Page 2 :
SUSPENSION SYSTEM, Defination - The suspension system of an automobile is one which separates the wheel/axle Assembly, from the body, OR, All parts which perform the function of isolating the automobile from the road shocks are collectively, called a suspension system., The primary function of the suspension system is to isolate the vehicle structure from shocks and, vibration due to irregularities of the road surface, , Need of Suspension:, 1. For absorbing shocks and vibration caused due to road irregularities., 2. For transmitting vehicle load to the wheels (Supporting the weight), 3. For maintaining the stability of vehicle (contact of the wheels to ground), 4. For providing cushioning and ride comfort to the passengers, 5. For preventing body squat and body dive., , Functions:, To safe guard passengers and goods against road shocks, To preserve the stability of vehicles while in motion (Pitching or Rolling), To provide the wheels always in contact with road while driving cornering and braking, To maintain proper steering geometry, To provide suitable riding and cushioning properties, To Allow rapid cornering without extreme body roll, To prevent excessive body squat or body dive., , Requirements:, 1. There should be minimum deflection., 2. It should be of low initial cost., 3. It should be of minimum weight., 4. It should have low maintenance and low operating cost., 5. It should have minimum tyre wear., , Types of Suspension, Types of Suspension System
Page 3 :
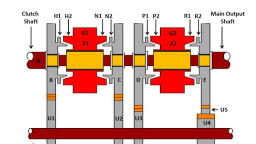
Rigid / Non independent, suspension System, , Independent Suspension System, , 1.Non-independent/Rigid suspension has both right and left wheel attached to the same solid axle., When one wheel hits a bump in the road, its upward movement causes a slight tilt of the other wheel., , 2.Independent suspension – The suspension system is separate for each wheel of the vehicle. It allows, one wheel to move up and down and other wheels has no effect , because each wheel is attached to its, own suspension units
Page 4 :
Components of Suspension System:, Springs, which neutralize the shocks from the road surface (Energy storage), Dampers, which act to improve comfort by limiting the free oscillation of the springs. (Energy, Dissipation), Stabilizer (sway bar or anti-roll bar), which prevents lateral swaying of the car., A linkage system, which acts to hold the above components in place and the control the longitudinal, and lateral movements of the wheels., , What is a leaf spring?, , , A leaf spring is a type of spring made by a number of plates (leaves) stacked upon each other in, increasing order of sizes. It is used to absorb shocks and vibrations in heavy commercial vehicles like, trucks, vans, buses etc., , Construction of Leaf spring-, , Following are the parts of leaf spring
Page 5 :
, , , , Metal plates or leaves, Central clamp, Rebound clips, , Flat metal plates or leaves- The leaf spring consists of a number of metal plates also known as, leaves layered upon each other in the decreasing order of their size. The leaves are given a curvature, called the camber which gives the leaf spring its semi-elliptic look., The master leaf has its ends rolled as shown in the figure. These rolled ends of the master leaf are, known as the eye., Just below the master leaf, another almost full-length leaf called the second master leaf and is placed to, support the master leaf. (refer figure) The remaining leaves are known as “graduated leaves“., , Central clamp, The central clamp’s function is to hold all the leaves together. It consists of U bolts and a central bolt so, that the leaves don’t fall apart., , Rebound clips, The rebound clips are made up of steel bands placed at a certain position on either side of the central, clamp and its main function is to prevent the leaf spring from failing during a rebound., A leaf spring usually does not break when it is compressed i.e. when the axle of the automobile, undergoes a bump. However, when the force is suddenly removed the leaf spring might fail., This is because when the spring is being compressed from below, each leaf is supported by the leaf, below it, but, when the load is suddenly released it would not find support if not for the rebound clips, which hold them together and provide support., , Assembly of leaf spring, The leaf spring is placed below the axle and U bolts are passed over the axle and the plate for U bolts is, placed below the leaf spring such that the leaf spring is sandwiched between the axle at the top and the, plate at its bottom when tightened. Refer to the figure given below.
