Page 1 :
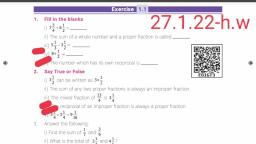
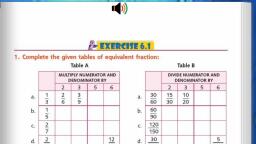
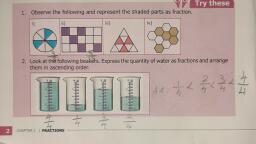
(a) A fraction is a number representing a part of a whole. The whole may be a single object or a group of objects., (b) When expressing a situation of counting parts to write a fraction, it must be ensured that all parts are equal., In 5/7, 5 is called the numerator and 7 is called the denominator., Exercise: 7.1, Question 1., Write the fraction representing the shaded portion., Solution:, (i) Total number of parts = 4, Number of shaded parts = 2, ∴ Fraction = 2/4, (ii) Total number of parts = 9, Number of shaded parts = 8, ∴ Fraction = 8/9, iii) Total number of parts = 8, Number of shaded parts = 4, ∴ Fraction = 4/8, (iv) Total number of parts = 4, Number of shaded parts = 1, ∴ Fraction = 1/4, (v) Total number of parts = 7, Number of shaded parts = 3, ∴ Fraction = 3/7, (You should solve question VI to X), Question 2., Colour the part according to the given fraction., Question 3., Identify the error, if any., Solution:, (a) Since the shaded part is not half., ∴ This is not 1/2., (b) Since, the parts are not equal., ∴ Shaded part is not 1/4 ., (You should solve (c) ), Question 4., What fraction of a day is 8 hours?, Solution:, Since, a day has 24 hours and we have 8 hours,, ∴ Required fraction = 8/24, Question 5., What fraction of a hour is 40 minutes?, Solution:, Since I hours = 60 minutes, ∴ Fraction of 40 minutes = 40/60, Question 6., Arya, Abhimanyu and Vivek shared lunch. Arya has brought two sandwiches, one made of vegetable and one of Jam. The other two boys forgot to bring their lunch. Arya agreed to share his sandwiches so that each person will have an equal share of each sandwich., (a) How can Arya divide his sandwiches so that each person has an equal share?, (b) What part of a sandwich will each boy receive?, Solution:, (a) Arya has divided his sandwich into three equal parts., So, each of them will get one part., (b) Each one of them will receive 1/3 part., ∴ Required fraction = 1/3, Question 7., Kanchan dyes dresses. She had to dye 30 dresses. She has so far finished 20 dresses. What fraction of dresses has she finished?, Solution:, Total number of dresses to be dyed = 30, Number of dresses finished = 20, ∴ Required fraction = 20/30 = 2/3, Question 8., Write the natural numbers from 2 to 12. What fraction of them are prime numbers?, Solution:, Natural numbers between 2 and 12 are;, 2,3,4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10,11, 12, Number of given natural numbers = 11, Number of prime numbers = 5, ∴ Required fraction = 5/11, Question 9., Write the natural numbers from 102 to 113. What fraction, of them are prime numbers?, Solution:, Natural numbers from 102 to 113 are;, 102,103,104,105,106, 107,108, 109,110, 111, 112,113, Total number of given natural numbers = 12, Prime numbers are 103, 107, 109, 113, ∴ Number of prime numbers = 4, ∴ Required fraction = 4/12 = 1/3, Question 10., What fraction of these circles has X’s in them?, Solution:, Total number of circles = 8, Number of circles having X’s in them = 4, Required fraction = 4/8 = 1/2, Question 