Page 1 :
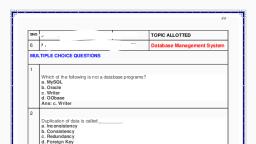
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, 1. A relational database consists of a, collection of, a) Tables, b) Fields, c) Records, d) Keys, , 4. The term attribute refers to a, ___________ of a table., a) Record, b) Column, c) Tuple, d) Key, , Answer: a, Explanation: Fields are the column of, the relation or tables. Records are, each row in a relation. Keys are the, constraints in a relation., , Answer: b, Explanation: Attribute is a specific, domain in the relation which has, entries of all tuples., , 2. A ________ in a table represents a, relationship among a set of values., a) Column, b) Key, c) Row, d) Entry, , 5. For each attribute of a relation,, there is a set of permitted values,, called the ________ of that attribute., a) Domain, b) Relation, c) Set, d) Schema, , Answer: c, Explanation: Column has only one set, of values. Keys are constraints and, row is one whole set of attributes., Entry is just a piece of data., , Answer: a, Explanation: The values of the, attribute should be present in the, domain. Domain is a set of values, permitted., , 3. The term _______ is used to refer, to a row., a) Attribute, b) Tuple, c) Field, d) Instance, , 6. Database __________ which is the, logical design of the database, and, the database _______ which is a, snapshot of the data in the database, at a given instant in time., a) Instance, Schema, b) Relation, Schema, c) Relation, Domain, d) Schema, Instance, , Answer: b, Explanation: Tuple is one entry of the, relation with several attributes which, are fields., , 2
Page 2 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, Answer: d, Explanation: Instance is an instance, of time and schema is a, representation., 7. Course(course_id,sec_id,semester), Here the course_id,sec_id and, semester are __________ and course, is a _________, a) Relations, Attribute, b) Attributes, Relation, c) Tuple, Relation, d) Tuple, Attributes, Answer: b, Explanation: The relation course has, a set of attributes, course_id,sec_id,semester ., 8. Department (dept name, building,, budget) and Employee (employee_id,, name, dept name, salary), Here the dept_name attribute, appears in both the relations. Here, using common attributes in relation, schema is one way of relating, ___________ relations., a) Attributes of common, b) Tuple of common, c) Tuple of distinct, d) Attributes of distinct, Answer: c, Explanation: Here the relations are, connected by the common attributes., , 3, , 9. A domain is atomic if elements of, the domain are considered to be, ____________ units., a) Different, b) Indivisbile, c) Constant, d) Divisible, Answer: b, Explanation: None., 10. The tuples of the relations can be, of ________ order., a) Any, b) Same, c) Sorted, d) Constant, Answer: a, Explanation: The values only count., The order of the tuples does not, matter., 11. Which one of the following is a, set of one or more attributes taken, collectively to uniquely identify a, record?, a) Candidate key, b) Sub key, c) Super key, d) Foreign key, Answer: c, Explanation: Super key is the superset, of all the keys in a relation.
Page 3 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, 12. Consider attributes ID, CITY and, NAME. Which one of this can be, considered as a super key?, a) NAME, b) ID, c) CITY, d) CITY, ID, , 15. Which one of the following, attribute can be taken as a primary, key?, a) Name, b) Street, c) Id, d) Department, , Answer: b, Explanation: Here the id is the only, attribute which can be taken as a key., Other attributes are not uniquely, identified., , Answer: c, Explanation: The attributes name,, street and department can repeat for, some tuples. But the id attribute has, to be unique. So it forms a primary, key., , 13. The subset of a super key is a, candidate key under what condition?, a) No proper subset is a super key, b) All subsets are super keys, c) Subset is a super key, d) Each subset is a super key, Answer: a, Explanation: The subset of a set, cannot be the same set. Candidate, key is a set from a super key which, cannot be the whole of the super set., 14. A _____ is a property of the entire, relation, rather than of the individual, tuples in which each tuple is unique., a) Rows, b) Key, c) Attribute, d) Fields, Answer: b, Explanation: Key is the constraint, which specifies uniqueness., , 4, , 16. Which one of the following, cannot be taken as a primary key?, a) Id, b) Register number, c) Dept_id, d) Street, Answer: d, Explanation: Street is the only, attribute which can occur more than, once., 17. An attribute in a relation is a, foreign key if the _______ key from, one relation is used as an attribute in, that relation., a) Candidate, b) Primary, c) Super, d) Sub, Answer: b, Explanation: The primary key has to
Page 4 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, be referred in the other relation to, form a foreign key in that relation., , d) Primary, , 18. The relation with the attribute, which is the primary key is referenced, in another relation. The relation, which has the attribute as a primary, key is called, a) Referential relation, b) Referencing relation, c) Referenced relation, d) Referred relation, , Answer: a, Explanation: A relation, say r1, may, include among its attributes the, primary key of another relation, say, r2. This attribute is called a foreign, key from r1, referencing r2. The, relation r1 is also called the, referencing relation of the foreign, key dependency, and r2 is called the, referenced relation of the foreign, key., , Answer: b, Explanation: None., 19. The ______ is the one in which, the primary key of one relation is, used as a normal attribute in another, relation., a) Referential relation, b) Referencing relation, c) Referenced relation, d) Referred relation, Answer: c, Explanation: None., 20. A _________ integrity constraint, requires that the values appearing in, specified attributes of any tuple in, the referencing relation also appear, in specified attributes of at least one, tuple in the referenced relation., a) Referential, b) Referencing, c) Specific, , 5, , 21. Using which language can a user, request information from a, database?, a) Query, b) Relational, c) Structural, d) Compiler, Answer: a, Explanation: Query language is a, method through which the database, entries can be accessed., 22. Student(ID, name, dept name,, tot_cred), In this query which attributes form, the primary key?, a) Name, b) Dept, c) Tot_cred, d) ID
Page 5 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, Answer: d, Explanation: The attributes name,, dept and tot_cred can have same, values unlike ID., 23. Which one of the following is a, procedural language?, a) Domain relational calculus, b) Tuple relational calculus, c) Relational algebra, d) Query language, Answer: c, Explanation: Domain and Tuple, relational calculus are non-procedural, language. Query language is a, method through which database, entries can be accessed., 24. The_____ operation allows the, combining of two relations by, merging pairs of tuples, one from, each relation, into a single tuple., a) Select, b) Join, c) Union, d) Intersection, Answer: b, Explanation: Join finds the common, tuple in the relations and combines it., 25. The result which operation, contains all pairs of tuples from the, two relations, regardless of whether, their attribute values match., a) Join, , 6, , b) Cartesian product, c) Intersection, d) Set difference, Answer: b, Explanation: Cartesian product is the, multiplication of all the values in the, attributes., 26. Which one of the following is, used to define the structure of the, relation, deleting relations and, relating schemas?, a) DML(Data Manipulation Langauge), b) DDL(Data Definition Langauge), c) Query, d) Relational Schema, Answer: b, Explanation: Data Definition language, is the language which performs all, the operation in defining structure of, relation., 27. Which one of the following, provides the ability to query, information from the database and to, insert tuples into, delete tuples from,, and modify tuples in the database?, a) DML(Data Manipulation Langauge), b) DDL(Data Definition Langauge), c) Query, d) Relational Schema
Page 6 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, Answer: a, Explanation: DML performs the, change in the values of the relation., , CREATE TABLE employee (name, VARCHAR, id INTEGER), , 30. The basic data type char(n) is a, _____ length character string and, varchar(n) is _____ length character., a) Fixed, equal, b) Equal, variable, c) Fixed, variable, d) Variable, equal, , What type of statement is this?, a) DML, b) DDL, c) View, d) Integrity constraint, , Answer: c, Explanation: Varchar changes its, length accordingly whereas char has, a specific length which has to be filled, by either letters or spaces., , Answer: b, Explanation: Data Definition language, is the language which performs all, the operation in defining structure of, relation., , 31. An attribute A of datatype, varchar(20) has the value “Avi”. The, attribute B of datatype char(20) has, value ”Reed”. Here attribute A has, ____ spaces and attribute B has ____, spaces., a) 3, 20, b) 20, 4, c) 20, 20, d) 3, 4, , 28., , 29., SELECT * FROM employee, What type of statement is this?, a) DML, b) DDL, c) View, d) Integrity constraint, Answer: a, Explanation: Select operation just, shows the required fields of the, relation. So it forms a DML., , 7, , Answer: a, Explanation: Varchar changes its, length accordingly whereas char has, a specific length which has to be filled, by either letters or spaces., 32. To remove a relation from an SQL, database, we use the ______, command.
Page 7 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, a) Delete, b) Purge, c) Remove, d) Drop table, Answer: d, Explanation: Drop table deletes the, whole structure of the relation .purge, removes the table which cannot be, obtained again., 33., DELETE FROM r; //r - relation, This command performs which of the, following action?, a) Remove relation, b) Clear relation entries, c) Delete fields, d) Delete rows, , c) Relational, d) DDL, Answer: b, Explanation: The values are, manipulated. So it is a DML., 35. Updates that violate __________, are disallowed., a) Integrity constraints, b) Transaction control, c) Authorization, d) DDL constraints, Answer: a, Explanation: Integrity constraint has, to be maintained in the entries of the, relation., 36., , Answer: b, Explanation: Delete command, removes the entries in the table., , Name, , 34., , Bob, , INSERT INTO instructor VALUES, (10211, ’Smith’, ’Biology’, 66000);, , Callie, , What type of statement is this?, a) Query, b) DML, , 8, , Annie, , Derek, Which of these query will display the, the table given above ?, a) Select employee from name, b) Select name
Page 8 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, c) Select name from employee, d) Select employee, Answer: c, Explanation: The field to be displayed, is included in select and the table is, included in the from clause., 37. Here which of the following, displays the unique values of the, column?, SELECT ________ dept_name, FROM instructor;, a) All, b) From, c) Distinct, d) Name, Answer: c, Explanation: Distinct keyword selects, only the entries that are unique., 38. The ______ clause allows us to, select only those rows in the result, relation of the ____ clause that, satisfy a specified predicate., a) Where, from, b) From, select, c) Select, from, d) From, where, Answer: a, Explanation: Where selects the rows, on a particular condition. From gives, , 9, , the relation which involves the, operation., 39. The query given below will not, give an error. Which one of the, following has to be replaced to get, the desired output?, SELECT ID, name, dept name, salary, * 1.1, WHERE instructor;, a) Salary*1.1, b) ID, c) Where, d) Instructor, Answer: c, Explanation: Where selects the rows, on a particular condition. From gives, the relation which involves the, operation. Since Instructor is a, relation it has to have from clause., 40. The ________ clause is used to, list the attributes desired in the result, of a query., a) Where, b) Select, c) From, d) Distinct, Answer: b, Explanation: None, 41. This Query can be replaced by, which one of the following?
