Page 1 :
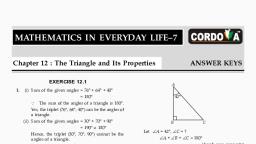
MATHEMATICS IN EVERYDAY LIFE–7, ANSWER KEYS, , Chapter 12 : The Triangle and Its Properties, EXERCISE 12.1, (i) Sum of the given angles = 76° + 64° + 40°, = 180°, The sum of the angles of a triangle is 180°., Yes, the triplet (76°, 64°, 40°) can be the angles of, a triangle., (ii) Sum of the given angles = 30° + 70° + 90°, = 190° 180°, Hence, the triplet (30°, 70°, 90°) cannot be the, angles of a triangle., (iii) Sum of the given angles = 56° + 62° + 62°, = 180°, Hence, the triplet (56°, 62°, 62°) can be the angles, of a triangle., (iv) Sum of the given angles = 20° + 148° + 30°, = 198° 180°, Hence, the triplet (20°, 148°, 30°) cannot be the, angles of a triangle., 2. Let A, B and C be the three angles of a triangle., Let A = 60°, B = 75°, C = ?, Sum of the angles of a triangle is 180°., , A + B + C = 180°, , 60° + 75° + C = 180°, , 135° + C = 180°, , C = 180° – 135°, , C = 45°, Hence, the third angle is 45°., 3. Let the third angle be x., Then, other two equal angles are 2x each., , 2x + 2x + x = 180°, ( Sum of the angles of a triangle is 180°), , 5x = 180°, , A, , 1., , 180, = 36°, 5, Hence, the angles of the triangle are 72°, 72° and 36°., 4. Let ABC be a right angled triangle, right angle at B., B = 90°, , , 42°, , B, , C, , Let A = 42°, C = ?, A + B + C = 180°, (Angle sum property), , 42° + 90° + C = 180°, , 132° + C = 180°, , C = 180° – 132°, , C = 48°, Hence, the other acute angle is 48°., 5. Let all the three angles of a triangle be x., , x + x + x = 180°, (Angle sum property), , x = 180°, 180, = 60°, 3, Hence, the measure of each angle is 60°., , , , 6., , x=, , (i), , C, , 40°, A, , D, , B, , In right angled triangle ABC, C = 90°, BAC + ACB + CBA = 180°, , , BAC + 90° + 40° = 180°, , , , BAC = 180° – 130° = 50°, , Hence,, , BAC = 50, , x=, , (ii) In ADC,, , , CAD = BAC, CAD = 50°, D = 90°, , Mathematics In Everyday Life-7, , 1
Page 3 :
EXERCISE 12.2, 1. Let interior opposite angles of a triangle be 2x and, 3x. Therefore,, Exterior angle = sum of interior opposite angles of triangle, A, , 120° = 2x + 3x, , , 5x = 120°, , , , x=, , ext. A = ABC + ACB, , …(i), , ext. B = BAC + ACB, , …(ii), , ext. C = BAC + ABC, , …(iii), , Adding equations (i), (ii) and (iii), we get,, ext. A + ext. B + ext. C, = 2ABC + 2ACB + 2BAC, , 48°, , 120, = 24°, 5, , 72°, , = 2(ABC + BAC + ACB), , 120°, , = 2 × 180°, , D, B, C, Thus, the interior opposite angles are 2 × 24° = 48°, and 3 × 24° = 72°., , ext. A + ext. B + ext. C = 360°, , Now, in ABC,, , Hence Proved., , A + B + C = 180°, (Angle sum property), , ( Angle sum property), , D, , 4., , 48° + 72° + C = 180°, , , , C, , , , C = 180° – 120°, , , , C = 60°, , 130°, y, , Hence, the measures of angles of the triangle are 48°,, 72° and 60°., 70°, , A, , 2., , D, 70°, 90°, , B, , C, , , B = BCD – A, , x = 130° – 70°, , x = 60°, , B = x = 60°., Now, A + B + C = 180°, (Angle sum property), 70° + 60° + y = 180°, , E, , In ABC, ACE = A + B, = 70° + 40° = 110°, Now,, , B, , (i) In ABC,, BCD = A + B, , x, 40°, , x, , A, , ACE = ACD + DCE, ( Adjacent angles), , , , , 110° = x + 90°, , x = 110° – 90° = 20°, Hence, the value of x is 20°., , y = 180° – 130°, y = 50°, , Hence, x = 60° and y = 50°., , 3. Let ABC be a triangle. In ABC, AB, BC and CA are, produced to D, E and F respectively to make exterior, angles., Now,, , (ii), , C, y, , 40°, , F, A, , 50°, A, , D, , B, , Mathematics In Everyday Life-7, , C, , E, , 85°, , x, D, , B, , In ACD,, DAC + ACD + CDA = 180°, ( Angle sum property), , 50° + y + 85° = 180°, 3
Page 4 :
, , , y + 135° = 180°, y = 180° – 135°, , P, , y = 45, , Now, in BDC,, , , 150°, , CDA = BCD + DBC, 85° = 40° + x, x = 85° – 40°, , , , Hence, x = 45° and y = 45°., 5. In the given figure,, , 30°, , x, , , , y, , , , 70° = x + 30°, [Exterior angle property], x = 70° – 30°, , 150, = 75°, 2, , Thus,, Now,, , P = Q = 75°, P + Q + R = 180°, ( Angle sum property), , , , 75° + 75° + R = 180°, , , , R = 180° – 150°, , , , R = 30°, , 8. We know that, the sum of the two sides of a triangle, is always greater than the third side., i.e., the third side has to be less than the sum of the, two sides., Therefore,, , y + 70° = 180°, y = 180° – 70°, , the third side has to be < (6 + 8) cm = 14 cm., And, the third side is always greater than the, difference of two sides. Then,, , (Linear pair), , The third side has to be more than (8 – 6) cm = 2 cm., , y = 110, , Hence, x = 40° and y = 110°., 6. Let the interior opposite angles of a triangle be, 5x and 7x., Therefore,, Exterior angle = Sum of the interior opposite angles, , 5x + 7x = 120°, , 12x = 120°, , x = 10°, Then,, 5x = 5 × 10° = 50°, 7x = 7 × 10° = 70°, Now,, third angle of the triangle = 180° – (50° + 70°), = 60°, Hence, all the interior angles of the triangle are 50°,, 70° and 60°., 7. In PRQ, side QR is extended to S, and RP = RQ., Therefore,, P = Q = x (given), Then,, PRS = P + Q, 150° = x + x, , 4, , x=, , Hence, P = Q = 75°, R = 30°., 70°, , x = 40, , Now,, , , Q, 2x = 150°, , , , x = 45, , , , x, , R, , S, , Hence, the length of the third side could be any, length greater than 2 cm but less than 14 cm., 9., , (i) Sides are 6 cm, 3 cm and 2 cm., Now, 6 + 3 > 2, 3 + 2 < 6, 6 + 2 > 3, Since, 3 + 2 < 6, so, it is not possible to draw a, triangle with sides 6 cm, 3 cm and 2 cm., (ii) Sides are 3 cm, 6 cm and 7 cm., Now,, , 3 + 6 > 7, 6 + 7 > 3, 3 + 7 > 6, , Hence, it is possible to draw a triangle with, sides 3 cm, 6 cm and 7 cm., (iii) Sides are 10.2 cm, 5.8 cm and 4.5 cm., Now, 10.2 + 5.8 > 4.5, 5.8 + 4.5 > 10.2,, 4.5 + 10.2 > 5.8, Hence, it is possible to draw a triangle with, sides 10.2 cm, 5.8 cm and 4.5 cm., 10., , P, , Q, , S, , R, , Answer Keys
Page 5 :