11., Kristin received a CD player for her birthday. She bought 3 CDs and received 5 others as gifts. What fraction of her total CDs did she buy and what fraction did she receive as gifts?, Solution:, Number of CDs bought by her from the market = 3, Number of CD’s received as gifts = 5, ∴ Total number of CDs = 3 + 5 = 8, ∴ Fraction of CD (bought) = 3/8 and the fraction of CDs (gifted) = 5/8, Representing Fractions on the Number Line, We all know that a fraction is a number which is not a ,, (such as 1/2, 5/7 etc), We already know how to represent whole numbers on the number line. Let us consider the image shown, here, the digits 0 and 1 are represented on the number line., We know that 1/2 is greater than 0 and less than 1, so it should lie between, 0 and 1. Since we have to show 1/2, we divide the gap between 0 and 1 into two equal parts and show 1 part as1/2, So, the point represents (1-0)/2 = ½, We must note that, 0/5 = 0 here and 5/5 = 1., We know that 1/5 and 3/5 is greater than 0 and less than 1, so it should lie between 0 and 1. Since we have to show 1/5 and 3/5, we divide the gap between 0 and 1 into five equal parts and show 1 part as1/5, So, the point represents (1-0)/5 = 1/5, So, the point represents (3-0)/5 = 3/5, Exercise: 7.2, Question 1., Draw number lines and locate the points on them., We have divided the number line from 0 to 1 into four equal parts., C represents 2/4 i,e., 1/2, B represents 1/4, D represents 3/4, and E represents 4/4 , i.e., 1., From the above number line, we have, C represents 2/5, D represents 3/5, E represents 4/5, and I represent 8/5, (You should solve ( b) ), Proper Fraction, A fraction where the numerator is less than the denominator, then it is known as a proper fraction., i.e., Numerator < Denominator, For example,3/5, 7/9, Improper Fraction, A fraction where the numerator is greater than the denominator, then it is known as an improper fraction., i.e., Numerator > Denominator, For example, 7/3 ,6/2, Mixed Fraction, A mixed fraction is the combination of a natural number and fraction. It is basically an improper fraction., Question 2., Express the following as mixed fractions:, Quotient = Whole number, Reminder = Numerator, Divisor = Denominator, (You should solve question d,e,f), Question 3., Express the following as improper fractions:, Whole number x Denominator + Numerator, Denominator, Equivalent Fractions, Equivalent fractions can be defined as fractions with different numerators and denominators that represent the same value or proportion of the whole., Each proper or improper fraction has many equivalent fractions. To find an equivalent fraction of a given fraction, we may multiply or divide both the numerator and the denominator of the given fraction by the same number., Finding the simplest form of a fraction means reducing the top and bottom of the fraction to the smallest whole number possible., Exercise 7.3, Question 1., Write the fractions. Are all these fractions equivalent?, Since all the fractions in their simplest form are not equal., ∴ They are not equivalent fractions., Question 2., Write the fractions and pair up the equivalent fractions from each