Page 9 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, SELECT name, course_id, FROM instructor, teaches, WHERE instructor_ID= teaches_ID;, a) Select name,course_id from, teaches,instructor where, instructor_id=course_id;, b) Select name, course_id from, instructor natural join teaches;, c) Select name, course_id from, instructor;, d) Select course_id from instructor, join teaches;, Answer: b, Explanation: Join clause joins two, tables by matching the common, column., 42., SELECT * FROM employee WHERE, salary>10000 AND dept_id=101;, Which of the following fields are, displayed as output?, a) Salary, dept_id, b) Employee, c) Salary, d) All the field of employee relation, Answer: d, Explanation: Here * is used to select, all the fields of the relation., 43., , 10, , Employee_id, , Name, , Salary, , 1001, , Annie, , 6000, , 1009, , Ross, , 4500, , 1018, , Zeith, , 7000, , This is Employee table., Which of the following employee_id, will be displayed for the given query?, SELECT * FROM employee WHERE, employee_id>1009;, a) 1009, 1001, 1018, b) 1009, 1018, c) 1001, d) 1018, Answer: d, Explanation: Greater than symbol, does not include the given value, unlike >=., 44., SELECT name ____ instructor name,, course id, FROM instructor, teaches, WHERE instructor.ID= teaches.ID;, Which keyword must be used here to, rename the field name?, a) From, b) Rename, c) As
Page 10 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, d) Join, , d) $, , Answer: c, Explanation: As keyword is used to, rename., , Answer: a, Explanation: The % character, matches any substring., , 45., , 47. ’_ _ _ ’ matches any string of, ______ three characters. ’_ _ _ %’, matches any string of at ______ three, characters., a) Atleast, Exactly, b) Exactly, Atleast, c) Atleast, All, d) All, Exactly, , SELECT * FROM employee WHERE, dept_name="Comp Sci";, In the SQL given above there is an, error . Identify the error., a) Dept_name, b) Employee, c) “Comp Sci”, d) From, Answer: c, Explanation: For any string operations, single quoted(‘) must be used to, enclose., 46., SELECT emp_name, FROM department, WHERE dept_name LIKE ’ _____, Computer Science’;, Which one of the following has to be, added into the blank to select the, dept_name which has Computer, Science as its ending string?, a) %, b) _, c) ||, , Answer: b, Explanation: None., 48., SELECT name, FROM instructor, WHERE dept name = ’Physics’, ORDER BY name;, By default, the order by clause lists, items in ______ order., a) Descending, b) Any, c) Same, d) Ascending, Answer: d, Explanation: Specification of, descending order is essential but it, not for ascending., 49., , 11
Page 11 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, SELECT *, FROM instructor, ORDER BY salary ____, name ___;, To display the salary from greater to, smaller and name in ascending order, which of the following options should, be used?, a) Ascending, Descending, b) Asc, Desc, c) Desc, Asc, d) Descending, Ascending, Answer: c, Explanation: None., 50. The union operation is, represented by, a) ∩, b) U, c) –, d) *, Answer: b, Explanation: Union operator, combines the relations., 51. The intersection operator is used, to get the _____ tuples., a) Different, b) Common, c) All, d) Repeating, Answer: b, Explanation: Intersection operator, ignores unique tuples and takes only, common ones., , 12, , 52. The union operation, automatically __________ unlike the, select clause., a) Adds tuples, b) Eliminates unique tuples, c) Adds common tuples, d) Eliminates duplicate, Answer: d, Explanation: None., 53. If we want to retain all duplicates,, we must write ________ in place of, union., a) Union all, b) Union some, c) Intersect all, d) Intersect some, Answer: a, Explanation: Union all will combine, all the tuples including duplicates., 54., (SELECT course id, FROM SECTION, WHERE semester = ’Fall’ AND YEAR=, 2009), EXCEPT, (SELECT course id, FROM SECTION, WHERE semester = ’Spring’ AND, YEAR= 2010);, This query displays, a) Only tuples from second part
Page 12 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, b) Only tuples from the first part, which has the tuples from second, part, c) Tuples from both the parts, d) Tuples from first part which do not, have second part, , 57. _____ clause is an additional filter, that is applied to the result., a) Select, b) Group-by, c) Having, d) Order by, , Answer: d, Explanation: Except keyword is used, to ignore the values., , Answer: c, Explanation: Having is used to, provide additional aggregate, filtration to the query., , 55. For like predicate which of the, following is true., i) % matches zero OF more, characters., ii) _ matches exactly one, CHARACTER., , 58. _________ joins are SQL server, default, a) Outer, b) Inner, c) Equi, d) None of the mentioned, , a) i-only, b) ii-only, c) i & ii, d) None of the mentioned, , Answer: b, Explanation: It is optional to give the, inner keyword with the join as it is, default., , Answer: a, Explanation:% is used with like and _, is used to fill in the character., , 59. The _____________ is essentially, used to search for patterns in target, string., a) Like Predicate, b) Null Predicate, c) In Predicate, d) Out Predicate, , 56. The number of attributes in, relation is called as its, a) Cardinality, b) Degree, c) Tuples, d) Entity, Answer: b, Explanation: None., , 13, , Answer: a, Explanation: Like predicate matches, the string in the given pattern.
Page 13 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, 60. Aggregate functions are functions, that take a ___________ as input and, return a single value., a) Collection of values, b) Single value, c) Aggregate value, d) Both Collection of values & Single, value, Answer: a, Explanation: None., 61., SELECT __________, FROM instructor, WHERE dept name= ’Comp. Sci.’;, Which of the following should be, used to find the mean of the salary ?, a) Mean(salary), b) Avg(salary), c) Sum(salary), d) Count(salary), Answer: b, Explanation: Avg() is used to find the, mean of the values., 62., SELECT COUNT (____ ID), FROM teaches, WHERE semester = ’Spring’ AND, YEAR = 2010;, If we do want to eliminate duplicates,, we use the keyword ______in the, , 14, , aggregate expression., a) Distinct, b) Count, c) Avg, d) Primary key, Answer: a, Explanation: Distinct keyword is used, to select only unique items from the, relation., 63. All aggregate functions except, _____ ignore null values in their input, collection., a) Count(attribute), b) Count(*), c) Avg, d) Sum, Answer: b, Explanation: * is used to select all, values including null., 64. A Boolean data type that can take, values true, false, and________, a) 1, b) 0, c) Null, d) Unknown, Answer: d, Explanation: Unknown values do not, take null value but it is not known., 65. The ____ connective tests for set, membership, where the set is a, collection of values produced by a
Page 14 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, select clause. The ____ connective, tests for the absence of set, membership., a) Or, in, b) Not in, in, c) In, not in, d) In, or, Answer: c, Explanation: In checks, if the query, has the value but not in checks if it, does not have the value., 66. The phrase “greater than at least, one” is represented in SQL by _____, a) < all, b) < some, c) > all, d) > some, Answer: d, Explanation: >some takes atlest one, value above it ., 67. Which of the following is used to, find all courses taught in both the Fall, 2009 semester and in the Spring 2010, semester ., a), SELECT course id, FROM SECTION AS S, WHERE semester = ’Fall’ AND YEAR=, 2009 AND, EXISTS (SELECT *, FROM SECTION AS T, , 15, , WHERE semester = ’Spring’ AND, YEAR= 2010 AND, S.course id= T.course id);, b), SELECT name, FROM instructor, WHERE salary > SOME (SELECT salary, FROM instructor, WHERE dept name = ’Biology’);, c), SELECT COUNT (DISTINCT ID), FROM takes, WHERE (course id, sec id, semester,, YEAR) IN (SELECT course id, sec id,, semester, YEAR, FROM teaches, WHERE teaches.ID= 10101);, d), (SELECT course id, FROM SECTION, WHERE semester = ’Spring’ AND, YEAR= 2010), Answer: a, Explanation: None., , 68. We can test for the nonexistence, of tuples in a subquery by using the, _____ construct., a) Not exist
Page 15 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, b) Not exists, c) Exists, d) Exist, Answer: b, Explanation: Exists is used to check, for the existence of tuples., 69., SELECT dept_name, ID, avg (salary), FROM instructor, GROUP BY dept_name;, This statement IS erroneous because, a) Avg(salary) should not be selected, b) Dept_id should not be used in, group by clause, c) Misplaced group by clause, d) Group by clause is not valid in this, query, Answer: b, Explanation: Any attribute that is not, present in the group by clause must, appear only inside an aggregate, function if it appears in the select, clause, otherwise the query is treated, as erroneous., 70. SQL applies predicates in the, _______ clause after groups have, been formed, so aggregate functions, may be used., a) Group by, b) With, c) Where, , 16, , d) Having, Answer: b, Explanation: The with clause provides, away of defining a temporary relation, whose definition is available only to, the query in which the with clause, occurs., 71. Aggregate functions can be used, in the select list or the_______clause, of a select statement or subquery., They cannot be used in a ______, clause., a) Where, having, b) Having, where, c) Group by, having, d) Group by, where, Answer: b, Explanation: To include aggregate, functions having clause must be, included after where., 72. The ________ keyword is used to, access attributes of preceding tables, or subqueries in the from clause., a) In, b) Lateral, c) Having, d) With, Answer: b, Explanation:, Eg : SELECT name, salary, avg salary, FROM instructor I1, lateral, (SELECT avg(salary) AS avg salary
Page 16 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, FROM instructor I2, WHERE I2.dept name= I1.dept, name);, Without the lateral clause, the, subquery cannot access the, correlation variable, I1 from the outer query., 73. Which of the following creates a, temporary relation for the query on, which it is defined?, a) With, b) From, c) Where, d) Select, Answer: a, Explanation: The with clause provides, a way of defining a temporary, relation whose definition is available, only to the query in which the with, clause occurs., 74. A Delete command operates on, ______ relation., a) One, b) Two, c) Several, d) Null, Answer: a, Explanation: Delete can delete from, only one table at a time., 75., Delete from r where P;, , 17, , The above command, a) Deletes a particular tuple from the, relation, b) Deletes the relation, c) Clears all entries from the relation, d) All of the mentioned, Answer: a, Explanation: Here P gives the, condition for deleting specific rows., 76. Which one of the following, deletes all the entries but keeps the, structure of the relation., a) Delete from r where P;, b) Delete from instructor where dept, name= ’Finance’;, c) Delete from instructor where, salary between 13000 and 15000;, d) Delete from instructor;, Answer: d, Explanation: Absence of condition, deletes all rows., 77. _________ are useful in SQL, update statements, where they can, be used in the set clause., a) Multiple queries, b) Sub queries, c) Update, d) Scalar subqueries, Answer: d, Explanation: None.