In PQS,, , Now,, , PQ + QS > PS, …(i), Since, sum of the two sides of a triangle always, greater than the third side., Similarly, in PSR, PR + RS > PS, …(ii), Adding (i) and (ii), we get, PQ + QS + PR + RS > PS + PS, , PQ + (QS + RS) + PR > 2PS, , PQ + QR + PR > 2PS, ( QR = QS + RS), 11., A, , M, , , , , , , 4, = 72°, 7, , (Linear pair), , 3, exterior A + exterior A = 180°, 7, 10, exterior A = 180°, 7, 7, exterior A = 180° ×, = 126°, 10, 3, exterior A =, × 126° = 54°, 7, B, , 7 cm, , 1. In triangle ABC, C = 90°., By Pythagoras theorem,, A, AB2 = AC2 + BC2, 252 = 72 + BC2, 25, cm, BC2 = (625 – 49) cm2, 2, 2, BC = 576 cm, BC2 = (24)2 cm2, Hence, BC = 24 cm., C, B, 2. In right angled ABD, D = 90°, AB2 = BD2 + AD2, (By Pythagoras theorem), A, , AD2 = AB2 – BD2, , , AD2 = (132 – 52) cm2, , , , AD2 = (169 – 25) cm2, , , , AD2 = 144 cm2, , , , AD2 = (12)2 cm2, , , , AD = 12 cm, , B 5 cm D, , cm, 15, , 12. Interior A =, , , , B = 126° ×, , EXERCISE 12.3, , AB + BM > AM, …(i), Since, sum of the two sides of a triangle is always, greater than third side., Similarly, inAMC,, AC + CM > AM, …(ii), Adding (i) and (ii), we get, AB + BM + AC + CM > AM + AM, , AB + 2BM + AC > 2AM, AM is the median, BM = CM, , AB + BC + AC > 2AM, ( BC = 2BM), AB + BC + CA > 2AM, Hence proved., , , , 7, B = 126°, 4, , Now, A + B + C = 180°, , 54° + 72° + C = 180°, , 126° + C = 180°, , C = 180° – 126° = 54°, Hence, A = 54°, B = 72° and C = 54°., , In ABM,, , , , 3, B, 4, , , 3, , 3B 4 C C 4 B, , , , C, , 3, of exterior A, 7, Interior A + exterior A = 180°, , 126° = B +, , 13, cm, , B, , , , Exterior A = B + C, , C, , x, , Now, in right angled ADC, D = 90°., AC2 = AD2 + DC2(By Pythagoras theorem), , , (15)2 = (12)2 + x2, , , , x2 = (152 – 122) cm2, , , , x2 = (225 – 144) cm2, , , , x2 = 81 cm2, , , , x2 = (9)2 cm2, , , , x = 9 cm, , Hence, the value of x is 9 cm., , A, Mathematics In Everyday Life-7, , C, 5
Page 6 :
3. Let W be the window at the height of 8 cm from, ground at point G, and L be the foot of ladder., Then, WG = 8 m,, WL = 10 cm, GL = x (given), In right angled WGL,, (WL)2 = (WG)2 + (GL)2, (By Pythagoras theorem), 2, 2, 2, (10) = (8) + (GL), , , x2 = (25)2 – (15)2, , x2 = 625 – 225, , x2 = 400, , x2 = (20)2, , x = 20, Hence, the length of the third side is 20 cm., 6., , Q, N, , 8m, , W, , G, , 24 m, 10, m, , E, , x, , 6, , 10 m, , P, , W, , S, , L, , , x2 = (10)2 – (8)2, , x2 = 100 – 64, , x2 = 36, , x2 = 62, , x= 6, Hence, the value of x is 6 m., 4. (i) 3, 7, 9, The largest side is 9. Then,, 32 + 72 = 9 + 49, = 58, 2, and, 9 = 81, 2, Thus,, 3 + 7 2 92, Hence, 3, 7, 9 is not a Pythagorean triplet., (ii) 7, 24, 25, The largest side is 25. Then, (7)2 + (24)2 = 49 + 576, = 625, 2, and, (25) = 625, 2, Thus,, 7 + (24)2 = (25) 2, Hence, 7, 24, 25 is a Pythagorean triplet., (iii) 4, 5, 7, The largest side is 7., Then, 42 + 52 = 16 + 25 = 41, and, (7)2 = 49, Thus,, 42 + 5 2 72, Hence, 4, 5, 7 is not a Pythagorean triplet., 5. Let the third side be x cm. Then,, (Hypotenuse)2 = (Base)2 + (Perpendicular)2, (25)2 = (15)2 + x2, (By Pythagoras theorem), , O, , In right angled OPQ, P = 90°, , , OQ2 = OP2 + PQ2, (By Pythagoras theorem), , , , OQ = (10 m) + (24 m)2, , , , OQ2 = (100 + 576) m2, , , , OQ2 = 676 m2, , , , OQ2 = (26 m)2, , 2, , 2, , , OQ = 26 m, Hence, the distance of man from the starting point is, 26 m., 7. The sides of a triangle are 15 cm, 36 cm and 39 cm., The largest side is 39 cm., Now,, (15)2 + (36)2 = (225 + 1296), = 1521, (39)2 = 1521, , And, , Thus,, (15)2 + (36)2 = (39)2, Hence, it is a right angled triangle., 8. Let WL be the ladder and L be the foot of the ladder., Let W be a point on the wall WG to which the ladder, reaches., Let the height of the wall WG be x m., We have,, Length of ladder (WL) = 4.5 m, GL = 2.7 m, , W, , x, , G, , 4.5 m, , 2.7 m, , L, Answer Keys