row., (The following pairs fractions: represent the equivalent fractions., (a) and ii) = 1/2, (b) and (iv) = 2/3, (c) and (i) = 1/3, (d) and (v) = 1/4, (e) and (iii) = 34, Question 3., Replace in each of the following by the correct number:, a), (You should solve(e)), Question 4., Find the equivalent fraction of 35 having, (a) denominator 20, (b) numerator 9, (c) denominator 30, (d) numerator 27, Solution:, (a) Here, we require denominator 20., Let N be the numerator of the fractions., ∴ The required fraction is 12/20, (b) Here, we required numerator 9., Let D be the denominator of the fraction., ∴ The required fraction is 15/20, (c) Here, we required denominator 30., Let N be the numerator of the fraction., ∴ The required fraction is 18/30., (You should solve (d)), Question 5., Find the equivalent fraction of 36/48 with, (a) numerator 9, (b) denominator 4, Solution:, (a) Given that numerator = 9, So, the equivalent fraction is 9/12., (b) Given that denominator = 4, ∴ N/4 = 36/48 ⇒ N x 48 = 4 x 36, ⇒ N = 4x36/48 = 3, So, the equivalent fraction is 3/4 ., Question 6., Check whether the given fractions are equivalent:, Solution:, (a) 5/9 and 30/54, We have 5 x 54 = 270, and 9 x 30 = 270, Here 5 x 54 = 9 x 30, ∴ 5/9 and 30/54 are equivalent fractions., (b) 3/10 and 12/50, We have 3 x 50 = 150, and 10 x 12 = 120, Here 3 x 50 ≠ 10 x 12, ∴ 3/10 and 12/50 are not equivalent fractions., (You should solve (c) ), Question 7., Reduce the following fractions to simplest form:, (You should solve (d and e) ), Question 8., Ramesh had 28 pencils, Sheelu had 50 pencils and Jamaal had 80 pencils. After 4 months, Ramesh used up 10 pencils, Sheelu used up 25 pencils and Jamaal used up 40 pencils. What fraction did each use up? Check if each has used up an equal fraction of her/his pencils., Solution:, Ramesh used up 10 pencils out of 20 pencils., Sheelu used up 25 pencils out of 50 pencils., Jamaal used up 40 pencils out of 80 pencils., Yes, each has used up an equal fractions, i.e., 1/2., Question 9., Match the equivalent fractions and write two more for each., Two additional examples of equivalent fractions are, Two additional examples of equivalent fractions are, Two additional examples of equivalent fractions are, Two additional examples of equivalent fractions are, Two additional examples of equivalent fractions are, Like fraction, The fractions with the same denominators are called like fractions., (2/9, 3/9, 5/9, 9/9), (3/10, 7/10, 1/10, 9/10), Unlike fraction, The fractions with different denominators are called unlike fractions., (1/2, 1/4, 2/3, 5/6), (3/8, 2/3, 3/5, 2/7), Comparing like fractions, Two fractions with the same denominator, the fraction with the greater numerator is greater., or, Any two like fractions can be compared by comparing their numerators. The fraction with larger numerator is greater than the fraction with smaller numerator, for example, 2/5 < 4/5, 2/9 < 4/9 < 6/9, Comparing unlike fractions, We can see from the above example that if the numerator is the same in two fractions, the fraction with the smaller denominator is greater of the two., 3/10 < 3/5 < 3/4 or 3/4 > 3/5 > 3/10, Which is larger ³/₄ or ⁵/₁₂ ?, , Solution:, , Let us first find the LCM (least common multiple) of the denominators 4 and 12., , We have,, Therefore, LCM (least common multiple) of 4 and 12 is 2 × 2 × 3 = 12., , Now we convert the given fractions to equivalent fractions with denominator 12, , We have,, 3/4 = (3 × 3)/(4 × 3) = 9/12, , 5/12 = (5 × 1)/(12 × 1) = 5/12, Now we will observe the numerator, that is 9 > 5., , So, ⁹/₁₂ > ⁵/₁₂, , Therefore, ³/₄ > ⁵/₁₂., Exercise : 7.4, Question 1., Write shaded portion as fraction. Arrange them in ascending and descending order using correct sign ‘<‘, ‘=’, ‘>’ between the fractions., (c) Show 2/4, 4/6 , 8/6 and 6/6 on the number line. Put appropriate signs between the fractions given., Solution:, (a) Total number of divisions = 8, (i) Number of shaded parts = 3, ∴ Fraction = 3/8, (ii) Total number of divisions = 8, Number of shaded parts = 6, ∴ Fraction = 6/8, (iii) Total number of divisions = 8, Number of shaded parts = 4, ∴ Fraction = 4/8, (iv) Total number of divisions = 8, Number of shaded part = 1, ∴ Fraction = 1/8, Now the fractions are:, 3/8, 6/8, 4/8 and 1/8 with same denominator, (b)(i) Total number of divisions = 9, Number of shaded parts = 8, ∴ Fraction = 8/9, (ii) Total number of divisions = 9, Number of shaded parts = 4, ∴ Fraction = 4/9, (iii) Total number of divisions = 9, Number of shaded parts = 3, ∴ Fraction = 3/9, (iv) Total number of divisions = 9, Number of shaded parts = 6, ∴ Fraction = 6/9, ∴ Fractions are 8/9, 4/9, 3/9, 6/9 with same denominator., Question 2., Compare the fractions and put an appropriate sign., Here, denominators of the two fractions are same and 3 < 5., Here, numerators of the fractions are same and 7 > 4., Here, denominators of the two fractions are same and 4 < 5., (You should solve this problem), Question 3., Make five more such pairs and put appropriate signs., Solution:, Question 4., Look at the figures and write ’<’, or ’>’ ’=’ between the given pairs of fractions., Make five more such problems and solve them with your friends, Solution:, Make five more such problems yourself., Question 5., How quickly can you do this? Fill appropriate sign. ‘<‘, ‘=’, ‘>’, (You should solve problem f,g,h,I,j), Question 6., The following fractions represent just three different numbers. Separate them into three groups of equivalent fractions, by changing each one to its simplest form., Now grouping the above fractions into equivalent fractions, we have, Question 7., Find answers to the following. Write and indicate how you solved them., By cross-multiplying, we get, 5 x 5 = 25 and 4 x 9 = 36, Since 25 ≠ 36, By cross-multiplying, we get, 9 x 9 = 81 and 16 x 5 =80, Since 81 ≠ 80, By cross-multiplying, we get, 4 x 20 = 80 and 5 x 16 = 80, Since 80 = 80, (You should solve this problem), Question 8., Ila read 25 pages of a book containing 100 pages., Lalita read 2/5 of the same book. Who read less?, Solution:, Ila reads 25 pages out of 100 pages., Lalita reads 2/5 of the same book., Comparing 1/4 and 2/5 , we get, 1 x 5 = 5 and 2 x 4 = 8, Since 5 < 8, ∴ 1/4 < 2/5, Hence Ila reads less pages., Question 9., Rafiq exercised for 3/6 of an hour, while Rohit exercised for 3/4 of