Page 17 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, 78. The problem of ordering the, update in multiple updates is avoided, using, a) Set, b) Where, c) Case, d) When, , any legal query expression. The view, name is represented by v., , Answer: c, Explanation: The case statements can, add the order of updating tuples., , Here the tuples are selected from the, view.Which one denotes the view., a) Course_id, b) Watson, c) Building, d) physics_fall_2009, , 79. Which of the following creates a, virtual relation for storing the query?, a) Function, b) View, c) Procedure, d) None of the mentioned, Answer: b, Explanation: Any such relation that is, not part of the logical model, but is, made visible to a user as a virtual, relation, is called a view., 80. Which of the following is the, syntax for views where v is view, name?, a) Create view v as “query name”;, b) Create “query expression” as view;, c) Create view v as “query, expression”;, d) Create view “query expression”;, Answer: c, Explanation: <query expression> is, , 18, , 81., SELECT course_id, FROM physics_fall_2009, WHERE building= ’Watson’;, , Answer: c, Explanation: View names may appear, in a query any place where a relation, name may appear., 82. Materialised views make sure, that, a) View definition is kept stable, b) View definition is kept up-to-date, c) View definition is verified for error, d) View is deleted after specified time, Answer: b, Explanation: None., 83. Updating the value of the view, a) Will affect the relation from which, it is defined, b) Will not change the view definition, c) Will not affect the relation from, which it is defined
Page 18 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, d) Cannot determine, Answer: a, Explanation: None., 84. SQL view is said to be updatable, (that is, inserts, updates or deletes, can be applied on the view) if which, of the following conditions are, satisfied by the query defining the, view?, a) The from clause has only one, database relation, b) The query does not have a group, by or having clause, c) The select clause contains only, attribute names of the relation and, does not have any expressions,, aggregates, or distinct specification, d) All of the mentioned, Answer: d, Explanation: All of the conditions, must be satisfied to update the view, in sql., 85. Which of the following is used at, the end of the view to reject the, tuples which do not satisfy the, condition in where clause?, a) With, b) Check, c) With check, d) All of the mentioned, Answer: c, Explanation: Views can be defined, , 19, , with a with check option clause at the, end of the view definition; then, if a, tuple inserted into the view does not, satisfy the view’s where clause, condition, the insertion is rejected by, the database system., 86. For the view Create view, instructor_info as, SELECT ID, name, building, FROM instructor,, department, WHERE instructor.dept, name= department.dept name;, If we insert tuple into the view as, insert into instructor info values, (’69987’, ’White’, ’Taylor’);, What will be the values of the other, attributes in instructor and, department relations?, a) Default value, b) Null, c) Error statement, d) 0, Answer: b, Explanation: The values take null if, there is no constraint in the attribute, else it is an Erroneous statement., 87., CREATE VIEW faculty AS, SELECT ID, name, dept name
Page 19 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, FROM instructor;, Find the error in this query., a) Instructor, b) Select, c) View …as, d) None of the mentioned, Answer: d, Explanation: Syntax is – create view v, as <query expression>;., 88. A _________ consists of a, sequence of query and/or update, statements., a) Transaction, b) Commit, c) Rollback, d) Flashback, Answer: a, Explanation: Transaction is a set of, operation until commit., 89. Which of the following makes the, transaction permanent in the, database?, a) View, b) Commit, c) Rollback, d) Flashback, Answer: b, Explanation: Commit work commits, the current transaction., 90. In order to undo the work of, transaction after last commit which, , 20, , one should be used?, a) View, b) Commit, c) Rollback, d) Flashback, Answer: c, Explanation: Rollback work causes, the current transaction to be rolled, back; that is, it undoes all the updates, performed by the SQL statements in, the transaction., 91. Consider the following action:, TRANSACTION....., Commit;, ROLLBACK;, What does Rollback do?, a) Undoes the transactions before, commit, b) Clears all transactions, c) Redoes the transactions before, commit, d) No action, Answer: d, Explanation: Once a transaction has, executed commit work, its effects can, no longer be undone by rollback, work., 92. In case of any shut down during, transaction before commit which of, the following statement is done, automatically?
Page 20 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, a) View, b) Commit, c) Rollback, d) Flashback, Answer: c, Explanation: Once a transaction has, executed commit work, its effects can, no longer be undone by rollback, work., , 95. A transaction completes its, execution is said to be, a) Committed, b) Aborted, c) Rolled back, d) Failed, Answer: a, Explanation: A complete transaction, always commits., , 93. In order to maintain the, consistency during transactions,, database provides, a) Commit, b) Atomic, c) Flashback, d) Retain, , 96. Which of the following is used to, get back all the transactions back, after rollback?, a) Commit, b) Rollback, c) Flashback, d) Redo, , Answer: b, Explanation: By atomic, either all the, effects of the transaction are, reflected in the database, or none are, (after rollback)., , Answer: c, Explanation: None., , 94. Transaction processing is, associated with everything below, except, a) Conforming an action or triggering, a response, b) Producing detail summary or, exception report, c) Recording a business activity, d) Maintaining a data, Answer: a, Explanation: None., , 21, , 97. ______ will undo all statements, up to commit?, a) Transaction, b) Flashback, c) Rollback, d) Abort, Answer: c, Explanation: Flashback will undo all, the statements and Abort will, terminate the operation., 98. To include integrity constraint in, an existing relation use :, a) Create table
Page 21 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, b) Modify table, c) Alter table, d) Drop table, Answer: c, Explanation: SYNTAX – alter table, table-name add constraint, where, constraint can be any constraint on, the relation., 99. Which of the following is not an, integrity constraint?, a) Not null, b) Positive, c) Unique, d) Check ‘predicate’, Answer: b, Explanation: Positive is a value and, not a constraint., 100., CREATE TABLE Employee(Emp_id, NUMERIC NOT NULL, Name, VARCHAR(20) , dept_name, VARCHAR(20), Salary NUMERIC, UNIQUE(Emp_id,Name));, INSERT INTO Employee, VALUES(1002, Ross, CSE, 10000), INSERT INTO Employee, VALUES(1006,Ted,Finance, );, INSERT INTO Employee, VALUES(1002,Rita,Sales,20000);, What will be the result of the query?, a) All statements executed, , 22, , b) Error in create statement, c) Error in insert into Employee, values(1006,Ted,Finance, );, d) Error in insert into Employee, values(1008,Ross,Sales,20000);, Answer: d, Explanation: The not null, specification prohibits the insertion, of a null value for the attribute., The unique specification says that no, two tuples in the relation can be, equal on all the listed attributes., 101., CREATE TABLE Manager(ID, NUMERIC,Name, VARCHAR(20),budget, NUMERIC,Details VARCHAR(30));, Inorder to ensure that the value of, budget is non-negative which of the, following should be used?, a) Check(budget>0), b) Check(budget<0), c) Alter(budget>0), d) Alter(budget<0), Answer: a, Explanation: A common use of the, check clause is to ensure that, attribute values satisfy specified, conditions, in effect creating a, powerful type system.
Page 22 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, 102. Foreign key is the one in which, the ________ of one relation is, referenced in another relation., a) Foreign key, b) Primary key, c) References, d) Check constraint, , 104. Domain constraints, functional, dependency and referential integrity, are special forms of _________, a) Foreign key, b) Primary key, c) Assertion, d) Referential constraint, , Answer: b, Explanation: The foreign-key, declaration specifies that for each, course tuple, the department name, specified in the tuple must exist in, the department relation., , Answer: c, Explanation: An assertion is a, predicate expressing a condition we, wish the database to always satisfy., , 103., CREATE TABLE course, (..., FOREIGN KEY (dept name), REFERENCES department, . . . );, Which of the following is used to, delete the entries in the referenced, table when the tuple is deleted in, course table?, a) Delete, b) Delete cascade, c) Set null, d) All of the mentioned, Answer: b, Explanation: The delete “cascades” to, the course relation, deletes the tuple, that refers to the department that, was deleted., , 23, , 105. Which of the following is the, right syntax for the assertion?, a) Create assertion ‘assertion-name’, check ‘predicate’;, b) Create assertion check ‘predicate’, ‘assertion-name’;, c) Create assertions ‘predicates’;, d) All of the mentioned, Answer: a, Explanation: None., 106. Data integrity constraints are, used to:, a) Control who is allowed access to, the data, b) Ensure that duplicate records are, not entered into the table, c) Improve the quality of data, entered for a specific property (i.e.,, table column), d) Prevent users from changing the, values stored in the table
Page 23 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, Answer: c, Explanation: None., 107. Which of the following can be, addressed by enforcing a referential, integrity constraint?, a) All phone numbers must include, the area code, b) Certain fields are required (such as, the email address, or phone number), before the record is accepted, c) Information on the customer must, be known before anything can be, sold to that customer, d) When entering an order quantity,, the user must input a number and, not some text (i.e., 12 rather than ‘a, dozen’), Answer: c, Explanation: The information can be, referred to and obtained., 108. Dates must be specified in the, format, a) mm/dd/yy, b) yyyy/mm/dd, c) dd/mm/yy, d) yy/dd/mm, Answer: b, Explanation: yyyy/mm/dd is the, default format in sql., 109. A ________ on an attribute of a, relation is a data structure that allows, the database system to find those, , 24, , tuples in the relation that have a, specified value for that attribute, efficiently, without scanning through, all the tuples of the relation., a) Index, b) Reference, c) Assertion, d) Timestamp, Answer: a, Explanation: Index is the reference to, the tuples in a relation., 110., Create index studentID_index on, student(ID);, Here which one denotes the relation, for which index is created?, a) StudentID_index, b) ID, c) StudentID, d) Student, Answer: d, Explanation: The statement creates, an index named studentID index on, the attribute ID of the relation, student., 111. Which of the following is used to, store movie and image files?, a) Clob, b) Blob, c) Binary
Page 24 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, d) Image, , 114., , Answer: b, Explanation: SQL therefore provides, large-object data types for character, data (clob) and binary data (blob)., The letters “lob” in these data types, stand for “Large OBject”., , CREATE DOMAIN YearlySalary, NUMERIC(8,2), CONSTRAINT salary VALUE test, __________;, , 112. The user defined data type can, be created using, a) Create datatype, b) Create data, c) Create definetype, d) Create type, Answer: d, Explanation: The create type clause, can be used to define new, types.Syntax : create type Dollars as, numeric(12,2) final; ., 113. Values of one type can be, converted to another domain using, which of the following?, a) Cast, b) Drop type, c) Alter type, d) Convert, Answer: a, Explanation: Example of cast :cast, (department.budget to, numeric(12,2)). SQL provides drop, type and alter type clauses to drop or, modify types that have been created, earlier., , 25, , In order to ensure that an instructor’s, salary domain allows only values, greater than a specified value use:, a) Value>=30000.00, b) Not null;, c) Check(value >= 29000.00);, d) Check(value), Answer: c, Explanation: Check(value ‘condition’), is the syntax., 115. Which of the following closely, resembles Create view?, a) Create table . . .like, b) Create table . . . as, c) With data, d) Create view as, Answer: b, Explanation: The ‘create table . . . as’, statement closely resembles the, create view statement and both are, defined by using queries. The main, difference is that the contents of the, table are set when the table is, created, whereas the contents of a, view always reflect the current query, result.
