Page 1 :
COURSE TITLE, COURSE CODE, COURSE CATEGORY, PERIODS PER WEEK, PERIODS PER SEMESTER, CREDITS, , : DIGITAL ELECTRONICS, : 3042, :B, :4, : 60, :4, TIME SCHEDULE, , MODULE, 1, 2, 3, 4, , TOPIC, , PERIODS, 15, , Number systems and logic gates, , 15, , Logic families and combinational logic circuits, , 15, , Sequential logic circuits, , 15, , Counters, ADC and DAC, TOTAL, , Course Outcome :, MODULE, , GO, , 1, , 2, , 3, , 4, , On completion of the study of this course the students will be able:, , 1, , To understand various number systems, , 2, , To understand the simplification of Boolean expressions, , 3, , To comprehend various logic families, , 4, , To understand combinational logic circuits, , 5, , To understand the working of flip-flops, , 6, , To comprehend shift registers, , 7, , To understand the working of various counters, , 8, , To understand ADC and DAC, , GO - General Outcome, , Specific outcome:, MODULE I Number system and logic gates, 1.1.0 To understand various number systems, 1.1.1 To state the need of a binary number system in modern digital technology, 1.1.2 To describe the features of a binary number system with examples, 1.1.3 To compare binary number system with decimal number system, 1.1.4 To explain the conversion from decimal to binary and vice versa with suitable examples, , 60
Page 2 :
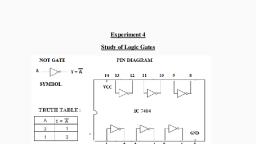
1.1.5, 1.1.6, 1.1.7, 1.1.8, , To list the features of Hexadecimal number system with suitable examples, To explain the Conversion of hexadecimal into decimal and binary and vice versa, To state the need for binary codes, To describe BCD codes, excess-3 code, Gray code, 1.1.9 To describe alpha numeric codes such as ASCII code and EBCDIC, 1.1.10 To explain binary arithmetic such as addition, subtraction, multiplication and division, with examples, 1.1.11 To explain binary subtraction using 1's complement and 2's complement method, , 1.2.0, , To understand the simplification of Boolean expressions, 1.2.1 To explain the operation of AND, OR, NOT, NAND, NOR, EXOR and EXNOR with their, symbols and truth tables, 1.2.2 To realize AND,OR, NOT, EXOR and EXNOR using universal gates, 1.2.3 To state Demorgan's theorems, 1.2.4 To state the rules and laws of Boolean algebra, 1.2.5 To explain Sum Of Product (SOP) expression, Product Of Sum (POS) expression ,, minterms and maxterms, 1.2.6 To state the need for simplifying Boolean expression, 1.2.7 To simplify Boolean expressions with the help of logic rules and truth tables, 1.2.8 To state the basic principle of Karnaugh map, 1.2.9 To explain two variables, three variables and four variables K-maps and their, reductions with the help of suitable examples, 1.2.10 To state Don’t care terms and their role in solving K-maps, 1.2.11 To list the advantages and disadvantages of K-map, , MODULE II Logic families and combinational logic circuits, 2.1.0 To comprehend the various logic families, 2.1.1 To state various scales of Integration- SSI, MSI, LSI, VLSI and ULSI, 2.1.2 To explain the circuit of TTL inverter, 2.1.3 To define the terms VIL, VIH, VOL, VOH, Noise margin, noise immunity, propagation, delay, fan- in and fan-out, 2.1.4 To explain the working principle of CMOS NAND gate, 2.1.5 To list the features of CMOS logic family, 2.1.6 To list the features of ECL logic family, 2.1.7 To compare TTL, ECL and CMOS logic families with respect to current sourcing and, current sinking, fan in, fan-out and power dissipation, 2.2.0, 2.2.1, 2.2.2, 2.2.3, 2.2.4, 2.2.5, 2.2.6, , To understand the combinational logic circuits, To describe combinational logic circuits, To design half adder, full adder, half subtractor, and full subtractor, To explain parallel adder, To explain the operation of 4x1 Multiplexer and 1x4 De-multiplexer, To list the various applications of Multiplexers and De-multiplexers, To explain the operation of 3 bit encoder
Page 3 :