an hour. Who exercised for a longer time?, Solution:, Rafiq exercised for 3/6 of an hour., Rohit exercised for 3/4 of an hour., Comparing 3/6 and 3/4 , we get, 3 x 4 = 12 and 3 x 6 = 18, Since 1/2 < 8, ∴ 3/4 > 3/6, Hence Rohit exercised for longer time., Question 10., In a class A of 25 students, 20 passed in first class, in another class B of 30 students, 24 passed in first class. In which class was a greater fraction of students getting first class?, Solution:, In class A, 20 students passed in first class out of 25 students., ∴ Fraction of students getting first class, In class B, 24 students passed in first class out of 30 students., ∴ Fraction of students getting first class, Comparing the two fractions, we get 4/5 = 4/5, Hence, both the class A and B have the same fractions., Adding or subtracting like fractions, Like fractions are fractions with the same denominator. Add or subtract the numerators and write the sum over the common denominator., Exercise 7.5, Write these fractions appropriately as additions or subtractions:, a) Total number of parts each rectangle has = 5, No. of shaded parts in first rectangle = 1 i.e 1 / 5, No. of shaded parts in second rectangle = 2 i.e 2 / 5, No. of shaded parts in third rectangle = 3 i.e 3 / 5, Clearly, fraction represented by third rectangle = Sum of the fractions represented by first and second rectangle, Hence, 1 / 5 + 2 / 5 = 3 / 5, (c) Here we may observe that first, second and third rectangles represents 2, 3 and 5 shaded parts out of 6 equal parts respectively. Clearly, fraction represented by third rectangle is the sum of fractions represented by first and second rectangles., Hence, 2 / 6 + 3 / 6 = 5 / 6, (You should solve problem (b) ), 2. Solve:, (a) 1 / 18 + 1 / 18, = (1 + 1) / 18, = 2 / 18, = 1 / 9, (b) 8 / 15 + 3 / 15, = (8 + 3) / 15, = 11 / 15, (c) 7 / 7 – 5 / 7, = (7 – 5) / 7, = 2 / 7, (d) 1 / 22 + 21 / 22, = (1 + 21) / 22, = 22 / 22, = 1, (e) 12 /15 – 7 / 15, = (12 – 7) / 15, = 5 / 15, = 1 / 3, (f) 5 / 8 + 3 / 8, = (5 + 3) / 8, = 8 / 8, = 1, (You should solve these problems), (g) 1 – 2 / 3 (1 = 3 / 3), (h) 1 / 4 + 0 / 4, (i) 3 – 12 / 5, 3. Shubham painted 2 / 3 of the wall space in his room. His sister Madhavi helped and painted 1 / 3 of the wall space. How much did they paint together?, Solutions:, Wall space painted by Shubham in a room = 2 / 3, Wall space painted by Madhavi in a room = 1 / 3, Total space painted by both = (2 / 3 + 1 / 3), = (2 + 1) / 3, = 3 / 3, = 1, ∴ Shubham and Madhavi together painted 1 complete wall in a room., 4. Fill in the missing fractions., (a) 7 / 10 – ▯ = 3 / 10, Given 7 / 10 – ▯ = 3 / 10, ▯ = 7 / 10 – 3 / 10, ▯ = (7 – 3) / 10, ▯ = 4 / 10, ▯ = 2 / 5, (b) ▯ – 3 / 21 = 5 / 21, Given ▯ – 3 / 21 = 5 / 21, ▯ = 5 / 21 + 3 / 21, ▯ = (5 + 3) / 21, ▯ = 8 / 21, (c) ▯ – 3 / 6 = 3 / 6, Given ▯ – 3 / 6 = 3 / 6, ▯ = 3 / 6 + 3 / 6, ▯ = (3 + 3) / 6, ▯ = 6 / 6, ▯ = 1, (You should solve this problem ), (d) ▯ + 5 / 27 = 12 / 27, 5. Javed was given 5 / 7 of a basket of oranges. What fraction of oranges was left in the basket?, Solutions:, Fraction of oranges given to Javed = 5 / 7, Fraction of oranges left in the basket = 1 – 5 / 7, = 7 / 