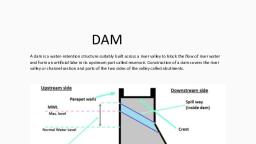
Page 1 :
UNIT : - 3 DAMS AND SPILLWAYS, 1. Gravity dam is most suitable when the foundation is _______________, a) weak, b) strong, c) with heavy overburden, d) rocky but cracked, View Answer, Answer: b, Explanation: A gravity dam is the one in which the stability against external load is achieved by the weight of the dam itself. This type of dam requires minimum maintenance. It can be constructed on any site where the natural foundation is strong enough to bear the weight of the dam., 2. Which of the following type of dam is built in areas where the foundation is not strong enough to bear the weight of concrete?, a) Rock-fill dam, b) Earth dam, c) Gravity dam, d) Arch dam, View Answer, Answer: b, Explanation: An earth dam is built up by compacting successive layers of the earth with vibrating or heavy machinery. It is built in areas where the earth is more easily available as compared to concrete or stone or rock., 3. Which of the following dam is partly earthen and partly rockfill?, a) Tehri dam, b) Koyna dam, c) Sardar Sarovar dam, d) Bhakra dam, View Answer, Answer: a, Explanation: The Koyna dam is a rubble-concrete dam which is built on Koyna River near Satara district in Maharashtra. The Sardar Sarovar Dam is a gravity dam on the Narmada River, Gujrat and Bhakra dam is also a concrete gravity dam., 5. In which of the following dam the weight of water is carried by a deck of RCC or by arches that share the weight burden?, a) Earth dams, b) Rockfill dams, c) A hollow masonry gravity dam, d) Timber dam, View Answer, Answer: c, Explanation: The Hollow Masonry Gravity dam contains less concrete or masonry (about 35 to 40%) than solid masonry gravity dam. They are difficult to build and the labor cost is too high to build its complex structure., 6. It is possible to construct steel dam only up to a height of ____________, a) 5 m, b) 10 m, c) 20 m, d) 50 m, View Answer, Answer: c, Explanation: Steel dams are not in common use and it is possible to build the dam up to a height of 18 to 20 m. They are used as coffer dams for the construction of permanent dams., 7. The temporary structures that are built to enclose certain worksite is ______________, a) storage dam, b) coffer dam, c) timber dam, d) steel dam, View Answer, Answer: b, Explanation: Coffer dams are temporary structures that are used to divert the flow to enable construction activity in the main river channel. It is also used to enclose certain work site. Steel and timber dams are also used as coffer dams., 8. Which of the following dam is suitable for narrow valleys?, a) Arch dam, b) Steel dam, c) Coffer dam, d) Timber dam, View Answer, Answer: a, Explanation: An arch dam is that dam in which stability of the dam against external forces is obtained partly due to the weight of the dam and partly due to transferring horizontal pressure to the abutments. The presence of sound abutments is an important requirement and is suitable for narrow valleys., 9. When sand and gravel foundation strata are available at a proposed dam site of moderate height, the dam may be of the type ________________, a) earthen or rockfill dam, b) masonry gravity dam, c) concrete gravity dam, d) double arch dam, View Answer, Answer: a, Explanation: The piles of loose rocks and boulders in the river bed are nothing but rockfill. On the upstream face of the dam, a slab of reinforced concrete is often laid to make it watertight., 10. According to the Hydraulic design, the dams are classified as _________, a) diversion and detention Dams, b) storage and diversion dams, c) overflow and non-overflow dam, d) arch and buttress dam, View Answer, Answer: c, Explanation: The dams are classified as Over-flow dam and Non-over flow dam according to the hydraulic design. When water flows over the crest of the dam it is known as the overflow dam. The dams which do not allow water to flow over the crest of the dam is called non-overflow dam., Sanfoundr, 5. In which of the following dam the weight of water is carried by a deck of RCC or by arches that share the weight burden?, a) Earth dams, b) Rockfill dams, c) A hollow masonry gravity dam, d) Timber dam, View Answer, Answer: c, Explanation: The Hollow Masonry Gravity dam contains less concrete or masonry (about 35 to 40%) than solid masonry gravity dam. They are difficult to build and the labor cost is too high to build its complex structure., 6. It is possible to construct steel dam only up to a height of ____________, a) 5 m, b) 10 m, c) 20 m, d) 50 m, View Answer, Answer: c, Explanation: Steel dams are not in common use and it is possible to build the dam up to a height of 18 to 20 m. They are used as coffer dams for the construction of permanent dams., 7. The temporary structures that are built to enclose certain worksite is ______________, a) storage dam, b) coffer dam, c) timber dam, d) steel dam, View Answer, Answer: b, Explanation: Coffer dams are temporary structures that are used to divert the flow to enable construction activity in the main river