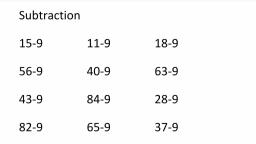
Page 1 :
PART-A, , ff ADAPTATIONS IN, S38 animats, , Adaptation of animals in different habitats, , * Adaptations in body structure Adaptations in body functioning, * Adaptations in behaviour, , ¢ Terrestrial Animals * Aquatic animals * Amphibians « Arboreal animals, Aerial animals > Migration, , *Herbivores * Carnivores »*Omnivores * Scavengers» Parasites, , Safety from predators through, * Strong legs * Big size * Hard shells, , , , @ <Fishes live in water. Can we live in water the, way they do? Have you ever wondered why, fishes can live in water and we can’t?, , As a very young kid, you must have heard and, enacted the following hindi rhyme, C0 Beet set At Wit =, sat Saar oF &, Bet TUS, St SIT, amet Pravet, ae sient’?, , Although it is just a nursery rhyme, it tells us, about the life of a fish. The body of fish is, suitable for living in water., , A place with suitable living conditions for an, organism is known as its habitat. For example,, water is the habitat of fish and it cannot live, without water. Not only fish, but all the animals on, Earth are suited to live in their particular habitats.
Page 2 :
Streamlined body of the fish makes, swimming easier, , Did You Know?, Some animals like tortoises and snails, - have hard shells to protect themselves, from their enemies. Whenever they sense, _ danger they hide inside their shells., , Arctic fox, , , , Ground squirrel, , PART-A, , <But the question is why is the habitat of an, , organism best suited for its survival? What special, features do fishes have to be able to survive in, water which we do not have?, , Fishes have fins to swim, a streamlined body for, easy movement, scales on body to prevent decay, from water and gills to breathe in water. These, special features that help fish to live in water are, , called adaptations. Animals develop special, features to adjust and survive in different, , conditions or environments., , “@@<ADAPTATIONS, , Every animal has specific features which enable it, to survive in its habitat. Adaptations help the, animal to survive and flourish in its habitat., Without adapting, organisms cannot survive., , Types of Adaptations, , Adaptations are of three types:, , (a) Adaptations in body structure of an organism:, In many animals, the shape, size or colour of, their bodies change to fit better in their habitat., For example, animals like polar bear and Arctic, fox have white coloured fur which helps them, in hiding in snow., , (b) Adaptations in body functioning of an, organism: Over a period of time, some, animals change the way their body functions., In such cases, we say that the animal has, adapted its body functioning. For example,, desert rats do not sweat thereby preventing, water loss. This makes them fit for dry,, desert conditions., , (c) Adaptations in behaviour of an organism: If, an animal changes the way it acts to stay, alive, we say that it has adapted its behaviour, according to the habitat. For example, ground, squirrel remains inactive during harsh winters.
Page 3 :
PART-A, , <Most animals have a combination of all three, types of adaptations to help them fit better in, their habitat. Let us study some cases in detail., , ADAPTATIONS BASED ON HABITATS, , Land, water and air are the three main habitats., eas | On the basis of their habitats, animals can be, , Classified as terrestrial, aquatic, amphibians,, arboreal and aerial., , Terrestrial, , a Terrestrial Animals, f _ Amphibian The animals that live on land are known as, , _— Arboreal terrestrial animals. Some of the commonly, , Aerial known terrestrial animals are lions, tigers,, camels, goats, zebras, polar bears, snakes,, lizards and earthworms. These may be living, either on the surface or in burrows below the, Earth's surface., , Most of the terrestrial animals have welldeveloped sense organs. These help them to, search for food and protect themselves from, their enemies. Also, terrestrial animals have, lungs to breathe in oxygen. Many terrestrial, animals have strong legs to run fast while some, have horns to fight., , Animals living in forests, like lions and tigers, have strong legs which help them to run and, catch their prey. On the other hand, deer and, zebras use their strong legs to run away from, their enemies, to protect themselves., , Animals that live in cold regions, like polar, bears, Arctic foxes and yaks, have a thick and, Thick fur hairy coat on their bodies. It protects them from, cold. Mountain goats are adapted to climb up, sma) and down the slopes of hills. They have small,, hooves clivided hooves that make them good climbers., , A mountain goat has a thick coat and, , , , , , , , , , , i \, 7}, , , , Terrestrial Animal - Deer, , small hooves to climb
Page 4 :
Frogs are hibernating, , Thick skin Fat, , in the hump, , Padded and broad feet, , A camel is adapted to hot conditions, of a desert, , , , Gill filaments, , A fish breathes through gills, , , , PART-A, , <A very special adaptation is found in the animals, which live in extremely cold habitats. This is called, hibernation, in which they sleep throughout winter., , These animals eat very well during summer and, store a lot of fat in their bodies. During hibernation,, they keep alive by using this stored fat. Frogs and, lizards are some hibernating animals., , Animals that live in hot desert areas, like camels,, have padded hooves to move fast in hot sand. They, have thick skin that protects them from the extreme, heat of the Sun during the day and also from cold, at night. It also prevents loss of water through their, skin. A camel can survive without water and food, for some time by using the fat stored in its hump., , Reptiles like snakes do not have legs but have, scales which help them to move., , , , A snake crawls through scales, , Aquatic Animals, The animals that live in water are known as aquatic, animals. These may be living either in water or near, water. Fishes, octopuses, whales, ducks, crabs,, turtles and seals are some of the aquatic animals., Bodies of aquatic animals are waterproof so that, water does not damage their body parts., , Fishes have boat-shaped (streamlined) body, tail, and fins which enable them to swim in water., They breathe in oxygen dissolved in water through, their gills.
Page 5 :
PART-A, , @@ Whales and dolphins are also aquatic animals, but they have lungs to breathe in oxygen. They, come to the surface of water to take in oxygen, from air., , Water birds like ducks live, near water. They have, webbed feet which help, them in swimming. Turtles, have paddle-like limbs to, swim in water., , , , , , , A turtle has paddle-like limbs, , e@<Amphibians, , The animals that can live both on land, , and in water are known as amphibians., , Frogs, toads, salamanders and newts are, ‘ fs : some amphibians. These animals have, , - Seas > multiple organs to breathe. They breathe, , Sslemander hes multiple organs to breathe through lungs on land and through their, moist skin in water., , Frogs are the most well, known amphibians. They, move on land with their legs, and swim in water with the, help of their webbed feet., , /, , , , Frogs can live both on land, and in water, , @<Arboreal Animals, , The animals that spend most of their time on, trees are known as arboreal animals. Monkeys,, tree lizards, squirrels (tree squirrels and flying, squirrels), chameleons and koalas are some of, the arboreal animals., , They have strong limbs (arms and legs) and, muscular tails to climb up and down the trees, , . 2 < and branches. Monkeys use their tails to swing, A monkey has strong limbs and a muscular tail from trees.