Page 7 :
In right angled WGL, by Pythagoras theorem., (WL)2 = (WG)2 + (GL)2, (4.5)2 = x2 + (2.7)2, , , x2 = 20.25 – 7.29, , , , x2 = 12.96, , , , x2 = (3.6)2, , , x = 3.6, Hence, the height of the wall to which the ladder, reaches is 3.6 m., 9. Let AB and CD be the two poles of heights 9 m and, 14 m respectively and the distance between two, poles BD = 12 m. Draw a line AE BD., C, , A, , 12 m, , E, 14 m, , 12 m, , D, , 9m, B, , Then,, , CE = DC – DE, = (14 – 9) m ( DE = AB = 9 m), =5m, In right angled AEC,, AC2 = (AE)2 + (CE)2, , AC2 = (12)2 + (5)2, , AC2 = 144 + 25, , AC2 = 169, , AC2 = (13)2, , AC = 13, Hence, the distance between the tops of the two, poles AB and CD is 13 m., 10. The sides of a triangle are of lengths 6.5 cm, 6 cm, and 2.5 cm., Now, the largest side is 6.5 cm. Then,, (6)2 + (2.5)2 = (36 + 6.25), = 42.25, and, (6.5)2 = 42.25, , (6)2 + (2.5)2 = (6.5)2, Hence, it is a right angled triangle and the length of, the hypotenuse is 6.5 cm., 11. In right angled ADB,, , (AB)2 = (AD)2 + (BD)2, (By Pythagoras theorem), 2, 2, , (AD) = (10) – (8)2, , (AD)2 = (100 – 64), , (AD)2 = 36, , (AD)2 = (6)2, Thus,, AD = 6 cm, In right BDC,, (BC)2 = (BD)2 + (DC)2, (17)2 = (8)2 + (DC)2, , 289 = 64 + (DC)2, , DC2 = 289 – 64, , DC2 = 225, , DC2 = (15)2, , DC = 15 cm, Hence, the length of AC = AD + DC, , AC = 6 cm + 15 cm, , AC = 21 cm, 12. Let ABCD be a rectangle in which AB = 3.6 cm,, BC = 1.5 cm., In right angled ABC,, (AC)2 = (AB)2 + (BC)2, (AC)2 = (3.6 cm)2 + (1.5 cm)2, (AC)2 = 12.96 cm2 + 2.25 cm2, (AC)2 = (12.96 + 2.25) cm2, C, , D, , 1.5 cm, , A, , 3.6 cm, , B, , (AC)2 = 15.21 cm2, (AC)2 = (3.9 cm)2, AC = 3.9 cm, Hence, the length of the diagonal of the rectangle is, 3.9 cm., 13. In isosceles triangle ABC, C = 90°, AC = BC, AB cannot be equal to any of AC and BC as it is, hypotanuse., A, , A, , 8 cm, , 10, c, , m, , B, 17, cm, , D, , Mathematics In Everyday Life-7, , C, , B, , C, 7
Page 8 :
By Pythagoras theorem,, AB2 = AC2 + BC2, = AC2 + AC2, 2, , AB = 2 AC, , ( BC = AC), , 2, , Hence proved., , MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS, 1. 132, 392, 262, 102, , = 52 + 122,, = 362 + 152, = 242 + 102, + 152 = 100 + 225 = 325, 252 = 625, 102 + 152 252, So, (10, 15, 25) is not a Pythagorean triplet., Hence, option (b) is correct., 2. In ABC, ACD is an exterior angle., ACD = BAC + ABC, 110° = 70° + x, , x = 110° – 70° = 40°, Hence, option (a) is correct., 3. In ABC, B = 90°, AB = 5 cm, AC = 13 cm, BC = ?, By Pythagoras theorem,, AC2 = AB2 + BC2, (13)2 = (5)2 + (BC)2, , BC2 = 169 – 25 = 144, BC2 = (12)2, BC2 = (12)2, Thus,, BC = 12 cm, Hence, option (b) is correct., 4. Let the width of the rectangle be x m., Diagonal AC = 15 m, AB = 12 m, In ABC, B = 90°., By Pythagoras