channel. It is also used to enclose certain work site. Steel and timber dams are also used as coffer dams., 8. Which of the following dam is suitable for narrow valleys?, a) Arch dam, b) Steel dam, c) Coffer dam, d) Timber dam, View Answer, Answer: a, Explanation: An arch dam is that dam in which stability of the dam against external forces is obtained partly due to the weight of the dam and partly due to transferring horizontal pressure to the abutments. The presence of sound abutments is an important requirement and is suitable for narrow valleys., 9. When sand and gravel foundation strata are available at a proposed dam site of moderate height, the dam may be of the type ________________, a) earthen or rockfill dam, b) masonry gravity dam, c) concrete gravity dam, d) double arch dam, View Answer, Answer: a, Explanation: The piles of loose rocks and boulders in the river bed are nothing but rockfill. On the upstream face of the dam, a slab of reinforced concrete is often laid to make it watertight., 10. According to the Hydraulic design, the dams are classified as _________, a) diversion and detention Dams, b) storage and diversion dams, c) overflow and non-overflow dam, d) arch and buttress dam, View Answer, Answer: c, Explanation: The dams are classified as Over-flow dam and Non-over flow dam according to the hydraulic design. When water flows over the crest of the dam it is known as the overflow dam. The dams which do not allow water to flow over the crest of the dam is called non-overflow dam., Sanfoundr, 5. In which of the following dam the weight of water is carried by a deck of RCC or by arches that share the weight burden?, a) Earth dams, b) Rockfill dams, c) A hollow masonry gravity dam, d) Timber dam, View Answer, Answer: c, Explanation: The Hollow Masonry Gravity dam contains less concrete or masonry (about 35 to 40%) than solid masonry gravity dam. They are difficult to build and the labor cost is too high to build its complex structure., 6. It is possible to construct steel dam only up to a height of ____________, a) 5 m, b) 10 m, c) 20 m, d) 50 m, View Answer, Answer: c, Explanation: Steel dams are not in common use and it is possible to build the dam up to a height of 18 to 20 m. They are used as coffer dams for the construction of permanent dams., 7. The temporary structures that are built to enclose certain worksite is ______________, a) storage dam, b) coffer dam, c) timber dam, d) steel dam, View Answer, Answer: b, Explanation: Coffer dams are temporary structures that are used to divert the flow to enable construction activity in the main river channel. It is also used to enclose certain work site. Steel and timber dams are also used as coffer dams., 8. Which of the following dam is suitable for narrow valleys?, a) Arch dam, b) Steel dam, c) Coffer dam, d) Timber dam, View Answer, Answer: a, Explanation: An arch dam is that dam in which stability of the dam against external forces is obtained partly due to the weight of the dam and partly due to transferring horizontal pressure to the abutments. The presence of sound abutments is an important requirement and is suitable for narrow valleys., 9. When sand and gravel foundation strata are available at a proposed dam site of moderate height, the dam may be of the type ________________, a) earthen or rockfill dam, b) masonry gravity dam, c) concrete gravity dam, d) double arch dam, View Answer, Answer: a, Explanation: The piles of loose rocks and boulders in the river bed are nothing but rockfill. On the upstream face of the dam, a slab of reinforced concrete is often laid to make it watertight., 10. According to the Hydraulic design, the dams are classified as _________, a) diversion and detention Dams, b) storage and diversion dams, c) overflow and non-overflow dam, d) arch and buttress dam, View Answer, Answer: c, Explanation: The dams are classified as Over-flow dam and Non-over flow dam according to the hydraulic design. When water flows over the crest of the dam it is known as the overflow dam. The dams which do not allow water to flow over the crest of the dam is called non-overflow dam., 9. The axis of a gravity dam is the ______________________, a) line of the crown of the dam on the downstream side, b) line of the crown of the dam on the upstream side, c) centre-line of the top width of the dam, d) line joining mid-points of the base, View Answer, Answer: b, Explanation: The axis of the dam is taken as the reference line which is defined separately in the plan and in the cross-section of the dam. In plan, it is the horizontal trace of the U/s edge of the top of the dam. In the cross-section, the vertical line passing through the U/s edge of the top of the dam is considered as the axis of the dam., 10. Presence of tail-water in a gravity dam ____________________, a) increases the principal stress and decreases the shear stress, b) increases both the principal stress and the shear stress, c) decreases the principal stress and increases the shear stress, d) decreases both the principal stress