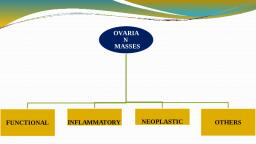
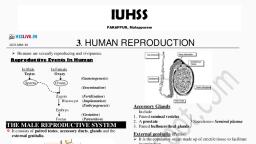
Page 1 :
oY 4G, 1:24PM Zr © Bl Bal GO, Hlanoveroe OLpia GIG CUrmuiny Wate Hr ure Upper vaynia mn, , about 46 % of cases; however, these septa can also be identified in, the mid (40 %) or lower (14 %) vagina [16]. Patients are usually, asymptomatic, presenting only at the onset of menses or later in life, due to dyspareunia. MR imaging is used to determine the thickness, of the septum and differentiate a high septum from congenital, absence of the cervix. Longitudinal vaginal septum occurs either, secondary to failure of fusion of the mullerian ducts or incomplete, resorption of the vaginal septum [17]. Longitudinal vaginal septa, usually occurs in combination with uterine anomalies, mostly uterus, didelphys. On MR imaging longitudinal septum appears as a thin,, dark T2 signal structure separate from the high T2 signal vaginal, mucosa., , , , , , , , , , , Transverse, vaginal septum, , Logitudinal, vaginal septum, , Imperforate hymen, , Fig. 27.21 Classification of vaginal anomalies, , , , Endometrium, , Endometrium is the innermost glandular lining of the uterus. The, endometrium demonstrates a wide spectrum of normal, morphological appearances during the prepubertal years, menarche,, and postmenopausal years. Hence, it is pertinent to evaluate and, interpret the endometrial appearance in lieu of the patient’s age,, stage of the menstrual cycle, coexistent medical illnesses, and drug, therapy. At birth, the endometrium appears as a thin line, with or, without distension of the endometrial canal [18]. On achieving, , a @ <q