Page 25 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, 116. In contemporary databases, the, top level of the hierarchy consists of, ______ each of which can contain, _____, a) Catalogs, schemas, b) Schemas, catalogs, c) Environment, schemas, d) Schemas, Environment, Answer: a, Explanation: None., 117. Which of the following, statements creates a new table temp, instructor that has the same schema, as an instructor., a) create table temp_instructor;, b) Create table temp_instructor like, instructor;, c) Create Table as temp_instructor;, d) Create table like temp_instructor;, Answer: b, Explanation: None., 118. The database administrator who, authorizes all the new users, modifies, the database and takes grants, privilege is, a) Super user, b) Administrator, c) Operator of operating system, d) All of the mentioned, Answer: d, Explanation: The authorizations, , 26, , provided by the administrator to the, user is a privilege., 119. Which of the following is a basic, form of grant statement?, a), GRANT 'privilege list', ON 'relation name or view name', TO 'user/role list';, b), GRANT 'privilege list', ON 'user/role list', TO 'relation name or view name';, c), GRANT 'privilege list', TO 'user/role list', d), GRANT 'privilege list', ON 'relation name or view name', ON 'user/role list';, Answer: a, Explanation: The privilege list allows, the granting of several privileges in, one command ., 120. Which of the following is used to, provide privilege to only a particular, attribute?, a) Grant select on employee to Amit, b) Grant update(budget) on
Page 26 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, department to Raj, c) Grant update(budget,salary,Rate), on department to Raj, d) Grant delete to Amit, Answer: b, Explanation: This grant statement, gives user Raj update authorization, on the budget attribute of the, department relation., 121. Which of the following, statement is used to remove the, privilege from the user Amir?, a) Remove update on department, from Amir, b) Revoke update on employee from, Amir, c) Delete select on department from, Raj, d) Grant update on employee from, Amir, Answer: b, Explanation: revoke on from ;, 122. Which of the following is used to, provide delete authorization to, instructor?, a), CREATE ROLE instructor ;, GRANT DELETE TO instructor;, , GRANT SELECT ON takes, TO instructor;, c), CREATE ROLE instructor;, GRANT DELETE ON takes, TO instructor;, d) All of the mentioned, Answer: c, Explanation: The role is first created, and the authorization is given on, relation takes to the role., 123. Which of the following is true, regarding views?, a) The user who creates a view, cannot be given update authorization, on a view without having update, authorization on the relations used to, define the view, b) The user who creates a view, cannot be given update authorization, on a view without having update, authorization on the relations used to, define the view, c) If a user creates a view on which no, authorization can be granted, the, system will allow the view creation, request, d) A user who creates a view receives, all privileges on that view, , b), CREATE ROLE instructor;, , 27, , Answer: c, Explanation: A user who creates a
Page 27 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, view does not necessarily receive all, privileges on that view., 124. If we wish to grant a privilege, and to allow the recipient to pass the, privilege on to other users, we, append the __________ clause to the, appropriate grant command., a) With grant, b) Grant user, c) Grant pass privelege, d) With grant option, Answer: d, Explanation: None., 125. In authorization graph, if DBA, provides authorization to u1 which, inturn gives to u2 which of the, following is correct?, a) If DBA revokes authorization from, u1 then u2 authorization is also, revoked, b) If u1 revokes authorization from u2, then u2 authorization is revoked, c) If DBA & u1 revokes authorization, from u1 then u2 authorization is also, revoked, d) If u2 revokes authorization then u1, authorization is revoked, Answer: c, Explanation: A user has an, authorization if and only if there is a, path from the root of the, authorization graph down to the, node representing the user., , 28, , 126. Which of the following is used to, avoid cascading of authorizations, from the user?, a) Granted by current role, b) Revoke select on department from, Amit, Satoshi restrict;, c) Revoke grant option for select on, department from Amit;, d) Revoke select on department from, Amit, Satoshi cascade;, Answer: b, Explanation: The revoke statement, may specify restrict in order to, prevent cascading revocation. The, keyword cascade can be used instead, of restrict to indicate that revocation, should cascade., 127. The granting and revoking of, roles by the user may cause some, confusions when that user role is, revoked. To overcome the above, situation, a) The privilege must be granted only, by roles, b) The privilege is granted by roles, and users, c) The user role cannot be removed, once given, d) By restricting the user access to, the roles, Answer: a, Explanation: The current role, associated with a session can be set, by executing set role name. The
Page 28 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, specified role must have been, granted to the user, else the set role, statement fails., 128. A __________ is a special kind of, a store procedure that executes in, response to certain action on the, table like insertion, deletion or, updation of data., a) Procedures, b) Triggers, c) Functions, d) None of the mentioned, Answer: b, Explanation: Triggers are, automatically generated when a, particular operation takes place., 129. Triggers are supported in, a) Delete, b) Update, c) Views, d) All of the mentioned, Answer: c, Explanation: The triggers run after an, insert, update or delete on a table., They are not supported for views., 130. The CREATE TRIGGER statement, is used to create the trigger. THE, _____ clause specifies the table name, on which the trigger is to be, attached. The ______ specifies that, this is an AFTER INSERT trigger., a) for insert, on, , 29, , b) On, for insert, c) For, insert, d) None of the mentioned, Answer: b, Explanation: The triggers run after an, insert, update or delete on a table., They are not supported for views., 131. What are the after triggers?, a) Triggers generated after a, particular operation, b) These triggers run after an insert,, update or delete on a table, c) These triggers run after an insert,, views, update or delete on a table, d) All of the mentioned, Answer: b, Explanation: AFTER TRIGGERS can be, classified further into three types as:, AFTER INSERT Trigger, AFTER UPDATE, Trigger, AFTER DELETE Trigger., 132. The variables in the triggers are, declared using, a) –, b) @, c) /, d) /@, Answer: b, Explanation: Example : declare, @empid int; where empid is the, variable.
Page 29 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, 133. The default extension for an, Oracle SQL*Plus file is:, a) .txt, b) .pls, c) .ora, d) .sql, Answer: d, Explanation: Example :None., 134. Which of the following is NOT an, Oracle-supported trigger?, a) BEFORE, b) DURING, c) AFTER, d) INSTEAD OF, Answer: b, Explanation: Example: During trigger, is not possible in any database., 135. What are the different in, triggers?, a) Define, Create, b) Drop, Comment, c) Insert, Update, Delete, d) All of the mentioned, Answer: c, Explanation: Triggers are not possible, for create, drop., 136. Triggers ________ enabled or, disabled, a) Can be, b) Cannot be, c) Ought to be, , 30, , d) Always, Answer: a, Explanation: Triggers can be, manipulated., 137. Which prefixes are available to, Oracle triggers?, a) : new only, b) : old only, c) Both :new and : old, d) Neither :new nor : old, Answer: c, Explanation: None., 138. OLAP stands for, a) Online analytical processing, b) Online analysis processing, c) Online transaction processing, d) Online aggregate processing, Answer: a, Explanation: OLAP is the, manipulation of information to, support decision making., 139. Data that can be modeled as, dimension attributes and measure, attributes are called _______ data., a) Multidimensional, b) Singledimensional, c) Measured, d) Dimensional, Answer: a, Explanation: Given a relation used for
Page 30 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, data analysis, we can identify some of, its attributes as measure attributes,, since they measure some value, and, can be aggregated upon.Dimension, attribute define the dimensions on, which measure attributes, and, summaries of measure attributes, are, viewed., 140. The generalization of cross-tab, which is represented visually is, ____________ which is also called as, data cube., a) Two dimensional cube, b) Multidimensional cube, c) N-dimensional cube, d) Cuboid, Answer: a, Explanation: Each cell in the cube is, identified for the values for the three, dimensional attributes., 141. The process of viewing the, cross-tab (Single dimensional) with a, fixed value of one attribute is, a) Slicing, b) Dicing, c) Pivoting, d) Both Slicing and Dicing, Answer: a, Explanation: The slice operation, selects one particular dimension from, a given cube and provides a new subcube. Dice selects two or more, , 31, , dimensions from a given cube and, provides a new sub-cube., 142. The operation of moving from, finer-granularity data to a coarser, granularity (by means of aggregation), is called a ________, a) Rollup, b) Drill down, c) Dicing, d) Pivoting, Answer: a, Explanation: The opposite, operation—that of moving, fromcoarser-granularity data to finergranularity data—is called a drill, down., 143. In SQL the cross-tabs are created, using, a) Slice, b) Dice, c) Pivot, d) All of the mentioned, Answer: a, Explanation: Pivot (sum(quantity) for, color in (’dark’,’pastel’,’white’))., 144., { (item name, color, clothes size),, (item name, color), (item name,, clothes size), (color, clothes size),, (item name), (color), (clothes size), (), }
Page 31 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, This can be achieved by using which, of the following ?, a) group by rollup, b) group by cubic, c) group by, d) none of the mentioned, Answer: d, Explanation: ‘Group by cube’ is used ., 145. What do data warehouses, support?, a) OLAP, b) OLTP, c) OLAP and OLTP, d) Operational databases, Answer: a, Explanation: None., 146., SELECT item name, color, clothes, SIZE, SUM(quantity), FROM sales, GROUP BY rollup(item name, color,, clothes SIZE);, How many grouping is possible in this, rollup?, a) 8, b) 4, c) 2, d) 1, Answer: b, Explanation: { (item name, color,, , 32, , clothes size), (item name, color),, (item name), () }., 147. Which one of the following is the, right syntax for DECODE?, a) DECODE (search, expression, result, [, search, result]… [, default]), b) DECODE (expression, result [,, search, result]… [, default], search), c) DECODE (search, result [, search,, result]… [, default], expression), d) DECODE (expression, search, result, [, search, result]… [, default]), Answer: d, Explanation: None., 148. Relational Algebra is a, __________ query language that, takes two relations as input and, produces another relation as an, output of the query., a) Relational, b) Structural, c) Procedural, d) Fundamental, Answer: c, Explanation: This language has, fundamental and other operations, which are used on relations., 149. Which of the following is a, fundamental operation in relational, algebra?, a) Set intersection, b) Natural join
Page 32 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, c) Assignment, d) None of the mentioned, Answer: d, Explanation: The fundamental, operations are select, project, union,, set difference, Cartesian product, and, rename., 150. Which of the following is used to, denote the selection operation in, relational algebra?, a) Pi (Greek), b) Sigma (Greek), c) Lambda (Greek), d) Omega (Greek), , another., a) Union, b) Set-difference, c) Difference, d) Intersection, Answer: b, Explanation: The expression r − s, produces a relation containing those, tuples in r but not in s., 153. Which is a unary operation:, a) Selection operation, b) Primitive operation, c) Projection operation, d) Generalized selection, , Answer: b, Explanation: The select operation, selects tuples that satisfy a given, predicate., , Answer: d, Explanation: Generalization Selection, takes only one argument for, operation., , 151. For select operation the, ________ appear in the subscript and, the ___________ argument appears, in the paranthesis after the sigma., a) Predicates, relation, b) Relation, Predicates, c) Operation, Predicates, d) Relation, Operation, , 154. Which is a join condition, contains an equality operator:, a) Equijoins, b) Cartesian, c) Natural, d) Left, , Answer: a, Explanation: None., 152. The ___________ operation,, denoted by −, allows us to find tuples, that are in one relation but are not in, , 33, , Answer: a, Explanation: None., 155. In precedence of set operators,, the expression is evaluated from, a) Left to left, b) Left to right, c) Right to left