and the shear stress, View Answer, Answer: d, Explanation: The principal stress is given by the formula –, P = Pv sec(Φ)2 – p’ tan(Φ)2 where Pv is the intensity of vertical pressure and p’ is the tail-water pressure, The shear stress on the horizontal plane near the toe is given by –, S = (Pv – p’) tan(Φ), From both the equations, it is clear that the tail-water pressure is opposite in nature and it reduces the value of principal stress and shear stress., Sanfoundry Global Education & Learning Series – Irrigation Engineering., To practice all are, 1. In high dams, the safety against sliding should be checked only for friction., a) True, b) False, View Answer, Answer: b, Explanation: The safety against sliding should be checked only for friction in case of low dams and in high dams, the shear strength of the joint (i.e. an additional shear resistance) is also considered for economical design. The dam section is given an extra slope or batter on the U/s or D/s side as per requirements for achieving stability., 2. For full reservoir condition in a gravity dam, the critical combination of vertical and horizontal earthquake accelerations to be considered for checking the stability is ________________________, a) vertically upward and horizontally downstream, b) vertically downward and horizontally downstream, c) vertically upward and horizontally upstream, d) vertically downward and horizontally upstream, View Answer, Answer: b, Explanation: Horizontal inertia force should be considered to be acting at the center of the gravity of the mass regardless of the shape of cross-section and it acts horizontally downstream in worst cases under full reservoir case. This force would produce the worst results is it is additive to the hydrostatic water pressure (acting towards the downstream)., 8. A concrete gravity dam having a maximum reservoir level at 200 m and the RL of the bottom of the dam 100 m. The maximum allowable compressive stress in concrete is 3000 KN/m2 and the specific gravity of concrete is 2.4. Calculate the height of the dam and check whether it is a high dam or low dam., a) H = 90 m High gravity dam, b) H = 90 m Low gravity dam, c) H = 214.2 m High gravity dam, d) H = 214.2 m Low gravity dam, View Answer, Answer: a, Explanation: The limiting height of the dam is given by-, H = f / ϒw (Sc + 1) where f = allowable stress of dam material = 3000 KN/m2, Sc = 2.4, and ϒw = 9.81 KN/m2., H = 3000 / 9.81 x 3.4 = 89.9 m., This value is more than the height of the dam so it is a high gravity dam., 9. The axis of a gravity dam is the ______________________, a) line of the crown of the dam on the downstream side, b) line of the crown of the dam on the upstream side, c) centre-line of the top width of the dam, d) line joining mid-points of the base, View Answer, Answer: b, Explanation: The axis of the dam is taken as the reference line which is defined separately in the plan and in the cross-section of the dam. In plan, it is the horizontal trace of the U/s edge of the top of the dam. In the cross-section, the vertical line passing through the U/s edge of the top of the dam is considered as the axis of the dam., 10. Presence of tail-water in a gravity dam ____________________, a) increases the principal stress and decreases the shear stress, b) increases both the principal stress and the shear stress, c) decreases the principal stress and increases the shear stress, d) decreases both the principal stress and the shear stress, View Answer, Answer: d, Explanation: The principal stress is given by the formula –, P = Pv sec(Φ)2 – p’ tan(Φ)2 where Pv is the intensity of vertical pressure and p’ is the tail-water pressure, The shear stress on the horizontal plane near the toe is given by –, S = (Pv – p’) tan(Φ), From both the equations, it is clear that the tail-water pressure is opposite in nature and it reduces the value of principal stress and shear stress., Sanfoundry, 5. The most common vertical lift gates in modern days is _________________, a) sliding gates, b) free-roller gates, c) stoney gates, d) fixed wheel gates, View Answer, Answer: d, Explanation: The design and construction of free-roller gate are difficult as the rollers are not attached to the gate and the guide. Therefore, the rollers are attached to the gate. Large vertical lift gates are broken into two horizontal sections to reduce the load on the hoisting mechanism., 6. The working of Reinold’s gate is automatic., a) True, b) False, View Answer, Answer: a, Explanation: It is a rectangular gate fixed with rollers and it moves up and down along the upstream vertical face of the spillway. The gate is suspended by means of chains which pass over the pulleys and to the other end of the chains a counterweight is attached., 7. Which of the following gate is also called flush boards?, a) Dropping shutters, b) Tainter gates, c) Drum gates, d) Vertical lift gates, View Answer, Answer: a, Explanation: Dropping shutters are also called permanent flush boards. They are generally used to raise the water level by 1 to 