Page 6 :
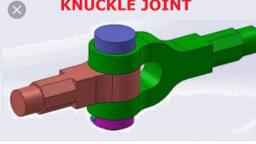
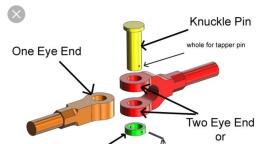
Out of the two eyes of the leaf spring, one eye is fixed whereas the other eye is connected to the, shackle. Both eyes are provided with bushings of an anti-friction material like rubber, brass, nylon, etc, , What is a leaf spring shackle?, The leaf spring shackle is a free-swinging part where one end of it is fixed to the frame and the other, part is connected to the eye of the leaf spring., , Working of leaf spring, When the vehicle goes over a bump, the axle tends to move up and down. However, as the leaf, spring is provided, it supports the axle and helps absorb the vibrations and shocks., Let us understand the working with an example!, Assume that a truck goes over a speed bump, this causes the wheel and the axle to be forced, upwards., So as the axle moves upwards, the leaf spring moves along with it but due to its semi-elliptical, shape and it absorbs as well as transfers the upward force to the chassis frame. (as shown in the, above image)., The shackle of the leaf spring helps it to expand when force is applied., , Types of leaf spring, The following are the different types of leaf springs:, , , , , , , Elliptic leaf spring, Semi elliptic leaf spring, Three quarter elliptic leaf spring, Quarter leaf spring, Transverse leaf spring
Page 7 :
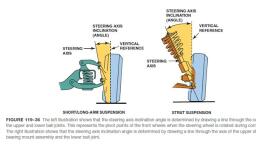
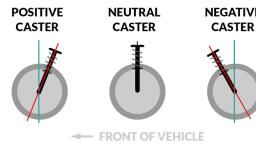
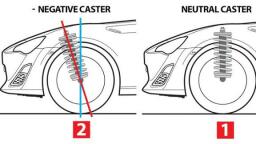
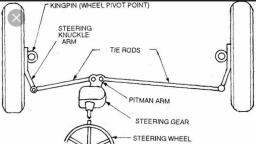
Advantages of leaf spring, The following are the advantages of leaf spring:, , , , , , , Leaf springs are light in weight and strong., It provides good damping action., It provides good support to the axle and the chassis., Leaf springs are simple in design., Leaf springs can withstand a large amount of load when compared to helical springs., , Applications of Leaf spring, The application of the leaf spring is to absorb shocks and vibrations in mostly heavy, commercial vehicles like trucks, vans, buses, railway carriages, etc., , Rigid Axle Front Suspension(construction and working), This type of suspension was universally used before the introduction of independent front wheel, suspension. It may use either two longitudinal leaf spring, as shown in the figure, or on transverse spring,, usually in conjunction with shock absorbers. These assemblies are mounted similar to rear leaf spring, suspensions., , In this type of suspension, the front wheel hubs rotate on antifriction bearings on steering spindle which, are attached to the steering knuckles. To permit the wheels to be turned by the steering gear, the steering, spindle and steering knuckle assemblies are hinged on the axle ends., The pin that forms the pivot of this hinge is usually referred to as the kingpin or steering knuckle pin., Where the forked portion is integral with the steering knuckle and fits over the end of the axle, the, construction is known as Reverse Elliot. In Elliot type construction, the ends of the axle are forked to hold, the steering knuckle extension between the ends., , AIR SUSPENSION SYSTEM
Page 8 :
Air springs are used in air suspension systems. The installation and configuration of air suspension systems, varies for different makes and models but the underlying principle remains the same. The metal spring, (coil or leaf) is removed, and an airbag also referred to as an air spring, is inserted or fabricated to fit in, the place of the factory spring. When air pressure is supplied to the airbag, the suspension can be adjusted, either up or down (lifted or lowered)., , It is used on many heavy-duty trucks, trailers, and buses on the road today, Characteristics of air springs:, 1. They are soft if the vehicle is not loaded but the stiffness increases when the load is increased by increasing the air pressure, inside the chamber. So, it gives the optimum riding comfort when the vehicle is lightly loaded and fully loaded conditions., 2. The height of the vehicle is kept constant by varying the air pressure whenever the load variation occurs., 3. Air springs increase vehicle stability by absorbing road shock., 4. Air spring systems are designed to maximize safe load-carrying capacity, stability, and overall ride quality., , Diagram Of Air Suspension System :, , Components Of Air Suspension System :, The components of the air suspension system are:, 1., , Air filter, , 2., , Air Accumulator, , 3., , Relief valve
Page 9 :