Page 33 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, d) From user specification, Answer: b, Explanation: The expression is, evaluated from left to right according, to the precedence., 156. Which of the following is not, outer join?, a) Left outer join, b) Right outer join, c) Full outer join, d) All of the mentioned, Answer: d, Explanation: The FULL OUTER JOIN, keyword combines the result of both, LEFT and RIGHT joins., 157. The assignment operator is, denoted by, a) ->, b) <c) =, d) ==, , b) Э t ∈ r (Q(t)), c) {t | Э s ε instructor (t[ID] = s[ID]∧, s[salary] > 80000)}, d) None of the mentioned, Answer: a, Explanation: This expression is in, tuple relational format., 159. A query in the tuple relational, calculus is expressed as:, a) {t | P() | t}, b) {P(t) | t }, c) {t | P(t)}, d) All of the mentioned, Answer: c, Explanation: The tuple relational, calculus, is a nonprocedural query, language. It describes the desired, information without giving a specific, procedure for obtaining that, information., 160., , Answer: b, Explanation: The result of the, expression to the right of the ← is, assigned to the relation variable on, the left of the ←., , {t | Э s ε instructor (t[name] =, s[name], ∧ Э u ε department (u[dept name] =, s[dept name], ∧ u[building] = “Watson”))}, , 158. Find the ID, name, dept name,, salary for instructors whose salary is, greater than $80,000 ., a) {t | t ε instructor ∧ t[salary] >, 80000}, , Which of the following best describes, the query?, a) Finds the names of all instructors, whose department is in the Watson, building, , 34
Page 34 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, b) Finds the names of all department, is in the Watson building, c) Finds the name of the dapartment, whose instructor and building is, Watson, d) Returns the building name of all, the departments, Answer: a, Explanation: This query has two, “there exists” clauses in our tuplerelational-calculus expression,, connected by and (∧)., 161. Which of the following symbol is, used in the place of except?, a) ^, b) V, c) ¬, d) ~, Answer: c, Explanation: The query ¬P negates, the value of P., 162. “Find all students who have, taken all courses offered in the, Biology department.” The, expressions that matches this, sentence is :, a) Э t ε r (Q(t)), b) ∀ t ε r (Q(t)), c) ¬ t ε r (Q(t)), d) ~ t ε r (Q(t)), , Answer: b, Explanation: ∀ is used denote “for, all” in SQL., 163. An ________ is a set of entities, of the same type that share the same, properties, or attributes., a) Entity set, b) Attribute set, c) Relation set, d) Entity model, Answer: a, Explanation: An entity is a “thing” or, “object” in the real world that is, distinguishable from all other objects., 164. Entity is a _________, a) Object of relation, b) Present working model, c) Thing in real world, d) Model of relation, Answer: c, Explanation: For example, each, person in a university is an entity., 165. The descriptive property, possessed by each entity set is, _________, a) Entity, b) Attribute, c) Relation, d) Model, Answer: b, Explanation: Possible attributes of, , 35
Page 35 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, the instructor entity set are ID, name,, dept name, and salary., 166. The function that an entity plays, in a relationship is called that entity’s, _____________, a) Participation, b) Position, c) Role, d) Instance, Answer: c, Explanation: A relationship is an, association among several entities., 167. The attribute name could be, structured as an attribute consisting, of first name, middle initial, and last, name. This type of attribute is called, a) Simple attribute, b) Composite attribute, c) Multivalued attribute, d) Derived attribute, Answer: b, Explanation: Composite attributes, can be divided into subparts (that is,, other attributes)., 168. The attribute AGE is calculated, from DATE_OF_BIRTH. The attribute, AGE is, a) Single valued, b) Multi valued, c) Composite, d) Derived, , 36, , Answer: d, Explanation: The value for this type of, attribute can be derived from the, values of other related attributes or, entities., 169. Not applicable condition can be, represented in relation entry as, a) NA, b) 0, c) NULL, d) Blank Space, Answer: c, Explanation: NULL always represents, that the value is not present., 170. Which of the following can be a, multivalued attribute?, a) Phone_number, b) Name, c) Date_of_birth, d) All of the mentioned, Answer: a, Explanation: Name and Date_of_birth, cannot hold more than 1 value., 171. Which of the following is a single, valued attribute, a) Register_number, b) Address, c) SUBJECT_TAKEN, d) Reference, Answer: a, Explanation: None.
Page 36 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, 172. In a relation between the, entities the type and condition of the, relation should be specified. That is, called as______attribute., a) Desciptive, b) Derived, c) Recursive, d) Relative, Answer: a, Explanation: Consider the entity sets, student and section, which, participate in a relationship set takes., We may wish to store a descriptive, attribute grade with the relationship, to record the grade that a student got, in the class., 172. _____________ express the, number of entities to which another, entity can be associated via a, relationship set., a) Mapping Cardinality, b) Relational Cardinality, c) Participation Constraints, d) None of the mentioned, Answer: a, Explanation: Mapping cardinality is, also called as cardinality ratio., 173. An entity in A is associated with, at most one entity in B, and an entity, in B is associated with at most one, entity in A.This is called as, a) One-to-many, b) One-to-one, , 37, , c) Many-to-many, d) Many-to-one, Answer: b, Explanation: Here one entity in one, set is related to one one entity in, other set., 174. An entity in A is associated with, at most one entity in B. An entity in B,, however, can be associated with any, number (zero or more) of entities in, A., a) One-to-many, b) One-to-one, c) Many-to-many, d) Many-to-one, Answer: d, Explanation: Here more than one, entity in one set is related to one one, entity in other set., 175. Data integrity constraints are, used to:, a) Control who is allowed access to, the data, b) Ensure that duplicate records are, not entered into the table, c) Improve the quality of data, entered for a specific property, d) Prevent users from changing the, values stored in the table, Answer: c, Explanation: The data entered will be, in a particular cell (i.e., table column).
Page 37 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, 176. Establishing limits on allowable, property values, and specifying a set, of acceptable, predefined options, that can be assigned to a property, are examples of:, a) Attributes, b) Data integrity constraints, c) Method constraints, d) Referential integrity constraints, Answer: b, Explanation: Only particular value, satisfying the constraints are entered, in the column., 177. Which of the following can be, addressed by enforcing a referential, integrity constraint?, a) All phone numbers must include, the area code, b) Certain fields are required (such as, the email address, or phone number), before the record is accepted, c) Information on the customer must, be known before anything can be, sold to that customer, d) Then entering an order quantity,, the user must input a number and, not some text (i.e., 12 rather than ‘a, dozen’), Answer: c, Explanation: None., 178. ______ is a special type of, integrity constraint that relates two, relations & maintains consistency, , 38, , across the relations., a) Entity Integrity Constraints, b) Referential Integrity Constraints, c) Domain Integrity Constraints, d) Domain Constraints, Answer: b, Explanation: None., 179. Which one of the following, uniquely identifies the elements in, the relation?, a) Secondary Key, b) Primary key, c) Foreign key, d) Composite key, Answer: b, Explanation: Primary key checks for, not null and uniqueness constraint., 180. Drop Table cannot be used to, drop a table referenced by a, _________ constraint., a) Local Key, b) Primary Key, c) Composite Key, d) Foreign Key, Answer: d, Explanation: Foreign key is used, when primary key of one relation is, used in another relation., 181. ____________ is preferred, method for enforcing data integrity, a) Constraints
Page 38 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, b) Stored Procedure, c) Triggers, d) Cursors, , b) Relationship set, c) Attributes of a relationship set, d) Primary key, , Answer: a, Explanation: Constraints are specified, to restrict entries in the relation., , Answer: a, Explanation: The first part of the, rectangle, contains the name of the, entity set. The second part contains, the names of all the attributes of the, entity set., , 182. Which of the following gives a, logical structure of the database, graphically?, a) Entity-relationship diagram, b) Entity diagram, c) Database diagram, d) Architectural representation, Answer: a, Explanation: E-R diagrams are simple, and clear—qualities that may well, account in large part for the, widespread use of the E-R model., 183. The entity relationship set is, represented in E-R diagram as, a) Double diamonds, b) Undivided rectangles, c) Dashed lines, d) Diamond, Answer: d, Explanation: Dashed lines link, attributes of a relationship set to the, relationship set., 184. The Rectangles divided into two, parts represents, a) Entity set, , 39, , 185. Consider a directed line(->) from, the relationship set advisor to both, entity sets instructor and student., This indicates _________ cardinality, a) One to many, b) One to one, c) Many to many, d) Many to one, Answer: b, Explanation: This indicates that an, instructor may advise at most one, student, and a student may have at, most one advisor., 186. We indicate roles in E-R, diagrams by labeling the lines that, connect ___________ to __________, a) Diamond , diamond, b) Rectangle, diamond, c) Rectangle, rectangle, d) Diamond, rectangle, Answer: d, Explanation: Diamond represents a
Page 39 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, relationship set and rectangle, represents a entity set., 187. An entity set that does not have, sufficient attributes to form a primary, key is termed a __________, a) Strong entity set, b) Variant set, c) Weak entity set, d) Variable set, Answer: c, Explanation: An entity set that has a, primary key is termed a strong entity, set., 188. For a weak entity set to be, meaningful, it must be associated, with another entity set, called the, a) Identifying set, b) Owner set, c) Neighbour set, d) Strong entity set, Answer: a, Explanation: Every weak entity must, be associated with an identifying, entity; that is, the weak entity set is, said to be existence dependent on, the identifying entity set. The, identifying entity set is said to own, the weak entity set that it identifies., It is also called as owner entity set., 189. Weak entity set is represented, as, a) Underline, , 40, , b) Double line, c) Double diamond, d) Double rectangle, Answer: c, Explanation: An entity set that has a, primary key is termed a strong entity, set., 190. If you were collecting and, storing information about your music, collection, an album would be, considered a(n) _____, a) Relation, b) Entity, c) Instance, d) Attribute, Answer: b, Explanation: An entity set is a logical, container for instances of an entity, type and instances of any type, derived from that entity type., 191. What term is used to refer to a, specific record in your music, database; for instance; information, stored about a specific album?, a) Relation, b) Instance, c) Table, d) Column, Answer: b, Explanation: The environment of, database is said to be an instance. A, database instance or an ‘instance’ is
Page 40 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, made up of the background, processes needed by the database., 192. The total participation by, entities is represented in E-R diagram, as, a) Dashed line, b) Double line, c) Double rectangle, d) Circle, Answer: b, Explanation: It is used to represent, the relation between several, attributes., 193. Given the basic ER and relational, models, which of the following is, INCORRECT?, a) An attribute of an entity can have, more than one value, b) An attribute of an entity can be, composite, c) In a row of a relational table, an, attribute can have more than one, value, d) In a row of a relational table, an, attribute can have exactly one value, or a NULL value, Answer: c, Explanation: It is possible to have, several values for a single attribute, provide it is a multi-valued attribute., 194. Which of the following indicates, the maximum number of entities that, , 41, , can be involved in a relationship?, a) Minimum cardinality, b) Maximum cardinality, c) ERD, d) Greater Entity Count, Answer: b, Explanation: In SQL (Structured Query, Language), the term cardinality refers, to the uniqueness of data values, contained in a particular column, (attribute) of a database table., 195. In E-R diagram generalization is, represented by, a) Ellipse, b) Dashed ellipse, c) Rectangle, d) Triangle, Answer: d, Explanation: Ellipse represents, attributes, rectangle represents, entity., 196. The entity set person is classified, as student and employee. This, process is called _________, a) Generalization, b) Specialization, c) Inheritance, d) Constraint generalization, Answer: b, Explanation: The process of, designating subgroupings within an, entity set is called specialization.