1.25 m. This type consists of shutters or plates made of steel which are hinged at the bottom., 8. Which one of the following gate is not suitable for curved crests?, a) Flush boards, b) Tainter gates, c) Drum gates, d) Vertical lift gates, View Answer, Answer: a, Explanation: In flush boards, the shutters are hinged at the bottom and are supported by struts. Whenever the water level rises above the top of the shutters they dropdown. Hence they are not suitable for curved crests., 9. Which of the following gate works on the principle of counterweights against the water pressure?, a) Dropping shutters, b) Stop logs and needles, c) Stoney roller gate, d) Drum gates, View Answer, Answer: a, Explanation: In dropping shutters, the shutters are hinged at the bottom and are supported by struts and these shutters can be raised or lowered from an overhead cableway or a bridge. They work on the principle of counterweights against the water pressure., 10. ________________ are used only for very minor works., a) Dropping gates, b) Stop logs and needles, c) Rectangular gates, d) Drum gates, View Answer, Answer: b, Explanation: A Stop log consists of wooden beams and planks placed on to one another and leakage between them is a big problem. Needles are wooden logs kept side by side and it is very difficult to handle these logs at the time of flow. Hence they are not used on any major works., 11. Which of the following gate is not suitable for smaller spillways?, a) Drum gates, b) Radial gates, c) Needles and stop logs, d) Fixed roller gates, View Answer, Answer: a, Explanation: Drum gates are suitable for longer spans of the order of 40 m or so and medium heights of 10 m or so. The drum is enclosed on all the three sides as well as on the ends thus forming a water-tight vessel. It requires a large recess and is not suitable for small spillways., 1. In a fixed roller of a spillway gate, the rollers are attached to the __________________, a) gate, b) groove gate, c) either gate or groove gate, d) guide grooves, View Answer, Answer: a, Explanation: Rollers are generally attached to the gate and ride in tracks on the downstream side of the groove, 6. What is the recommended value of shear friction factor against sliding?, a) More than unity, b) Less than unity, c) More than 3 to 5, d) Less than 3, View Answer, Answer: c, Explanation: Shear Friction Factor is given by –, SFF = sliding factor (SF) + B.q / ∑Ph where B = width of joint or section area = B x 1, q is the shear strength of the joint, and Ph is the sum of horizontal force causing sliding. SF must be greater than 1 and SFF must be greater than 3 to 5. This analysis is carried out for a full reservoir case as well as an empty case., 2. In the vertical Stoney spillway gate, the rollers are placed between the ______________, a) gate and u/s groove guide, b) gate and the d/s groove guide, c) u/s and d/s groove guide, d) attached to the gate and groove guides, View Answer, Answer: b, Explanation: A train of the roller is generally placed in between the gate and the d/s guide. These rollers may be placed independent of the gate and the guide thus eliminating the axle friction but rolls vertically between the two when the gate is moved., 3. The spillway gate which when lowered cannot be seen from a distance is of the type ______________________, a) Sliding gate, b) Roller gate, c) Tainter gate, d) USBR drum gate, View Answer, Answer: d, Explanation: The system of drum gates consists of a segment of a cylinder which may be raised or lowered into the recess made into the top of the spillway. Whenever the drum is lowered, the surface becomes coincident with the designed ogee shape of the crest., 1. The provision of drainage gallery in a gravity dam helps in reducing ____________________, a) hydrostatic pressure, b) seepage pressure, c) silt pressure, d) both hydrostatic pressure and seepage pressure, View Answer, Answer: b, Explanation: An opening or passage left in the dam which runs longitudinally is called the gallery. This is to provide space for drainage of water percolating through the upstream face of the dam or seeping through the foundation. It is also used for inspection purposes and for the mechanical equipment used in the operation of gates in spillways., 2. Which of the following attempts are made to reduce the uplift in order to economize on the provided section of a concrete gravity dam?, i. Providing drainage gallery to collect seepage water, ii. Constructing cut-off under upstream face, iii. Pressure grouting in dam foundation, iv. Provision of shear keys or keyways, a) i and ii, b) i, ii and iii, c) i, ii and iv, d) i, ii, iii and iv, View Answer, Answer: b, Explanation: In a gravity dam, the grout curtain is provided near the toe to reduce the exit gradient. A drainage gallery with its drainage pipe system provided in gravity dam reduces the uplift pressure at all levels below the upstream water level. Vertical cut-off walls are the most effective to reduce seepage flow and uplift force., 3. Transverse joints in