4., , Air spring, , 5., , Lift control valve, , 6., , Return valve, , 7., , Supply line, , Construction of Air Suspension :, The layout of an air suspension system has been shown in Fig. The four air springs, which may be either the bellows-type or the, piston type, are mounted on the same position where generally the coil springs are mounted. It also consists of an air, compressor, air accumulator, relief valve, lift control valve, leveling valve, and pipeline., , Working of Air Suspension :, An air compressor takes the atmospheric air through a filter and compresses it to a pressure of about 240 MPa, at which, pressure the air in the accumulator tank is maintained, which is also provided with a safety relief valve. This high-pressure air, goes through the lift control valve and the leveling valves, to the air springs as shown. Each air spring is filled with compressed, air which supports the weight of the vehicle. The air gets further compressed and absorbs the shock when the wheel, encounters a bump on the road., , Advantages of air suspension:, The advantage of air suspension is as follows:, 1) A variable space for wheel deflection is put to optimum use by virtue of the automatic control devices, 2) Because the vehicle altitude is also constant, changes in head lamp alignment due to varying loads are avoided., 3) The spring rate varies much less between the laden and unladen conditions, as compared with that of conventional steel spring. It reduces, the dynamic loading., 4) The improved standard of ride comfort and noise reduction attend with air springs reduces both driver and passenger fatigue., , Disadvantages of Air Suspension System :, Disadvantages of an air suspension system are as follows, , , , Higher initial cost, , , , Occupies more space., , , , The maintenance cost is more., , , , Due to lack of friction damping is necessary due to road shocks., , Application of Air suspension System :, The air suspension system is used in Modern Buses, Volvo, passenger cars, and trucks for comfort ride., , Difference Between Air Suspension System And Rigid Suspension System, Air Suspension System, , Rigid Suspension System, , 1. In this system air springs or air bellows are used, , 1. In this system leaf spring or coil spring or both are used., , 2. In air suspension system wheel deflection is controlled by automatic control devices., , 2 In this system there is no automatic control device., , 3. Increased riding comfort and decreased noise level., , 3 Riding comfort is less as compared to the air suspension system.
Page 10 :
Air Suspension System, , Rigid Suspension System, , 4. The springing rate varies much less between the laden and unladen conditions, as compared with, that of conventional springs., , 4. The springing rate is more as compared to the air suspension, system., , 5. Stiffness of the system increases with an increase in deflection., , 5. Stiffness of the system decreases with an increase in deflection., , 6. Application: Volvo bus, Luxury cars, , 6. Application: Heavy and medium-duty vehicles, passenger cars, etc., , 7. Reduced fatigue to the driver and passenger., , 7. More fatigue to the driver and passenger as compared to the air, suspension system., , 8. It consists of Compressor, reservoir, leveling valve, air springs or air bellows, etc., , 8. It consists of leaf spring, coil spring, shock absorber, shackle joint,, bracket, etc., , Types of Independent front suspension system, 1. Wishbone or Parallel link type., 2. Vertical guide type, 3. Trailing link type, 4. Macpherson strut type, 5. Swing half axle type., , Wishbone suspension system, , It is the most common type of independent suspension system., The use of coil springs with a damper in front axle is common in this type of suspension., The upper and lower wishbone arms are pivoted to the frame member.
Page 11 :
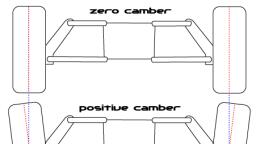
The spring is placed in between the lower wishbone and the under side of the cross member., The vehicle weight is transmitted from the body and the cross member to the coil spring, through which it goes to the lower wishbone member, -The shock absorber is placed inside the coil spring and is attached to the cross member and to, lower wishbone member., The wishbones not only position the wheels and transmit the vehicle load to the springs, but, these also resist acceleration, braking and cornering or side forces., The upper wishbone arm is generally kept shorter in length than the lower ones to keep the, wheel track constant and there by avoiding the excessive tyre wear., However a small change in the camber angle does occur with such an arrangement, , , There is no effect on one wheel while other wheel travels through ups and downs in the road., , VERTICAL GUIDE SUSPENSION-, , It is the first developed independent front suspension system. In this suspension the kingpin is directly, attached to the cross member of the frame and spacing rod. The coil spring is fitted as shown in the, figure., When the wheel travel over the, bumpy road, spring compress or expands and this makes the stub axle to slide up and down. In this type,, caster angle, camber angle and wheel direction are remained unchanged as the wheel moves up and, down.However, the disadvantage, is less strength., , Trailing link types, Construction, In this type of suspension system, coil springs are positioned between cross member and the trailing, link. On the other side of the trailing link, wheels are fixed. In some vehicles, torsion bars are used, instead of horizontal coil spring.