Page 41 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, 197. Which relationship is used to, represent a specialization entity?, a) ISA, b) AIS, c) ONIS, d) WHOIS, , name, and salary attributes. This, process is called, a) Commonality, b) Specialization, c) Generalization, d) Similarity, , Answer: a, Explanation: In terms of an E-R, diagram, specialization is depicted by, a hollow arrow-head pointing from, the specialized entity to the other, entity., , Answer: c, Explanation: Generalization is used to, emphasize the similarities among, lower-level entity sets and to hide the, differences., , 198. The refinement from an initial, entity set into successive levels of, entity subgroupings represents a, ________ design process in which, distinctions are made explicit., a) Hierarchy, b) Bottom-up, c) Top-down, d) Radical, Answer: c, Explanation: The design process may, also proceed in a bottom-up manner,, in which multiple entity sets are, synthesized into a higher-level entity, set on the basis of common features., 199. There are similarities between, the instructor entity set and the, secretary entity set in the sense that, they have several attributes that are, conceptually the same across the two, entity sets: namely, the identifier,, , 42, , 200. If an entity set is a lower-level, entity set in more than one ISA, relationship, then the entity set has, a) Hierarchy, b) Multilevel inheritance, c) Single inheritance, d) Multiple inheritance, Answer: d, Explanation: The attributes of the, higher-level entity sets are said to be, inherited by the lower-level entity, sets., 201. A _____________ constraint, requires that an entity belong to no, more than one lower-level entity set., a) Disjointness, b) Uniqueness, c) Special, d) Relational, Answer: a, Explanation: For example, student
Page 42 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, entity can satisfy only one condition, for the student type attribute; an, entity can be either a graduate, student or an undergraduate student,, but cannot be both., 202. Consider the employee workteam example, and assume that, certain employees participate in, more than one work team. A given, employee may therefore appear in, more than one of the team entity, sets that are lower level entity sets of, employee. Thus, the generalization is, _____________, a) Overlapping, b) Disjointness, c) Uniqueness, d) Relational, Answer: a, Explanation: In overlapping, generalizations, the same entity may, belong to more than one lower-level, entity set within a single, generalization., 203. In the __________ normal form,, a composite attribute is converted to, individual attributes., a) First, b) Second, c) Third, d) Fourth, Answer: a, Explanation: The first normal form is, , 43, , used to eliminate the duplicate, information., 204. A table on the many side of a, one to many or many to many, relationship must:, a) Be in Second Normal Form (2NF), b) Be in Third Normal Form (3NF), c) Have a single attribute key, d) Have a composite key, Answer: d, Explanation: The relation in second, normal form is also in first normal, form and no partial dependencies on, any column in primary key., 205. Tables in second normal form, (2NF):, a) Eliminate all hidden dependencies, b) Eliminate the possibility of a, insertion anomalies, c) Have a composite key, d) Have all non key fields depend on, the whole primary key, Answer: a, Explanation: The relation in second, normal form is also in first normal, form and no partial dependencies on, any column in primary key., 206. Which-one ofthe following, statements about normal forms is, FALSE?, a) BCNF is stricter than 3 NF, b) Lossless, dependency -preserving
Page 43 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, decomposition into 3 NF is always, possible, c) Loss less, dependency – preserving, decomposition into BCNF is always, possible, d) Any relation with two attributes is, BCNF, Answer: c, Explanation: We say that the, decomposition is a lossless, decomposition if there is no loss of, information by replacing r (R) with, two relation schemas r1(R1), andr2(R2)., 207. Functional Dependencies are the, types of constraints that are based, on______, a) Key, b) Key revisited, c) Superset key, d) None of the mentioned, Answer: a, Explanation: Key is the basic element, needed for the constraints., 208. Which is a bottom-up approach, to database design that design by, examining the relationship between, attributes:, a) Functional dependency, b) Database modeling, c) Normalization, d) Decomposition, , 44, , Answer: c, Explanation: Normalisation is the, process of removing redundancy and, unwanted data., 209. Which forms simplifies and, ensures that there are minimal data, aggregates and repetitive groups:, a) 1NF, b) 2NF, c) 3NF, d) All of the mentioned, Answer: c, Explanation: The first normal form is, used to eliminate the duplicate, information., 210. Which forms has a relation that, possesses data about an individual, entity:, a) 2NF, b) 3NF, c) 4NF, d) 5NF, Answer: c, Explanation: A Table is in 4NF if and, only if, for every one of its non-trivial, multivalued dependencies X, \twoheadrightarrow Y, X is a, superkey—that is, X is either a, candidate key or a superset thereof., 211. Which forms are based on the, concept of functional dependency:, a) 1NF
Page 44 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, b) 2NF, c) 3NF, d) 4NF, , b) Armstrong’s axioms, c) Armstrong, d) Closure, , Answer: c, Explanation: The table is in 3NF if, every non-prime attribute of R is nontransitively dependent (i.e. directly, dependent) on every superkey of R., , Answer: b, Explanation: By applying these rules, repeatedly, we can find all of F+,, given F., , 212., Empdt1(empcode, name, street, city,, state, pincode)., For any pincode, there is only one city, and state. Also, for given street, city, and state, there is just one pincode., In normalization terms, empdt1 is a, relation in, a) 1 NF only, b) 2 NF and hence also in 1 NF, c) 3NF and hence also in 2NF and 1NF, d) BCNF and hence also in 3NF, 2NF, and 1NF, Answer: b, Explanation: The relation in second, normal form is also in first normal, form and no partial dependencies on, any column in primary key., 213. We can use the following three, rules to find logically implied, functional dependencies. This, collection of rules is called, a) Axioms, , 45, , 214. An approach to website design, with the emphasis on converting, visitors to outcomes required by the, owner is referred to as:, a) Web usability, b) Persuasion, c) Web accessibility, d) None of the mentioned, Answer: b, Explanation: In computing, graphical, user interface is a type of user, interface that allows users to interact, with electronic devices., 125. A method of modelling and, describing user tasks for an, interactive application is referred to, as:, a) Customer journey, b) Primary persona, c) Use case, d) Web design persona, Answer: c, Explanation: The actions in GUI are, usually performed through direct
Page 45 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, manipulation of the graphical, elements., 216. Information architecture, influences:, a) Answer choice, b) Site structure, c) Labeling, d) Navigation design, Answer: b, Explanation: The actions in GUI are, usually performed through direct, manipulation of the graphical, elements., 217. Also known as schematics, a way, of illustrating the layout of an, individual webpage is a:, a) Wireframe, b) Sitemap, c) Card sorting, d) Blueprint, Answer: a, Explanation: An application, programming interface specifies how, some software components should, interact with each other., 218. A graphical or text depiction of, the relationship between different, groups of content on a website is, referred to as a:, a) Wireframe, b) Blueprint, c) Sitemap, , 46, , d) Card sorting, Answer: c, Explanation: An application, programming interface specifies how, some software components should, interact with each other., 219. Blueprints are intended to:, a) Prototype of the screen layout, showing navigation and main design, elements, b) Show the grouping of pages and, user journeys, c) Indicate the structure of a site, during site design and as a user, feature, d) Prototype typical customer, journeys or clickstreams through a, website, Answer: c, Explanation: A blueprint is a, reproduction of a technical drawing,, documenting an architecture or an, engineering design, using a contact, print process., 220. Storyboards are intended to:, a) Indicate the structure of a site, during site design and as a user, feature, b) Prototype of the screen layout, showing navigation and main design, elements, c) Integrate consistently available, components on the webpage (e.g.
Page 46 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, navigation, search boxes), d) Prototype typical customer, journeys or click streams through a, website, Answer: d, Explanation: An application, programming interface specifies how, some software components should, interact with each other., 221. Which of the following occupies, boot record of hard and floppy disks, and activated during computer, startup?, a) Worm, b) Boot sector virus, c) Macro virus, d) Virus, Answer: b, Explanation: A blueprint is a, reproduction of a technical drawing,, documenting an architecture or an, engineering design, using a contact, print process., 222. In ordered indices the file, containing the records is sequentially, ordered, a ___________ is an index, whose search key also defines the, sequential order of the file., a) Clustered index, b) Structured index, c) Unstructured index, d) Nonclustered index, , 47, , Answer: a, Explanation: Clustering index are also, called primary indices; the term, primary index may appear to denote, an index on a primary key, but such, indices can in fact be built on any, search key., 223. Indices whose search key, specifies an order different from the, sequential order of the file are called, ___________ indices., a) Nonclustered, b) Secondary, c) All of the mentioned, d) None of the mentioned, Answer: c, Explanation: Nonclustering index is, also called secondary indices., 224. An ____________ consists of a, search-key value and pointers to one, or more records with that value as, their search-key value., a) Index entry, b) Index hash, c) Index cluster, d) Index map, Answer: a, Explanation: The pointer to a record, consists of the identifier of a disk, block and an offset within the disk, block to identify the record within the, block.