concrete gravity dams are the ___________________________, a) horizontal construction joints at each lift height, b) vertical construction joints of full height and width, c) diagonal construction joints for torsion, d) longitudinal construction joints of full width, View Answer, Answer: b, Explanation: Transverse joints are vertical joints that run through the entire height and extend through the full width of the dam section. These joints are continuous from the upstream face to the downstream face., 4. Leakage through the transverse joints in a gravity dam is prevented by ____________, a) shear keys, b) keyways, c) water stops, d) galleries, View Answer, Answer: c, Explanation: Water bars or water stops are provided in the transverse as well as horizontal joints in concrete adjacent to the upstream face of the dam. The openings of the joints are sealed properly with water stops to avoid passage of seepage of water through the body., 5. In order to reduce uplift on a gravity dam, the type of grouting done is ____________________, a) curtain grouting near the heel, b) consolidation grouting near the heel, c) curtain grouting near the toe, d) consolidation grouting near the toe, View Answer, Answer: a, Explanation: Curtain grouting helps in forming a principal barrier against the seepage through the foundations and thus reduces the uplift pressure. This grouting can be accomplished from the foundation gallery or from other galleries within the dam., 6. The general value of lift for concrete is taken as __________________, a) 1.5 m, b) 2.5 m, c) 3 m, d) 4 m, View Answer, Answer: a, Explanation: The concrete is poured from a certain height in the first attempt and this height is called a lift. Maximum height of single pour of concrete is usually about 1.5 m. If this is reduced, more horizontal joints will get developed., 7. The horizontal joints that extends through the entire width of the dam section and are developed at each lift height is called as ___________________, a) transverse joints, b) longitudinal joints, c) construction joints, d) contraction joints, View Answer, Answer: b, Explanation: The longitudinal joint is developed at each lift height and extends through the entire width of the dam section. These joints shall run through the entire length of the dam but are staggered between transverse joints., 8. Which of the following joints justifies the two-dimensional analysis of gravity dams?, a) Longitudinal joints, b) Transverse joints, c) Construction joints, d) Contraction joints, View Answer, Answer: b, Explanation: Transverse joints are vertical joints that divide the dam length into a number of vertical cantilevers each of which is independent of the other. It runs through the entire height and extends through the full width of the dam section. Hence, it justifies the two-dimensional analysis of gravity dams., 9. The foundation pressure used in the pressure grouting is equal to _________________, a) 2.0 D N/cm2, b) 2.5 D N/cm2, c) 5.0 D N/cm2, d) 3.0 D N/cm2, View Answer, Answer: b, Explanation: The grouting pressure is kept as high as possible without lifting the foundation strata and the pressure used in this grouting is equal to 2.5D. It is carried out only after some portion of the dam section is laid and is generally done in stages of depth equal to 15 m or so., 1. In high dams, the safety against sliding should be checked only for friction., a) True, b) False, View Answer, Answer: b, Explanation: The safety against sliding should be checked only for friction in case of low dams and in high dams, the shear strength of the joint (i.e. an additional shear resistance) is also considered for economical design. The dam section is given an extra slope or batter on the U/s or D/s side as per requirements for achieving stability., 2. For full reservoir condition in a gravity dam, the critical combination of vertical and horizontal earthquake accelerations to be considered for checking the stability is ________________________, a) vertically upward and horizontally downstream, b) vertically downward and horizontally downstream, c) vertically upward and horizontally upstream, d) vertically downward and horizontally upstream, View Answer, Answer: b, Explanation: Horizontal inertia force should be considered to be acting at the center of the gravity of the mass regardless of the shape of cross-section and it acts horizontally downstream in worst cases under full reservoir case. This force would produce the worst results is it is additive to the hydrostatic water pressure (acting towards the downstream)., 3. The base width of a solid gravity dam is 35 m and the specific gravity of dam material is 2.45. What is the approximate allowable height of the dam having an elementary profile without considering the uplift?, a) 64.68 m, b) 54.80 m, c) 164 m, d) 80 m, View Answer, Answer: b, Explanation: The base width at bottom is given by B = H/Sc1/2 (c = 0 since uplift is not considered)., B = 35 m and Sc = 2.45, Allowable height of the dam H = 35 x 2.451/2 = 54.8 m.