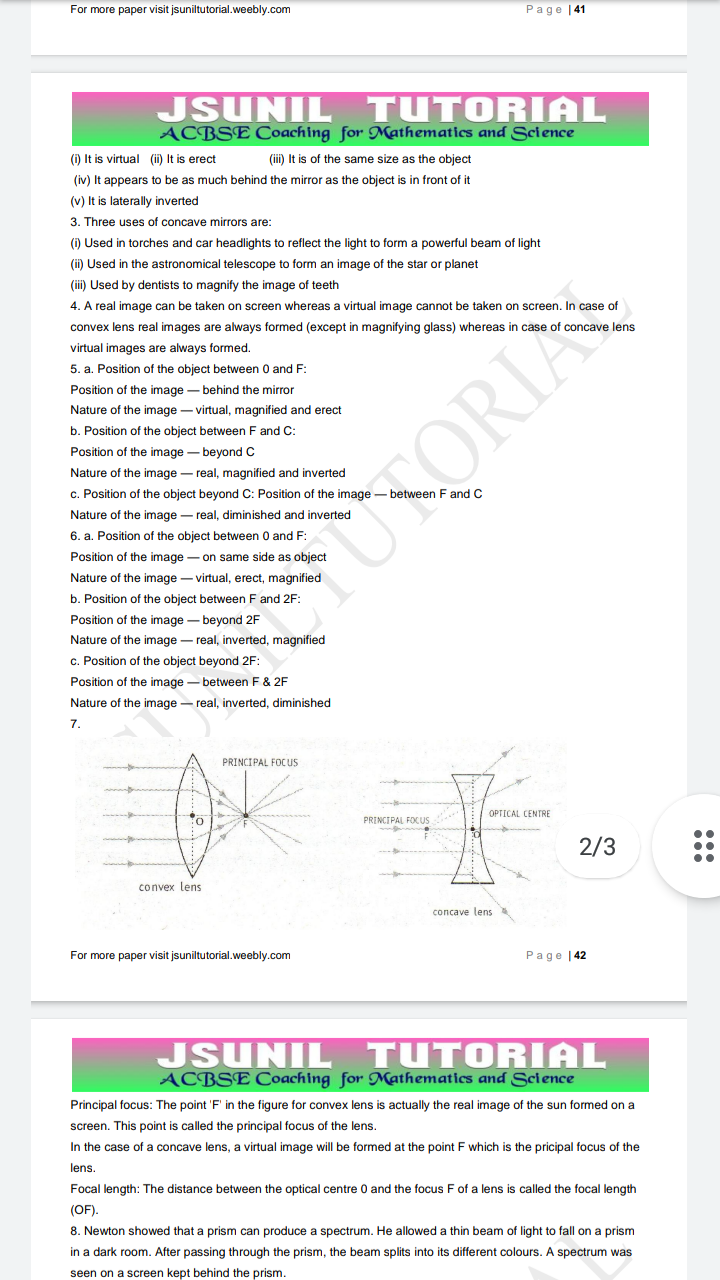
For more paper visit jsuniltutorial. weebly.com Page [41, , JSUNIL TUTORIAL, , , , , , (0 Itis virtual (i) tis erect (ii) Itis of the same size as the object, (iv) Itappears to be as much behind the mirror as the object isin front of it, , () itis laterally inverted, , 3. Three uses of concave mirrors are:, , ( Used in torches and car headlights to reflect the light to form a powerful beam of light, i) Used in the astronomical telescope to form an image of the star or planet,, , Used by dentists to magnify the image of teeth, , 4. Areal, ‘convex lens real images are aways formed (except in magnifying glass) whereas in case of concave lens, virtual images are always formed., , 5. a. Position ofthe object between 0 and F:, , Position of the image — behind the, Nature of the image — virtual, magnified and erect, , bb. Position of the object between F and C:, , Position of the image — beyond C, , Nature of the image — real, magnified and inverted, , «. Position of the object beyond C: Position of the image — between F and C, Nature of the image — real, diminished and inverted, , 6. a. Position of the object between 0 and F:, , Position of the image — on same side as object, , Nature of the image — virtual, erect, magnified, , ». Position of the object between F and 2F:, , Position of the image — beyond 2F, , Nature of the image — real, inverted, magnified, , «. Position of the object beyond 2F:, , Position of the image — between F & 2F, , Nature of the image — real, inverted, diminished, , , , , , 1age can be taken on screen whereas a virtual image cannot be taken on screen. In case of, , , , ror, , , , 7., ole A PRINCIPAL FOCUS *, : x roca us \ ities, anbee w ?, - 2/3, conver lens, concave lens, For more paper visit sunitutorial.weebly.com page |az, , JSUNIL TUTORIAL, , , , Principal focus: The point Fin the figure for convex lens is actually the eal image ofthe sun formed on @, screen. Ths point is called the principal focus ofthe lens., , In the case of a concave lens, a vual image willbe formed at he point F whichis the prcipal focus of the, lens., , Focal length: The distance between the optical centre 0 and the focus F ofa lens is called the focal length, (oF)., , ‘8 Newton showed that a prism can produce a spectrum. He allowed a thin beam of ight ofall on a prism, , in a dark room. Atte passing through the prism, the beam spits into its diferent colours. A spectrum was, , ‘seen on a screen kept behind the prism.
 Learn better on this topic
Learn better on this topic










































 Learn better on this topic
Learn better on this topic









