Page 1 :
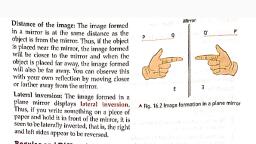
7th_ch-16 light_., , JSUNIL TUTORIAL, , , , Class 7% Living science solution 2017-18 Chapter 16. LIGHT, , , , P. 178 Oral Questions For Formative Assessment, 1.No 2.virtualimage 3.allbutE 4. 90°--the angle between the mirror and the incident ray, Page 182 Oral Questions For Formative Assessment, , 1. outwards 2. the rays meet (converge) at a point called the Principal Focus (F) after reflection, , 3. they diverge after reflection, , 4. No, the image is real forall other positions except when the object is between F and P in case of, ‘concave mirror., , 5. concave mirror, , 6. Convex because it forms smaller images and hence can be used to view a much larger area, , P 185 Oral Questions For Formative Assessment, , 1. yes, , 2. they will verge, , ‘3. they converge at a single point called the Principal Focus, , 4. This point lies at the centre of the lens and is called the optical centre of the lens., , 5. convex, , 66. No, there are seven colours but they appear as one, that is, white as our eyes can not distinguish them, separately., , P 186 For Formative and Summative Assessment, , Atd.2d 3c 4b Sb 6b 7d Be Sa 106, , B.1.false 2 false B.behind —4.focus —S. concave 6. true 7. concave, 8. converges 9. thick lens 10.at2F 11. false. 12. prism, , (C. 1. The angle formed by the ray of light or incident ray and the normal drawn at the point of incidence to, the mirror surface is called the angle of incidence of that ray of light., , 2. The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection., , '3. The image which can be formed on a screen is called a real image., , 4. In the image formed by a plane mirror, there is an interchange of left and right. Ths is called lateral, inversion., , ‘5. Because a convex mirror forms smaller images of objects, it can be used to view a much larger area than, ‘would be possible with a plane mirror., , 6. A convex lens bends all parallel rays passing through it inwards to meet or converge at a point called the, focus. Thus, iis said to have a real focus. A concave lens makes spread all parallel rays away or diverge, and it appears as if they were coming from a point called the focus. Thus, it is said to have a virtual focus., 7. The pattem formed by the seven colours of ordinary white light is called a spectrum., , '8. The convex lens forms a virtual image when the object is between 0 and F. Bigger than the object., , D. 1. see diagram, , 2. The characteristics of the image formed by a plane mirror are: ., For more paper visit jsunitutorial weebly.com Page [a, , JSUNIL TUTORIAL, , , , () Itis virtual (i) Itis erect (ii) Itis of the same size as the object, (iv) It appears to be as much behind the mirror as the object is in front of it, (v)Itis laterally inverted, , UF [al] tl 76% fii 9:35 a.m.
 Learn better on this topic
Learn better on this topic











































 Learn better on this topic
Learn better on this topic









