Page 1 :
Unit-4,, Along With Motion, Introductory discussions, , Which are the motions of the earth you are familiar with?, Rotation on earth’s own axis and revolution around the sun, , Which are the objects that move along with the earth when it moves?, All the things on earth such as buildings, mountains, trees and ourselves, are moving along with the earth., Can you be in a state of rest at least for a second?, No, because we are living on earth which is moving at a greater speed all, the time., What is meant by the teacher when she is saying that the buildings,, rocks and mountains are moving at a great speed?, The earth rotates about its axis at an approximate speed of 1,667 kilometre, per hour at the equatorial region. It revolves around the sun with a speed of, 1,06,000 kilometre per hour. So all the things on the earth will move along, with the earth with the same speed., Motion within the body, • Blood circulation, • Heart beat, • Contraction and expansion of lungs, • Motion of food through the digestive organs, • excretion of urine, • Transportation of nutrients through the blood, •, Instances where we experience the motion of air, , • While sitting on a sea shore, • While waving with a piece of paper, • While sitting under a working fan, • While standing on the top of a hill or a dam, • While seeing the motion of leaves of trees in the wind, What are the other types of motion that take place around you?, Enlist., • Flying of birds in the sky
Page 2 :
• Flow of water in rivers, • Running of vehicles, • Motion of ants, • Rotation of machines, • Force and motion, Discussions based on the activities using marbles mentioned in page 47 of, the text book., ● When did the marble, which was at rest, start moving?, When struck it with finger, that is when force is applied., ● When did it come to rest?, When blocked it’s path with the hand, that is when force is applied., ● When did it change its direction of motion?, When a scale is held in a slightly inclined position in its path, that is when, force is applied., ● When did the speed of the rolling marble increase?, When it was collided by another marble, that is when force is applied., ● What change in motion was brought about by applying force in each, situation?, 1. The marble which was at rest was set into motion., 2. The marble which was at motion was set into rest., 3. The direction of moving marble changed., 4. The speed of moving marble increased, What are the purposes for which players apply force on a ball?, 1. To move the ball at rest, 2. To stop the moving ball, 3. To change the direction of moving ball, 4. To increase or decrease the speed of a moving ball, 5., Force and motion, We can move objects at rest by applying force. We can also change the, state of motion of a body to a state of rest by applying force. We apply, force to change the direction of motion or to increase or decrease the speed, of motion., Types of motion, 1. The motion of a body along a straight line is linear motion., 2. The movement of a body about its own axis is rotation.
Page 3 :
3. The motion along a circular path is circular motion., 4. The to and fro motion of a body about a mean position is called, oscillation., 5. Fast oscillations are referred to as vibrations., Rotation, Circular, Linear, Oscillation Vibration, motion, motion, Rotation of a top Swirling a, Ripe mango Motion of the Motion of the, stone tied, falls, pendulum of prongs of an, to a rope, down, a clock, excited tuning, fork, Rotation of a fan Rotation of a Motion of a .motion of a Motion of the, fan Toy train lift Motion of hanging, diaphragm of a, running along a swing, lamp, drum, a circular, path, Rotation of earth Revolution of Motion of a Motion of, Motion of the, planets, bullet, viper, string of, around the, veena while, sun, playing it, Rotation of the, Motion of the Motion of an Motion of the Motion of the, wheels of vehicles chair, arrow, oscillating, string of, in a giant, boat in a, guitar while, wheel, park, playing it, Rotation of the, Motion of the Running of, Motion of a, blades of a mixer valve tube on an aeroplane, stretched, grinder, the wheel of through the, rubber band while, a bicycle, runway for, tapping on it, taking off, using a, finger, , I s the motion of the wiper of vehicles an oscillation?, Vipers of vehicles move to both sides about a mean position. So they are, oscillations., Distinguish between oscillation and vibrations.