2.2.7, , To explain various decoders such as BCD to decimal, binary to gray code and gray to, binary, , MODULE III Sequential logic circuits, 3.1.0, 3.1.1, 3.1.2, 3.1.3, 3.1.4, 3.1.5, 3.1.6, 3.1.7, 3.1.8, 3.1.9, 3.2.0, , To understand the working of flip-flops, To describe sequential logic circuits, To distinguish between synchronous and asynchronous sequential logic circuits, To explain latches & flip-flops, To explain SR flip flop using NAND & NOR gates, To explain JK flip-flop using NAND with the help of truth table, To state the race around condition in JK flip flop, To list the methods for eliminating race around condition, To explain the working of master slave JK flip flop (block level explanation only), To explain D and T flip flops with their characteristic tables, To comprehend shift registers, 3.2.1 To explain the functions of Shift registers, 3.2.2 To explain the working of shift registers:-serial-in serial-out, parallel-in parallel-out,, parallel-in, serial-out and serial- in parallel-out, 3.2.3 To differentiate between right shift and left shift registers, 3.2.4 To explain the working of ring counter and its applications, 3.2.5 To explain the working of Johnson counter and its applications, , MODULE IV Counters, ADC and DAC, 4.1.0, 4.1.1, 4.1.2, 4.1.3, 4.1.4, 4.2.0, 4.2.1, 4.2.2, 4.2.3, 4.2.4, , To understand the working of various counters, To differentiate between synchronous and asynchronous counters, To implement mod-10 asynchronous counter using JK flip flop, To explain mod-8 synchronous counter and its realization using JK flip flop, To explain 3 bit up-down counter using JK flip flop, To understand ADC and DAC, To list the different types of ADC and DAC, To state DAC specifications - resolution, accuracy and settling time, To explain Weighted resistor DAC and R-2R ladder type DAC, To explain different types of ADCs - Counter type, Successive approximation type and Flash type, , CONTENT DETAILS, MODULE I - Number systems and logic gates, Number systems - decimal, binary and hexa decimal number systems - conversion - use of binary codes types of binary codes - binary coded decimal, excess 3 code, gray code, ASCII code and EBCDIC - binary, addition, subtraction, multiplication and division - 1’s complement and 2’s complement subtraction -
Page 4 :
introduction to logic gates - AND, OR, NOT, NAND, NOR, EX-OR and EX-NOR operations - universal, property of NAND and NOR gates - realization of AND, OR, NOT, EX-OR and EX-NOR - laws of boolean, algebra and De-morgan's theorems - Sum Of Products (SOP) expression, Product Of Sum (POS), expression - min term and max term - simplification of boolean expressions using logic rules - truth, tables - Karnaugh map - 2, 3, 4 variables - K-map reduction - don't cares in K-map, MODULE II - Logic families and combinational logic circuits, Logic families - SSI, MSI, LSI, VLSI and ULSI - transistor transistor logic - VIL, VIH, VOL, VOH, noise margin,, noise immunity, propagation delay, fan-in and fan-out - TTL inverter - features of CMOS logic gates and, ECL logic family - comparison of TTL, ECL and CMOS logic families with respect to current sourcing and, current sinking, fan in, fan-out and power dissipation - combinational logic circuits - introduction design half adder, full adder, half subtractor and full subtractor - parallel adder-multiplexer / data, selector - 4 to 1 MUX - applications of MUX - demultiplexer - 1 to 4 demultiplexer - 3 bit encoder decoders - BCD to decimal, binary to gray code and gray to binary, , MODULE III - Sequential logic circuits, Sequential logic circuits - introduction - synchronous and asynchronous sequential logic circuits - SR flip, flop - SR latch - SR flip flop using NAND & NOR gates - JK flip flop with preset and clear inputs - D flip flop, - T flip flop - master slave JK flip-flop - flip flop IC 7476 - shift registers - serial in serial out, parallel in, parallel out, serial in parallel out, parallel in serial out shift registers - left shift and right shift registers applications of shift registers - ring counter - Johnson counter, MODULE IV - Counters, ADC and DAC, Binary counters - implementation of asynchronous mod-10 counter - implementation of mod-8, synchronous counter - 3-bit up down counter - DAC - specifications - resolution, accuracy, settling time different types - binary weighted resister method and R-2R ladder type - ADC - counter type successive approximation type - flash type, TEXT BOOKS, 1. M Morris Mano and Michael Cilettio - Digital Design - Pearson- 5th Edition, 2. Floyd and Jain -Digital Fundamentals - Pearson- 8th Edition, 3. Malvino and Leach -Digital Principles and Applications - Tata McGraw-Hill, REFERENCE, 1. A Anand Kumar- Fundamentals of digital circuits PHI, 2. Anil K Maini -Digital Electronics .Weiley