7 – 5 / 7, = (7 – 5) / 7, = 2 / 7, Adding or subtracting unlike fractions, Step I:, Obtain the fractions and their denominators., Step II:, Find the LCM (least common multiple) of the denominators., Step III:, Convert each fraction into an equivalent fraction having its denominator equal to the LCM (least common multiple) obtained in Step II., Step IV:, Add or subtract like fractions obtained in Step III., , For Example:, 1. Add ²/₃ and ³/₇., Solution:, The LCM (least common multiple) of the denominators 3 and 7 is 21., So, we convert the given fractions into equivalent fractions with denominator 21., We have,, , 2/3 + 3/7, = (2 × 7)/(3 × 7) + (3 × 3)/(7 × 3), , [since 21 ÷ 3 = 7 and 21 ÷ 7 = 3], , = 14/21 + 9/21, , = (14 + 9)/21, , = 23/21, Find the difference of ¹⁷/₂₄ and ¹⁵/₁₆., Solution:, The LCM (least common multiple) of the denominators 24 and 16 is 48., [Therefore, LCM = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 = 48], , So, we convert the given fractions into equivalent fractions with denominator 48., , We have,, = 17/24 = (17 × 2)/(24 × 2) = 34/48 [since 48 ÷ 24 = 2], , and, 15/16 = (15 × 3)/(16 × 3) = 45/48 [since 48 ÷ 16 = 3], , Clearly, 45/48 > 34/48, , Therefore, 15/16 > 17/24, , Hence, difference = 15/16 – 17/24, , = 45/48 – 34/48, , = (45 – 34)/48, , = 11/48., Add or subtract mixed fractions, 42/3 – 31/4 + 2 1/6, Solution:, We have,, , 42/3 – 31/4 + 21/6, , = (4 × 3 + 2)/3 – (3 × 4 + 1)/4 + (2 × 6 +1)/6, , = (12 + 2)/3 – (12 +1)/4 + (12+1)/6, , = 14/3 – 13/4 + 13/6, The LCM (least common multiple) of the denominators 3, 4 and 6 is 12., [Therefore, LCM = 2 × 2 × 3 = 12], , So, we convert the given fractions into equivalent fractions with denominator 12., , We have,, = (14 × 4)/(3 × 4) – (13 × 3)/(4 × 3) + (13 × 2)/(6 × 2), , = 56/12 – 39/12 + 26/12, , = (56 – 39 + 26)/12, , = (82 – 39)/12, , = 43/12, = 3⁷/₁₂, Exercise 7.6, 1. Solve, (a) 2 / 3 + 1/ 7, Taking LCM 21, (2 × 7) / 21 + (1 × 3) / 21, = (14 + 3) / 21, = 17 / 21, (b) 3 / 10 + 7 / 15, Taking LCM 30, = (3 × 3) / 30 + (7 × 2) / 30, = (9 + 14) / 30, = 23 / 30, (e) 2 / 5 + 1 / 6, Taking LCM 30, = [(2 × 6) + (1 × 5)] / 30, = (12 + 5) / 30, = 17 / 30, (f) 4 / 5 + 2 / 3, Taking LCM 15, = [(4 × 3) + (2 × 5)] / 15, = (12 + 10) / 15, = 22 / 15, (You should solve these problems), (c) 4 / 9 + 2 / 7, (d) 5 / 7 + 1 / 3, (l), (m) 16 / 5 – 7 / 5, (n) 4 / 3 – 1 / 2, 2. Sarita bought 2 / 5 metre of ribbon and Lalita 3 /4 metre of ribbon. What is the total length of the ribbon they bought?, Solutions:, Ribbon length bought by Sarita = 2 / 5 metre, Ribbon length bought by Lalita = 3 / 4 metre, Total length of the ribbon bought by both of them = 2 / 5 + 3 / 4, Taking LCM 20, = [(2 × 4) + (3 × 5)] / 20, = (8 + 15) / 20, = 23 / 20 metre, ∴ Total length of the ribbon bought by both Sarita and Lalita is 23 / 20 metre, 3. Naina was given piece of cake and Najma was given piece of cake. Find the total amount of cake was given to both of them., Solutions:, Fraction of cake Naina got =, = 3 / 2, Fraction of cake Najma got =, = 4 / 3, Total amount of cake given to both of them = 3 / 2 + 4 / 3, = [(3 × 3) + (4 × 2)] / 6, = (9 + 8) / 6, = 17 / 6, =, 4. Fill in