Page 47 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, 225. In a _______ clustering index,, the index record contains the searchkey value and a pointer to the first, data record with that search-key, value and the rest of the records will, be in the sequential pointers., a) Dense, b) Sparse, c) Straight, d) Continuous, Answer: a, Explanation: In a dense nonclustering, index, the index must store a list of, pointers to all records with the same, search-key value., 226. In a __________ index, an index, entry appears for only some of the, search-key values., a) Dense, b) Sparse, c) Straight, d) Continuous, Answer: a, Explanation: Sparse indices can be, used only if the relation is stored in, sorted order of the search key, that is, if the index is a clustering index., 227. Incase the indices values are, larger, index is created for these, values of the index. This is called, a) Pointed index, b) Sequential index, c) Multilevel index, , 48, , d) Multiple index, Answer: c, Explanation: Indices with two or, more levels are called multilevel, indices., 228. A search key containing more, than one attribute is referred to as a, _________ search key., a) Simple, b) Composite, c) Compound, d) Secondary, Answer: b, Explanation: The structure of the, index is the same as that of any other, index, the only difference being that, the search key is not a single, attribute, but rather is a list of, attributes., 229. In B+ tree the node which points, to another node is called, a) Leaf node, b) External node, c) Final node, d) Internal node, Answer: d, Explanation: Nonleaf nodes are also, referred to as internal nodes., 230. Insertion of a large number of, entries at a time into an index is, referred to as __________ of the
Page 48 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, index., a) Loading, b) Bulk insertion, c) Bulk loading, d) Increase insertion, Answer: c, Explanation: Bulk loading is used to, improve efficiency and scalability., 231. While inserting the record into, the index, if the search-key value, does not appear in the index., a) The system adds a pointer to the, new record in the index entry, b) The system places the record being, inserted after the other records with, the same search-key values, c) The system inserts an index entry, with the search-key value in the index, at the appropriate position, d) None of the mentioned, Answer: c, Explanation: If the index entry stores, pointers to all records with the same, search key value, the system adds a, pointer to the new record in the, index entry., 232. A(n) _________ can be used to, preserve the integrity of a document, or a message., a) Message digest, b) Message summary, c) Encrypted message, , 49, , d) None of the mentioned, Answer: c, Explanation: Encryption algorithms, are used to keep the contents safe., 233. A hash function must meet, ________ criteria., a) Two, b) Three, c) Four, d) None of the mentioned, Answer: b, Explanation: Only if the criteria is, fulfilled the values are hashed., 234. What is the main limitation of, Hierarchical Databases?, a) Limited capacity (unable to hold, much data), b) Limited flexibility in accessing data, c) Overhead associated with, maintaining indexes, d) The performance of the database, is poor, Answer: b, Explanation: In this, the data items, are placed in a tree like hierarchical, structure., 235. The property (or set of, properties) that uniquely defines, each row in a table is called the:, a) Identifier, b) Index
Page 49 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, c) Primary key, d) Symmetric key, , c) Index, d) Array, , Answer: c, Explanation: Primary is used to, uniquely identify the tuples., , Answer: a, Explanation: A bitmap is simply an, array of bits., , 236. The separation of the data, definition from the program is known, as:, a) Data dictionary, b) Data independence, c) Data integrity, d) Referential integrity, , 239., , Answer: b, Explanation: Data dictionary is the, place where the meaning of the data, are organized., 237. Bitmap indices are a specialized, type of index designed for easy, querying on ___________, a) Bit values, b) Binary digits, c) Multiple keys, d) Single keys, Answer: c, Explanation: Each bitmap index is, built on a single key., 238. A _______ on the attribute A of, relation r consists of one bitmap for, each value that A can take., a) Bitmap index, b) Bitmap, , 50, , SELECT *, FROM r, WHERE gender = ’f’ AND income level, = ’L2’;, In this selection, we fetch the, bitmaps for gender value f and the, bitmap for income level value L2, and, perform an ________ of the two, bitmaps., a) Union, b) Addition, c) Combination, d) Intersection, Answer: d, Explanation: We compute a new, bitmap where bit i has value 1 if the, ith bit of the two bitmaps are both 1,, and has a value 0 otherwise., 240. To identify the deleted records, we use the ______________, a) Existence bitmap, b) Current bitmap, c) Final bitmap, d) Deleted bitmap
Page 50 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, Answer: a, Explanation: The bitmaps which are, deleted are denoted by 0., 241. What is the purpose of the index, in sql server?, a) To enhance the query performance, b) To provide an index to a record, c) To perform fast searches, d) All of the mentioned, Answer: d, Explanation: A database index is a, data structure that improves the, speed of data retrieval operations on, a database table at the cost of, additional writes., 242. How many types of indexes are, there in sql server?, a) 1, b) 2, c) 3, d) 4, Answer: b, Explanation: They are clustered index, and non clustered index., 243. How non clustered index point, to the data?, a) It never points to anything, b) It points to a data row, c) It is used for pointing data rows, containing key values, d) None of the mentioned, , 51, , Answer: c, Explanation: Nonclustered indexes, have a structure separate from the, data rows. A nonclustered index, contains the nonclustered index key, values and each key value entry has a, pointer to the data row that contains, the key value., 244. Which one is true about, clustered index?, a) Clustered index is not associated, with table, b) Clustered index is built by default, on unique key columns, c) Clustered index is not built on, unique key columns, d) None of the mentioned, Answer: b, Explanation: Nonclustered indexes, have a structure separate from the, data rows. A nonclustered index, contains the nonclustered index key, values and each key value entry has a, pointer to the data row that contains, the key value., 245. What is true about indexes?, a) Indexes enhance the performance, even if the table is updated, frequently, b) It makes harder for sql server, engines to work to work on index, which have large keys, c) It doesn’t make harder for sql, server engines to work to work on
Page 51 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, index which have large keys, d) None of the mentioned, , c) Physical schema, d) External schema, , Answer: b, Explanation: Indexes tend to improve, the performance., , Answer: d, Explanation: An externally-defined, schema can provide access to tables, that are managed on any PostgreSQL,, Microsoft SQL Server, SAS, Oracle, or, MySQL database., , 246. A collection of data designed to, be used by different people is called, a/an, a) Organization, b) Database, c) Relationship, d) Schema, Answer: b, Explanation: Database is a collection, of related tables., 247. Which of the following is the, oldest database model?, a) Relational, b) Deductive, c) Physical, d) Network, Answer: d, Explanation: The network model is a, database model conceived as a, flexible way of representing objects, and their relationships., 248. Which of the following schemas, does define a view or views of the, database for particular users?, a) Internal schema, b) Conceptual schema, , 52, , 249. Which of the following are the, process of selecting the data storage, and data access characteristics of the, database?, a) Logical database design, b) Physical database design, c) Testing and performance tuning, d) Evaluation and selecting, Answer: b, Explanation: The physical design of, the database optimizes performance, while ensuring data integrity by, avoiding unnecessary data, redundancies., 250. Which of the following terms, does refer to the correctness and, completeness of the data in a, database?, a) Data security, b) Data constraint, c) Data independence, d) Data integrity
Page 52 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, Answer: d, Explanation: ACID property is, satisfied by transaction in database., 251. The relationship between, DEPARTMENT and EMPLOYEE is a, a) One-to-one relationship, b) One-to-many relationship, c) Many-to-many relationship, d) Many-to-one relationship, Answer: b, Explanation: One entity department, is related to several employees., 252. A table can be logically, connected to another table by, defining a, a) Super key, b) Candidate key, c) Primary key, d) Unique key, Answer: c, Explanation: A superkey is a, combination of attributes that can be, uniquely used to identify a database, record., 253. If the state of the database no, longer reflects a real state of the, world that the database is supposed, to capture, then such a state is called, a) Consistent state, b) Parallel state, c) Durable state, , 53, , d) Inconsistent state, Answer: d, Explanation: SQL data consistency is, that whenever a transaction is, performed, it sees a consistent, database., 254. Ensuring isolation property is the, responsibility of the, a) Recovery-management component, of the DBMS, b) Concurrency-control component of, the DBMS, c) Transaction-management, component of the DBMS, d) Buffer management component in, DBMS, Answer: b, Explanation: Concurrency control, ensures that correct results for, concurrent operations are generated, while getting those results as quickly, as possible., 255. _______________ is a, procedural extension of Oracle – SQL, that offers language constructs, similar to those in imperative, programming languages., a) SQL, b) PL/SQL, c) Advanced SQL, d) PQL
Page 53 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, Answer: b, Explanation: PL/SQL is an imperative, 3GL that was designed specifically for, the seamless processing of SQL, commands., 256. ___________ combines the data, manipulating power of SQL with the, data processing power of Procedural, languages., a) PL/SQL, b) SQL, c) Advanced SQL, d) PQL, Answer: a, Explanation: PL/SQL is an imperative, 3GL that was designed specifically for, the seamless processing of SQL, commands., 257. _______________ has made, PL/SQL code run faster without, requiring any additional work on the, part of the programmer., a) SQL Server, b) My SQL, c) Oracle, d) SQL Lite, Answer: c, Explanation: An Oracle database is a, collection of data treated as a unit., The purpose of a database is to store, and retrieve related information., , 54, , 258. A line of PL/SQL text contains, groups of characters known as, a) Lexical Units, b) Literals, c) Textual Units, d) Identifiers, Answer: a, Explanation: Lexical items can be, generally understood to convey a, single meaning, much as a lexeme,, but are not limited to single words., 259. We use ______________ name, PL/SQL program objects and units., a) Lexical Units, b) Literals, c) Delimiters, d) Identifiers, Answer: d, Explanation: The database object, name is referred to as its identifier., 260. Consider money is transferred, from (1)account-A to account-B and, (2) account-B to account-A. Which of, the following form a transaction?, a) Only 1, b) Only 2, c) Both 1 and 2 individually, d) Either 1 or 2, Answer: c, Explanation: The term transaction, refers to a collection of operations, that form a single logical unit of work.
Page 54 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, 261. A transaction is delimited by, statements (or function calls) of the, form __________, a) Begin transaction and end, transaction, b) Start transaction and stop, transaction, c) Get transaction and post, transaction, d) Read transaction and write, transaction, Answer: a, Explanation: The transaction consists, of all operations executed between, the begin transaction and end, transaction., 262. Identify the characteristics of, transactions, a) Atomicity, b) Durability, c) Isolation, d) All of the mentioned, Answer: d, Explanation: Because of the above, three properties, transactions are an, ideal way of structuring interaction, with a database., 263. Which of the following has “allor-none” property?, a) Atomicity, b) Durability, c) Isolation, , 55, , d) All of the mentioned, Answer: a, Explanation: Either all operations of, the transaction are reflected properly, in the database, or none are., 264. The database system must take, special actions to ensure that, transactions operate properly, without interference from, concurrently executing database, statements. This property is referred, to as, a) Atomicity, b) Durability, c) Isolation, d) All of the mentioned, Answer: c, Explanation: Even though multiple, transactions may execute, concurrently, the system guarantees, that, for every pair of transactions Ti, and Tj, it appears to Ti that either Tj, finished execution before Ti started, or Tj started execution after Ti, finished., 265. The property of a transaction, that persists all the crashes is, a) Atomicity, b) Durability, c) Isolation, d) All of the mentioned
Page 55 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, Answer: b, Explanation: After a transaction, completes successfully, the changes it, has made to the database persist,, even if there are system failures., 266. __________ states that only, valid data will be written to the, database., a) Consistency, b) Atomicity, c) Durability, d) Isolation, Answer: a, Explanation: If for some reason, a, transaction is executed that violates, the database’s consistency rules, the, entire transaction will be rolled back, and the database will be restored to a, state consistent with those rules., 267. Transaction processing is, associated with everything below, except, a) Producing detail summary or, exception reports, b) Recording a business activity, c) Confirming an action or triggering a, response, d) Maintaining a data, Answer: c, Explanation: Collections of operations, that form a single logical unit of work, are called transactions., , 56, , 268. The Oracle RDBMS uses the, ____ statement to declare a new, transaction start and its properties., a) BEGIN, b) SET TRANSACTION, c) BEGIN TRANSACTION, d) COMMIT, Answer: b, Explanation: Commit is used to store, all the transactions., 269. ____ means that the data used, during the execution of a transaction, cannot be used by a second, transaction until the first one is, completed., a) Consistency, b) Atomicity, c) Durability, d) Isolation, Answer: d, Explanation: Even though multiple, transactions may execute, concurrently, the system guarantees, that, for every pair of transactions Ti, and Tj, it appears to Ti that either Tj, finished execution before Ti started, or Tj started execution after Ti, finished., 270. In SQL, which command is used, to issue multiple CREATE TABLE,, CREATE VIEW and GRANT statements, in a single transaction?, a) CREATE PACKAGE
Page 56 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, b) CREATE SCHEMA, c) CREATE CLUSTER, d) All of the mentioned, Answer: b, Explanation: A database schema of a, database system is its structure, described in a formal language, supported by the database, management system and refers to, the organization of data as a, blueprint of how a database is, constructed., 271. In SQL, the CREATE TABLESPACE, is used, a) To create a place in the database, for storage of scheme objects,, rollback segments, and naming the, data files to comprise the tablespace, b) To create a database trigger, c) To add/rename data files, to, change storage, d) All of the mentioned, Answer: a, Explanation: Triggers are used to, initialize the actions for an activity., 272. Which character function can be, used to return a specified portion of a, character string?, a) INSTR, b) SUBSTRING, c) SUBSTR, d) POS, , 57, , Answer: c, Explanation: SUBSTR are used to, match the particular characters in a, string., 273. Which of the following is TRUE, for the System Variable $date$?, a) Can be assigned to a global, variable, b) Can be assigned to any field only, during design time, c) Can be assigned to any variable or, field during run time, d) Can be assigned to a local variable, Answer: b, Explanation: A database schema of a, database system is its structure, described in a formal language, supported by the database, management system and refers to, the organization of data as a, blueprint of how a database is, constructed., 275. What are the different events in, Triggers?, a) Define, Create, b) Drop, Comment, c) Insert, Update, Delete, d) Select, Commit, Answer: c, Explanation: A database trigger is a, procedural code that is automatically, executed in response to certain
Page 57 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, events on a particular table or view in, a database., 276. Which of the following is not a, property of transactions?, a) Atomicity, b) Concurrency, c) Isolation, d) Durability, Answer: d, Explanation: ACID properties are the, properties of transactions., 277. SNAPSHOT is used for (DBA), a) Synonym, b) Tablespace, c) System server, d) Dynamic data replication, Answer: d, Explanation: Snapshot gets the, instance of the database at that time., 278. Isolation of the transactions is, ensured by, a) Transaction management, b) Application programmer, c) Concurrency control, d) Recovery management, Answer: c, Explanation: ACID properties are the, properties of transactions., 279. Constraint checking can be, disabled in existing _______________, and _____________ constraints so, , 58, , that any data you modify or add to, the table is not checked against the, constraint., a) CHECK, FOREIGN KEY, b) DELETE, FOREIGN KEY, c) CHECK, PRIMARY KEY, d) PRIMARY KEY, FOREIGN KEY, Answer: a, Explanation: Check and foreign, constraints are used to constraint the, table data., 280. In order to maintain, transactional integrity and database, consistency, what technology does a, DBMS deploy?, a) Triggers, b) Pointers, c) Locks, d) Cursors, Answer: c, Explanation: Locks are used to, maintain database consistency., 281. A lock that allows concurrent, transactions to access different rows, of the same table is known as a, a) Database-level lock, b) Table-level lock, c) Page-level lock, d) Row-level lock, Answer: d, Explanation: Locks are used to, maintain database consistency.