theorem,, AC2 = AB2 + BC2, , D, , C, 15 m, , A, , 12 m, , , BC2 = (15)2 – (12)2, , x2 = 225 – 144, , x2 = 81, , x= 9, Hence, option (d) is correct., 8, , B, , 5. Sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle is, always greater than the third side., 5 + 6 = 11, These cannot be the length of the sides of a triangle., Hence, option (b) is correct., 6. The sum of exterior angles of a triangle is equal to, 360°., , 1 + 2 + 3 = 360°, Hence, option (b) is correct., 7. Let the equal angles of a triangle be x. Then, x + x + 80° = 180°, ( Angle sum property), 2x + 80° = 180°, , 2x = 100°, , x = 50°, Hence, option (c) is correct., 8. By Pythagoras theorem,, (Hypotenuse)2 = (Base)2 + (Height)2, 50 = x2 + x2, [ Base = Height = x (let)], 2, , 2x = 50, , x2 = 25, , x = 5 cm, The length of each leg is 5 cm., Hence, option (b) is correct., 9. Let ABCD be the rectangle whose length AB = 16 cm, and width BC = 12 cm, and AC be the diagonal., In ABC, B = 90°., By Pythagoras theorem,, D, , C, , 12 cm, , A, , 16 cm, , B, , AC2 = AB2 + BC2, , AC2 = (16)2 + (12)2, , AC2 = 256 + 144, , AC2 = 400, , AC2 = (20)2, , AC = 20, Thus, the length of each of its diagonals is 20 cm., Hence, option (a) is correct., 10. CD BA and AC is transversal. Then, BAC = ACD, ( Alternate interior angles), Answer Keys
Page 9 :
5. In an isosceles triangle, two angles are equal., (True), If two sides of a triangle are equal, then the, angles opposite to them are also equal., 6. The sum of the lengths of two sides of a triangle is, always less than the third side., (False), The sum of the lengths of two sides of a triangle is, always greater than the third side., 7. O is any point in the interior of a ABC, then, OA + OC > AC., (True), The sum of two sides of a triangle is always, greater than its third sides., , 24 cm, , , ACD = 50°, ( BAC = 50°), Now, ACB + ACD + DCE = 180°, ( BE is a straight line), , ACB + 50° + 60° = 180°, , ACB = 180° – 110° = 70°, Hence, option (c) is correct., 11. ABC is a right angled triangle, right angle at B., By Pythagoras theorem,, A, 2, 2, 2, (AC) = (AB) + (BC), x2 = (24 cm)2 + (7 cm)2, , x2 = (576 + 49) cm2, x, 2, 2, , x = 625 cm, , x2 = (25 cm)2, , x = 25 cm, C, B, 7 cm, Hence, option (d) is correct., 12., , A, , O, , A, , B, 35°, B, , 55°, C, , In ABC, A + B + C = 180°, , A + 35° + 55° = 180°, , A = 180° – 90°, , A = 90°, Therefore,, BAC is a right angled triangle., Then, (BC)2 = (AB)2 + (AC)2, Hence, option (b) is correct., , C, , In OAC, OA + OC > AC, 8. In a ABC, A = 110°, B = 40°, then the largest side, is BC and the smallest side is AB., A + B + C = 180°, , C = 180° – 110° – 40°, = 30°, , C, , 110°, , MENTAL MATHS CORNER, A, , Mark the following statement as ‘True’ or ‘False’., 1. A triangle with sides 2.5 cm, 2 cm and 1.5 cm is, possible., (True), , , 2.5 cm + 2 cm > 1.5 cm,, , 9., , 2 cm + 1.5 cm > 2.5 cm, and, , 2.5 cm + 1.5 cm > 2 cm, , 2. If AM is a median of ABC, then AB + BC + CA > 2AM., (True), 3. We can have a triangle with two right angles., , 10., , In this case, the sum of the angles of triangle