Page 4 :
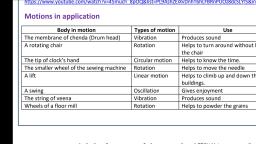
The to and fro motion of a body about a mean position is called oscillation., Fast oscillations are referred to as vibrations. All vibrations are also, oscillations, but all oscillations are not vibrations., Blow pipe peepi, Materials required:, , 10 cm long pipe of one inch diameter, a balloon, the empty case of a pen,, rubber band, 2 m long thread and cello tape., Method of making :, , Cut open the closed end of the balloon. Insert the pipe at one end of the, balloon and the empty case of a pen at the other. Tie them strongly using a, rubber band. Hold the pipe vertically and stretch the empty pen, horizontally. Now the balloon will appear like a stretched membrane. In, the middle of this stretched portion fix one end of the thread using cello, tape., Method of operation:, , Let anybody pull the free end of the thread. Pull the case of the pen and, blow through it. A sound like the trumpet of an elephant can be heard. The, thread will also vibrate with this sound., Motions in a sewing machine, , • Pedal-oscillation, • Two wheels-rotation, • Needle-linear motion, Motions in application, Body in motion, , Types of motion, , Use, , Vibration, , Produces sound, , Rotation, , Helps to turn around, without leaving, the chair, , The membrane of chenda (Drum head), , A rotating chair
Page 5 :
The tip of clock’s hand, , Circular motion, , The smaller wheel of the sewing machine Rotation, A lift, , Helps to know the time., , Helps to move the, needle, , Linear motion, Helps to climb up and, down the buildings., , A swing, , Oscillation, , Gives enjoyment, , The string of veena, , Vibration, , Produces sound, , Rotation, , Helps to powder the, grains, , Wheels of a floor mill, , What are the devices you have seen, in which the force applied at one part, is transferred to another part and used for motion? How is it enabled in, them?, , Bicycle, flour mill, sewing machines, vehicles etc. In these devices, parts, like chain, belt, string, gears and wheel and axel are used to transfer the, force applied at one part to other parts. In a bicycle, the force applied on, the pedal is transferred to the rear wheel through the chain and gears. In a, flour mill, the force from the motor is transmitted to the powdering, machines through belt and wheel and axle. In sewing machine, the force, applied on the pedal is reached at the needle through the string and two, wheels. In vehicles, the force from the engine is transmitted to the wheels, through gears and axle., , Gears, Gears are used in machines to change the direction of the motion, and to increase or decrease the speed of the motion., In this gear set, if the bigger gear is rotated in to right side, the small, one will be rotated in to left side with higher speed. In the same, way, If the small gear is rotated in to right side, the big gear will be, rotated in to left side with low speed. Thus the gears, help to change the speed and direction of motion., Gears are used in vehicles, clock, hand driller, rubber, sheet making machines, sugar cane juice making, machines, toys etc.
Page 6 :
Let us assess, 1. A man pulling a hand cart applies force on it in the following situations., What is the purpose, in each case, i. When he starts pulling the hand cart., Ans: To move the hand cart which is at the state of rest., ii. When it goes on a down hill., Ans: To decrease the speed of the hand cart., Iii. What are the changes force can bring about in the motion?, Ans: Set a body at rest in to motion, Stop a moving body, Change the direction of a moving body, Increase or decrease the speed of a moving body, 2. Which type of motion is dominant in the following situations?, i An aeroplane gaining speed on the runway before takeoff - Linear motion, ii. The motion of a valve tube in the rotating wheel of a bicycle - Circular, motion, iii Find one example each for other kinds of motion as well., Rotation – Spinning of a top, Oscillation – Motion of a pendulum, Vibration - Motion of the diaphragm of a drum, 3. The table on oscillation prepared by Lathika, Iqbal and Sonu is given, below., 2. Which type of motion is dominant in the following situations?, i An aeroplane gaining speed on the runway before takeoff - Linear motion, ii. The motion of a valve tube in the rotating wheel of a bicycle - Circular, motion, iii Find one example each for other kinds of motion as well., Rotation – Spinning of a top, Oscillation – Motion of a pendulum, Vibration - Motion of the diaphragm of a drum, 3. The table on oscillation prepared by Lathika, Iqbal and Sonu is given, below.
Page 7 :
i. Whose findings are correct?, Iqbal’s findings, ii. Which are the ones that cannot be considered as examples of, oscillation?, The motion of a giant wheel, The motion of an arrow, shot from a bow., iii. What is the difference between vibration and oscillation?, The to and fro motion of a body about a mean position is called oscillation., Fast oscillations are, referred to as vibrations. All vibrations are also oscillations, but all, oscillations are not vibrations., 4. Observe the arrangement of gears in the, figure., , i. When the first gear is rotated, which other gear, would also rotate in the same direction?, Gear number 3, ii. Which gear would be the slowest?, Gear number 1, 5. Complete the following concept map suitably.