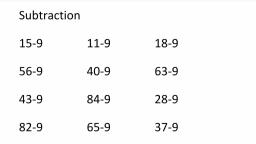
Page 1 :
PART-A, , zé, - GB ADAPTATIONS IN PLANTS, , Adaptation of plants in different habitats, , Adaptation of plants in * Mountains * Deserts » Marshes « Hot and damp soil « Plains, , Adaptation of plants « Floating plants « Fixed plants » Underwater plants, , Adaptation in plants in Saline soils__—_« Acidic soils, , , , @<Have you ever wondered why some plants, can grow only in soil and some others, survive only in water? Do you think they, must be different from each other in some, , ways?, Mountains, , Plants are found everywhere. You must have, seen them growing in deserts, ponds,, mountains and plains. Depending on the, surroundings where they grow, plants differ, , Desert from each other. Some can survive in hot, deserts whereas some can grow only in cold, regions. The kind of weather and soil that, plants need for their survival and growth is, called their habitat., , ame Did You Know?, Scientists have discovered that there are over 2,00,000, different types of plants all over the world., , Cerne, Coastal area Aplace with living conditions suitable for an organism, , _is known as its habitat., Different plants grow in different habitats
Page 2 :
PART-A, , © <Plants are found on land as well as in water., Broadly, the plants are divided into two groups, according to their habitat:, , ¢ Terrestrial plants: plants that grow on the land., ¢ Aquatic plants: plants that grow in water., , Terrestrial plants As different plants are found in different, surroundings, special features are developed by, the plants to adjust in these surroundings., These features are known as adaptations., , , , Adaptations are the reason why some plants, can survive in conditions where other plants, cannot. Let us study about different plants and, their adaptations., , i, , , , Aquatic plants, , pitas, , Features that help the organisms in surviving in different, kinds of habitats are called adaptations., , , , e@<TERRESTRIAL PLANTS, Plants growing on land are called terrestrial, plants. There are different types of habitats on, land, such as deserts and mountains. Let us, read how plants and trees adapt to such habitats., , (a) Plants in mountains: Mountain areas have, tall and straight plants. Trees like pines,, deodars and firs grow in the hills. They are, popularly known as coniferous trees or, conifers. There is heavy snowfall in winters, in hilly areas. Therefore, these trees have, long needle-like leaves from which snow, slips off easily. This helps them to survive in, freezing weather conditions. Coniferous, trees do not bear flowers but bear cones, which can withstand cold. Thick, woody and, straight stems of these trees with drooping, branches keep them from breaking away by, , Needle-like leaves and the cones of conifers heavy snowfall.
Page 3 :
Palm tree grows in deserts, , Cactus has spines and, fleshy green stems, , e@i<(b), , , , , , Mangroves grow in marshy areas, , , , Coconut tree grows near sea coast, , , , Banyan is a deciduous tree, , e@<(e), , PART-A, , Plants in deserts: The desert areas have very, few plants because of little rainfall. To prevent, the loss of water through stomata, the desert, plants have spines instead of leaves. Cactus,, palm and brittlebush are some of the plants, found here. As there are no leaves, the stem, of these plants is green, which helps in the, process of photosynthesis. The stem is also, fleshy and stores food and water for the plant., The roots of these plants are well developed, to reach underground water., , Plants in marshes: The marshy areas lie near, the seashore, where rivers empty into the sea., These areas are wet, humid and have clayey, soil with plenty of water. The plants found in, these areas are called mangroves. As the soil, is covered with water, the roots do not get air, to breathe and hence, they grow out of soil, and water. These roots are called breathing, roots. Kendelia and Ceriops are examples of, such plants., , Plants in hot and damp soil: The places near the, sea coasts are hot and damp. The plants, growing here need plenty of water and sunlight., The trees here have many leaves, and they do, not shed their leaves in winter. Therefore, they, are called evergreen trees. Some of the, evergreen trees are coconut, rubber, etc., , Plants in plains: The trees found in the plains, are deciduous trees. These trees can bear the, heat of summer and provide us shade., However, they shed their leaves in winter and, give us enough sunlight to protect us from, cold. Peepal, banyan, mango, gulmohar,, sheesham and sal are some of the deciduous, trees.
Page 4 :
PART-A, , SAQUATIC PLANTS, Did You Know? <cnrint —, sae neu ofiea ‘Aqua’ means water. Plants growing in water are, for many aquatic animals. called aquatic plants. As they live in water their, , leaves and other parts have thick waxy coating, to prevent water decay. Different types of plants, , <(a), , , , Water hyacinth - floating plant, , @4<(b), , , , , , Hydrilla - underwater plant, , grow in water. Some are fixed to the waterbed, while some float on the water surface. Some, plants remain completely submerged in water., Based on these characteristics, aquatic plants, are of the following types:, , Floating plants: As their name suggests,, these plants float on the water surface. For, example, duckweeds, water lettuces and, water hyacinths. They are small in size, light, in weight and their roots are not fixed to, the waterbed. The bodies of these plants, are usually spongy with lots of air spaces to, enable them to float. As they float on the, surface, they protect small water animals, from the heat of the Sun., , Fixed plants: Some aquatic plants have, small roots and are fixed to the waterbed,, at the bottom of the water bodies, for, example, water lilies and lotus plants. Water, lily has large saucer-shaped leaves and long, hollow stem. They help the plant to float, easily on water. Leaves have stomata on the, upper side only, to help in exchange of, gases. They also have a waxy, waterproof, coating to protect them from rotting., , Underwater plants: These plants remain, completely under water and hence are, called underwater or submerged plants., Pondweeds, hydrillas and tape grasses are, examples of such plants. Their roots remain, fixed at the bottom of the water body. Their, narrow, long, ribbon-like leaves move easily, with the flow of water.
Page 5 :
Did You Know?, , Some plants grow in, the areas where the, soil does not contain, , enough minerals., , , , , , Such plants eat insects to fulfill their, mineral requirements. They are known as, insectivorous plants. For example, Venus, flytraps, sundews and pitcher plants., , , , Cord grass survives in saline soil, , CEeeny, , Saline soil : Soil with high contents of salt., , , , Magnolias can survive in acidic soil, , Recap:, , | 1. A place with living conditions suitable for an 5., , organism is known as its habitat., , PART-A, , @<They have no stomata in their leaves and, , breathe through their body surface. They, remove carbon dioxide present in water,, released by other aquatic animals and hence,, keep the water bodies clean., , OTHER PLANTS, , Some of the members of plant kingdom can, survive in extremely saline soils. These plants, can tolerate high salt quantities in soil and do, not get dried up of water. Cord grass and salt, bush are the plants living in such conditions., These plants remove the extra salts in their, bodies by depositing them in the leaves which, later dry up and fall off the plant., , Similarly, some of the plants can live in acidic, soils. Magnolias and Rhododendrons grow well, in acidic soils as the acidity of soil does not, damage their bodies. They contain substances, to counter the acidity in their bodies., , So, the plant world is full of amazing plants, which are beautifully adapted to their habitats., This is the reason why the Earth has such a, great variety of plants all over it. We must, protect every member of the plant world to, admire these little wonders of nature., , Terrestrial plants grow in hills,, deserts, marshes, near sea coasts, , | 2. Plants are found in almost all the habitats found and plains., on the Earth. 6. Aquatic plants can be floating, fixed, 3. Plants that grow on land are called terrestrial or underwater., plants while plants which grow in water are called 7. Plants can survive in very tough, aquatic plants. conditions too., 4. Plants have different features to adjust in their 8. Some of the plants grow very well in, , surroundings. This is known as adaptation., , highly saline and acidic soils.