will be, more than 180°, which is not possible., (False), , 11., , 4. Two angles of a triangle are 30° and 70°, then the, third angle is 90°., (False), , 12., , , , 70° + 30° + 90° = 190° 180°, , Mathematics In Everyday Life-7, , 40°, , B, , Side opposite to largest angle of a triangle is always, greater than the other two., BC is greatest and AB is smallest., (True), A triangle can be drawn with sides 2.4 cm, 1.6 cm, and 4 cm., (False), 2.4 cm + 1.6 cm = 4 cm, So, it is not possible to draw a triangle with these, sides., Three numbers a, b and c form a pythagorean triplet,, if a2 + b2 – c2 = 0., (True), A triangle with two acute angles is not possible., (False), Of all the line segments that can be drawn to a given, line from a given point outside it, the perpendicular, line segment is the shortest., (True), , 9
Page 10 :
By Pythagoras theorem,, (25 cm)2 = (7 cm)2 + x2, , x2 = (625 – 49) cm2, , x2 = 576 cm2, , x2 = (24)2 cm2, , REVIEW EXERCISE, 1., , (i) In given right angled triangle by the Pythagoras, theorem,, , x, , 6 cm, , , 8 cm, , x2 = (8 cm)2 + (6 cm)2, x2 = 64 cm2 + 36 cm2, x2 = (64 + 36) cm2, x2 = 100 cm2, x2 = (10 cm)2, , , , , , , x = 10 cm, , , , 12 cm, , cm, , x, In any one of these right triangle,, 2, x, (13 cm)2 = (12 cm)2 , 2, ( By Pythagoras theorem), , x, , 2, , 2, , , , x, , 2, , 2, , , , Therefore,, , = (169 – 144) cm2, = (25 cm)2, , x, = 5 cm, 2, x = 10 cm, , (iii) In the given right angled triangle,, , cm, 25, , x, , 10, , 2. Let the angles of a triangle be x, 2x and x. Therefore,, x + 2x + x = 180°, (Angle sum property), , 4x = 180°, 180, = 45°, 4, Thus, the angles of a triangle are 45°, 90°, 45°. It is a, right angled isosceles triangle., (One of the angles is 90°), It is an isosceles triangle., (Two angles are equal), 3. Let the third angle of a triangle be x., Then, each of the two equal angles = 2x, Therefore,, 2x + x + 2x = 180° ( Angle sum property), , 5x = 180°, , , , 7 cm, , x=, , 180, = 36°, 5, Hence, the angles of a triangle are 72°, 72° and 36°., 4. (i) 1 cm, 1 cm, 1 cm, Sum of the lengths of any two sides is always, greater than the third side., 1 cm + 1 cm > 1 cm, Hence, it is possible to draw a triangle with the, given sides., (ii) 6 cm, 7 cm, 14 cm, 6 cm + 7 cm < 14 cm, So, it is not possible to draw a triangle with the, given sides., (iii) 5 cm, 7 cm, 12 cm, 5 cm + 7 cm = 12 cm, So, it is not possible to draw a triangle with the, given sides., (iv) 2 cm, 10 cm, 15 cm, 2 cm + 10 cm < 15 cm, So, it is not possible to draw a triangle with the, given sides., 5. Let GH be the street and L be the foot of the ladder., Let S and W be the windows at the heights of 35 m, and 12 m respectively from the ground. Then WL, and SL are two positions of the ladder., Let GL = x m, and LH = y m, , , 13, , 13, cm, , (ii) In the given triangle, two sides are equal. Then it, is an isosceles triangle. Then, the altitude divides, the triangle into two right angled triangle., , x = 24 cm, , x=, , Answer Keys
Page 11 :