Page 12 :
Working principle, , When the vehicle wheel passing over the bumps and pits, trailing arm oscillates like a springboard. The, road disturbance is absorbed by spring deflection. Multiplate shock absorber is used to dissipate the, stored energy in spring. This type of suspension system usage is very limited in vehicles, it is because of, the maintenance and repair of this suspension system are complex in nature., , Mac Pherson Strut types, , The MacPherson strut, which is named after Earle S. MacPherson, who developed the suspension, design in the late 1940s and patented it in 1953, is the most commonly used type., In this layout only the lower wishbone is used., , A strut containing shock absorber and the coil spring also carries the stub axle on which the wheel is, mounted
Page 13 :
The wishbone is hinged to the cross member and positions the wheel as well as takes the, accelerating, braking and side forces., This system is simpler in construction, The camber angle does not tend to change as the wheel moves up and down., This system will give maximum room in the engine compartment and therefore commonly used in, the front wheel drive cars., This system with an anti roll bar provides increased road safety, improve ride comfort, light and self, stabilizing steering., , Swing half axle types, , Wheels are firmly fixed on one end of the half axle and the other end of the half axle is fixed to, the center, point of the chassis frame. Coil spring and shock absorber are mounted as shownnin the figure., When the wheel passes thenbumps and pits, axle get oscillates. As thenvehicle moves on the, irregular roads, coil spring and shock absorber are stretchednor compressed simultaneously to, take thenroad disturbances., , Telescopic Shock Absorber, Function of shock absorber:, The shock absorber is a part of suspension system used as springing device to compromise between flexibility and stiffness. It, absorbs the energy of shock converted into the vertical movement of the axle by providing damping and dissipating the same into, heat., , Purpose of shock absorber:, (i) To control the vibrations on springs., (ii) To provide a comfortable ride., (iii) To act flexible and to be rigid enough., (iv) To resist the unnecessary motion of the spring., , Construction of Shock Absorber :
Page 14 :
The upper eye of the telescopic shock absorber is attached to the axle and the lower eye is attached to the chassis, frame as shown in Figure 4.55. A two-way valve V1 is connected to a rod. Another one two-way valve V2 is, connected to the lower end of the cylinder. The fluid occupies in the space between above and below the valve VI, and also the annular space between the cylinder and tube. A gland is provided on the head. Fluid scrapped out by, the rod is brought down into the annular space through the inclined passage., , Working of Shock Absorber :, When the vehicle comes across a bump, the lower eye will move up. So, the fluid follows from the lower side of the valve V1 to the, upper side. Due to less volume of the space above valve V1 than the volume of the rod, the pressure is exerted on valve V2 Thus,, the damping force is produced by this pressure of the fluid. The fluid will flow from the upper side of the valve V1 to the lower side, when the lower eye moves down and from the lower side of the valve V2 to its upper side., When a car absorbs shocks from the road surface, the suspension springs will compress and expand because the spring has the, characteristic of continuing to oscillate for a long time of oscillation to stop. So, a riding comfort will be poor even the damp, oscillation is supplied. Shock absorbers provide better road-holding characteristics and improved steering stability to tires., , The stronger is the damping force, the more will be the oscillations of the body. But, the shock from the damping, effect becomes greater than the strength of the stronger damping force. The damping force varies with the speed, of the piston., , Types of shock absorbers:, 1. Mechanical shock absorber (friction type), 2. Hydraulic shock absorber, , ., , Again the hydraulic shock absorbers are further divided into various types., 1. Van type, 2. Piston type, a. Single-acting, b. Double acting, 3. Telescopic type., , Advantages of telescopic shock absorber:, , , , This shock absorber is available in various size according to the requirement., Noise free operation
Page 15 :
, , , , Less maintenance required., Low manufacturing cost., High operating speed.