the boxes:, (a) ▯ – 5 / 8 = 1 / 4, (c) 1 / 2 – ▯ = 1 / 6, Solutions:, (a) ▯ – 5 / 8 = 1 / 4, ▯ = 1 / 4 + 5 / 8, ▯ = [(1 × 2 + 5)] / 8, ▯ = 7 / 8, (c) 1 / 2 – ▯ = 1 / 6, ▯ = 1 / 2 – 1 / 6, ▯ = [(1 × 3) – (1 × 1)] / 6, ▯ = (3 – 1) / 6, ▯ = 2 / 6, ▯ 1 / 3, (you should solve this problem ), (b) ▯ – 1 / 5 = 1 / 2, 5. Complete the addition and subtraction box., Solutions:, (a) 2 / 3 + 4 / 3, = (2 + 4) / 3, = 6 / 3, = 2, 1 / 3 + 2 / 3, = (1 + 2) / 3, = 3 / 3, = 1, 2 / 3 – 1 / 3, = (2 – 1) / 3, = 1 / 3, 4 / 3 – 2 / 3, = (4 – 2) / 3, = 2 / 3, 1 / 3 + 2 / 3, = (1 + 2) / 3, = 3 / 3, = 1, Hence, the complete given box is, (b) 1 / 2 + 1 / 3, = [(1 × 3) + (1 × 2)] / 6, = (3 + 2) / 6, = 5 / 6, 1 / 3 + 1 / 4, = [(1 × 4) + (1 × 3)] / 12, = (4 + 3) / 12, = 7 / 12, 1 / 2 – 1 / 3, = [(1 × 3) – (1 × 2)] / 6, = (3 – 2) / 6, = 1 / 6, 1 / 3 – 1 / 4, = [(1 × 4) – (1 ×3)] / 12, = (4 – 3) / 12, = 1 / 12, 1 / 6 + 1 / 12, = [(1 × 2) + 1] / 12, = (2 + 1) / 12, = 3 / 12, = 1 / 4, Hence, the complete given box is, 6. A piece of wire 7 / 8 metre long broke into two pieces. One piece was 1 / 4 metre long. How long is the other piece?, Solutions:, Total length of wire = 7 / 8 metre, Length of one piece of wire = 1 / 4 metre, Length of other piece of wire = Length of the original wire and this one piece of wire, = 7 / 8 – 1 / 4, = [(7 × 1) – (1 × 2)] / 8, = (7 – 2) / 8, = 5 / 8, ∴ Length of the other piece of wire = 5 / 8 metre, 7. Nandini’s house is 9 / 10 km from her school. She walked some distance and then took a bus for 1 / 2 km to reach the school. How far did she walk?, Solutions:, Distance of the school from house = 9 / 10 km, Distance she travelled by bus = 1 / 2 km, Distance walked by Nandini = Total distance of the school – Distance she travelled by bus, = 9 / 10 – 1 / 2, = [(9 × 1) – (1 × 5)] / 10, = (9 – 5) / 10, = 4 / 10, = 2 / 5 km, ∴ Distance walked by Nandini is 2 / 5 km, 8. Asha and Samuel have bookshelves of the same size partly filled with books. Asha’s shelf is 5 / 6 th full and Samuel’s shelf is 2/ 5 th full. Whose bookshelf is more full? By what fraction?, Solutions:, Fraction of Asha’s bookshelf = 5 / 6, Fraction of Samuel’s bookshelf = 2 / 5, Convert these fractions into like fractions, 5 / 6 = 5 / 6 × 5 / 5, = (5 × 5) / (6 × 5), = 25 / 30, 2 / 5 = 2 / 5 × 6 / 6, = (2 × 6) / (5 × 6), = 12 / 30, 25 / 30 > 12 / 30, 5 / 6 > 2 / 5, ∴ Asha’s bookshelf is more full than Samuel’s bookshelf, Difference = 5 / 6 – 2 / 5, = 25 / 30 – 12 / 30, = 13 / 30, 9. Jaidev takes minutes to walk across the school ground. Rahul takes 7 / 4 minutes to do the same. Who takes less time and by what fraction?, Solutions:, Time taken by Jaidev to walk across the school ground =, = 11 / 5 minutes, Time taken by Rahul to walk across the school ground = 7 / 4 minutes, Convert these fractions into like fractions, 11 / 5 = 11 / 5 × 4 / 4, = (11 × 4) / (5 × 4), = 44 / 20, 7 / 4 = 7 / 4 × 5 / 5, = (7 × 5) / (4 × 5), = 35 / 20, Clearly, 44 / 20 > 35 / 20, 11 / 5 > 7 / 4, ∴ Rahul takes less time than Jaidev to walk across the school ground, Difference = 11 / 5 – 7 / 4, = 44 / 20 – 35 / 20, = 9 / 20, Hence, Rahul walks across the school ground by 9 / 20 minutes