S, , 37, m, , 37, m, , G, , 35 m, , 12 m, , W, , L, x, , 7. Let WL be a ladder reaches to W on the wall when, set against it., Let G be the foot of the wall., Let the distance of the foot of ladder from the wall, be x m. i.e., GL = x m, In right angled WGL, G = 90°., , H, y, , W, , Now, in WGL, G = 90°., Then, by Pythagoras theorem,, (WL)2 = (WG)2 + (GL)2, (37 m)2 = (12 m)2 + (x)2, , x2 = (1369 – 144) m2, , x2 = 1225 m2, , x2 = (35 m)2, , G, , Again, in SHL, H =, (SL)2 =, (37)2 =, , y2 =, , y2 =, , y2 =, , (WL)2 = (WG)2 + (GL)2, , 90°., (SH)2 + (LH)2, (35)2 + (y)2, (1369 – 1225) m2, 144 m2, (12 m)2, , y = 12 m, , , , Hence, the width of street = x + y = (35 + 12) m, = 47 m., 6. Let ABCD be a rectangle whose length is 15 cm and, width is 8 cm. Let AC be its diagonal., In ABC, B = 90°., , D, , C, , 8 cm, , B, 15 cm, By Pythagoras theorem,, (AC)2 = (AB)2 + (BC)2, , (AC)2 = (15 cm)2 + (8 cm)2, , (AC)2 = (225 + 64) cm2, , (AC)2 = 289 cm2, , (AC)2 = (17 cm)2, AC = 17 cm, Hence, the length of the diagonal is 17 cm., , (5 m)2 = (4.8 m)2 + x2, , , x2 = (25 – 23.04) m2, , , , x2 = 1.96 m2, , , , x2 = (1.4 m)2, , , , x = 1.4 m, , Hence, the distance of the foot of ladder from the, wall is 1.4 m., 8. Let ABC be an isosceles right triangle. In which, C = 90°. Then the two equal angles are A and B., A + B + C = 180°, , , [ A = B = x (let)], , x + x + 90° = 180°, , , , 2x = 90°, , , , x = 45°, , Hence, A = 45°, B = 45°, C = 90°., 9. Exterior angle = Sum of the two interior opposite, angles., , A, , Mathematics In Everyday Life-7, , L, , x, , By Pythagoras theorem,, , x = 35 m, , , , 5m, , 4.8 m, , 60°, , x, , 2x, , , , , 2x = x + 60°, 2x – x = 60°, , , , x = 60°, , 11
Page 13 :
, 2x = x + 60°, , 2x – x = 60°, , x = 60°, Both the interior angles are equal., Third angle = 180° – (60° + 60°), = 180° – 120° = 60°, Thus, all the angles of the triangle are equal i.e. 60°., Hence, it is an “equilateral triangle”., 2. Let PQ be a tree of height (2.5 + x) m before it is, broke at point T., i.e., PT = TR = x m, Let the top P touch the ground at R after it broke., P, , Now, AD BC., In ABD,, ABD + BAD + ADB, , 60° + BAD + 90°, , BAD, BAD, (ii), , P, , Q, , 2.5 m, , T, , Q, , R, , 6m, , In TQR, Q = 90°, By Pythagoras theorem,, (TR)2 = (TQ)2 + (QR)2, , x2 = (2.5 m)2 + (6 m)2, , x2 = (6.25 + 36) m2, , x2 = 42.25 m2, , x = 6.5 m, Thus, PT = TR = 6.5 m, Hence, the height of the tree = PT + TQ, = (6.5 + 2.5) m, =9m, 3. (i) ABC is an equilateral triangle. Then, AB = BC = CA, i.e.,A =B = C = 60°, A, , B, , D, , Mathematics In Everyday Life-7, , = 180°, = 180°, = 180° – 150°, = 30°, , 3 cm, , T, , R, , Let the equal angles of isosceles triangle be x., Q = R = x, Now,, P + Q + R = 180°, , P + x + x = 180°, , P = 180° – 2x, Now, an altitude forms a right angle with the, base it intersects., Thus, there are 2 right angles formed at the foot, of the altitude PT., In PTQ,, QPT + PTQ + TQP = 180°, QPT + 90° + x = 180°, 1, QPT = 90° – x = (180° – 2x), 2, Similarly,, RPT = 90° – x, These angles are half the size of QPR, So, QPR is bisected by the altitude., So, it bisects the side QR also., Hence, QT = RT, , RT = 3 cm., , C, 13