Page 58 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, 282. Which of the following are, introduced to reduce the overheads, caused by the log-based recovery?, a) Checkpoints, b) Indices, c) Deadlocks, d) Locks, Answer: a, Explanation: Checkpoints are, introduced to reduce overheads, caused by the log-based recovery., 283. Which of the following protocols, ensures conflict serializability and, safety from deadlocks?, a) Two-phase locking protocol, b) Time-stamp ordering protocol, c) Graph based protocol, d) None of the mentioned, Answer: b, Explanation: Time-stamp ordering, protocol ensures conflict, serializability and safety from, deadlocks., 284. A system is in a ______ state if, there exists a set of transactions such, that every transaction in the set is, waiting for another transaction in the, set., a) Idle, b) Waiting, c) Deadlock, d) Ready, , 59, , Answer: c, Explanation: When one data item is, waiting for another data item in a, transaction then system is in, deadlock., 285. The deadlock state can be, changed back to stable state by using, _____________ statement., a) Commit, b) Rollback, c) Savepoint, d) Deadlock, Answer: b, Explanation: Rollback is used to, rollback to the point before lock is, obtained., 286. What are the ways of dealing, with deadlock?, a) Deadlock prevention, b) Deadlock recovery, c) Deadlock detection, d) All of the mentioned, Answer: d, Explanation: Deadlock prevention is, also called as deadlock recovery., Prevention is commonly used if the, probability that the system would, enter a deadlock state is relatively, high; otherwise, detection and, recovery are more efficient., 287. The most recent version of, standard SQL prescribed by the
Page 59 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, American National Standards, Institute is, a) SQL 2016, b) SQL 2002, c) SQL – 4, d) SQL2, Answer: a, Explanation: SQL-2016 is the most, recent version of standard SQL, prescribed by the ANSI., 288. ANSI-standard SQL allows the, use of special operators in, conjunction with the WHERE clause., A special operator used to check, whether an attribute value is null is, a) BETWEEN, b) IS NULL, c) LIKE, d) IN, Answer: b, Explanation: Exists is used to check, whether an attribute value is null or, not in conjunction with the where, clause., 289. The method of access that uses, key transformation is called as, a) Direct, b) Hash, c) Random, d) Sequential, , 60, , Answer: b, Explanation: Hash technique uses, particular hash key value., 290. Why do we need concurrency, control on B+ trees ?, a) To remove the unwanted data, b) To easily add the index elements, c) To maintain accuracy of index, d) All of the mentioned, Answer: c, Explanation: Indices do not have to, be treated like other database, structures., 291. How many techniques are, available to control concurrency on, B+ trees?, a) One, b) Three, c) Four, d) None of the mentioned, Answer: d, Explanation: Two techniques are, present., 292. In crabbing protocol locking, a) Goes down the tree and back up, b) Goes up the tree and back down, c) Goes down the tree and releases, d) Goes up the tree and releases, Answer: a, Explanation: It moves in a crab like, manner.
Page 60 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, 293. The deadlock can be handled by, a) Removing the nodes that are, deadlocked, b) Restarting the search after, releasing the lock, c) Restarting the search without, releasing the lock, d) Resuming the search, Answer: b, Explanation: Crabbing protocol, moves in a crab like manner., 294. The recovery scheme must also, provide, a) High availability, b) Low availability, c) High reliability, d) High durability, Answer: a, Explanation: It must minimize the, time for which the database is not, usable after a failure., 295. Which one of the following is a, failure to a system, a) Boot crash, b) Read failure, c) Transaction failure, d) All of the mentioned, Answer: c, Explanation: Types of system failure, are transaction failure, system crash, and disk failure., , 61, , 296. Which of the following belongs, to transaction failure, a) Read error, b) Boot error, c) Logical error, d) All of the mentioned, Answer: c, Explanation: Types of system, transaction failure are logical and, system error., 297. The system has entered an, undesirable state (for example,, deadlock), as a result of which a, transaction cannot continue with its, normal execution. This is, a) Read error, b) Boot error, c) Logical error, d) System error, Answer: c, Explanation: The transaction, can be, re-executed at a later time., 298. The transaction can no longer, continue with its normal execution, because of some internal condition,, such as bad input, data not found,, overflow, or resource limit exceeded., This is, a) Read error, b) Boot error, c) Logical error, d) System error
Page 61 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, Answer: c, Explanation: The transaction, can be, re-executed at a later time., 299. The assumption that hardware, errors and bugs in the software bring, the system to a halt, but do not, corrupt the nonvolatile storage, contents, is known as the, a) Stop assumption, b) Fail assumption, c) Halt assumption, d) Fail-stop assumption, Answer: d, Explanation: Well-designed systems, have numerous internal checks, at, the hardware and the software level,, that bring the system to a halt when, there is an error. Hence, the fail-stop, assumption is a reasonable one., 300. Which kind of failure loses its, data in head crash or failure during a, transfer operation., a) Transaction failure, b) System crash, c) Disk failure, d) All of the mentioned, Answer: c, Explanation: Copies of the data on, other disks, or archival backups on, tertiary media, such as DVD or tapes,, are used to recover from the failure., , 62, , 301. The log is a sequence of, _________ recording all the update, activities in the database., a) Log records, b) Records, c) Entries, d) Redo, Answer: a, Explanation: The most widely used, structure for recording database, modifications is the log., 302. In the ___________ scheme, a, transaction that wants to update the, database first creates a complete, copy of the database., a) Shadow copy, b) Shadow Paging, c) Update log records, d) All of the mentioned, Answer: a, Explanation: If at any point the, transaction has to be aborted, the, system merely deletes the new copy., The old copy of the database has not, been affected., 303. The ____________ scheme uses, a page table containing pointers to all, pages; the page table itself and all, updated pages are copied to a new, location.
Page 62 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, a) Shadow copy, b) Shadow Paging, c) Update log records, d) All of the mentioned, , c) Immediate-modification, d) Undo, , Answer: b, Explanation: Any page which is not, updated by a transaction is not, copied, but instead the new page, table just stores a pointer to the, original page., , Answer: a, Explanation: Deferred modification, has the overhead that transactions, need to make local copies of all, updated data items; further, if a, transaction reads a data item that it, has updated, it must read the value, from its local copy., , 304. The current copy of the, database is identified by a pointer,, called ____________ which is stored, on disk., a) Db-pointer, b) Update log, c) Update log records, d) All of the mentioned, , 306. If database modifications occur, while the transaction is still active,, the transaction is said to use the, ___________technique., a) Deferred-modification, b) Late-modification, c) Immediate-modification, d) Undo, , Answer: a, Explanation: Any page which is not, updated by a transaction is not, copied, but instead the new page, table just stores a pointer to the, original page., , Answer: c, Explanation: We say a transaction, modifies the database if it performs, an update on a disk buffer, or on the, disk itself; updates to the private part, of main memory do not count as, database modifications., , 305. If a transaction does not modify, the database until it has committed,, it is said to use the ___________, technique., a) Deferred-modification, b) Late-modification, , 63, , 307. ____________ using a log record, sets the data item specified in the log, record to the old value., a) Deferred-modification, b) Late-modification
Page 63 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, c) Immediate-modification, d) Undo, Answer: d, Explanation: Undo brings the, previous contents., 308. In the __________ phase, the, system replays updates of all, transactions by scanning the log, forward from the last checkpoint., a) Repeating, b) Redo, c) Replay, d) Undo, Answer: b, Explanation: Undo brings the, previous contents., 309. In order to reduce the overhead, in retrieving the records from the, storage space we use, a) Logs, b) Log buffer, c) Medieval space, d) Lower records, Answer: b, Explanation: The output to stable, storage is in units of blocks., 310. The order of log records in the, stable storage ____________ as the, order in which they were written to, , 64, , the log buffer., a) Must be exactly the same, b) Can be different, c) Is opposite, d) Can be partially same, Answer: a, Explanation: As a result of log, buffering, a log record may reside in, only main memory (volatile storage), for a considerable time before it is, output to stable storage., 311. Before a block of data in main, memory can be output to the, database, all log records pertaining to, data in that block must have been, output to stable storage. This is, a) Read-write logging, b) Read-ahead logging, c) Write-ahead logging, d) None of the mentioned, Answer: c, Explanation: The WAL rule requires, only that the undo information in the, log has been output to stable storage,, and it permits the redo information, to be written later., 312. Writing the buffered log to, __________ is sometimes referred to, as a log force., a) Memory
Page 64 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, b) Backup, c) Redo memory, d) Disk, Answer: d, Explanation: If there are insufficient, log records to fill the block, all log, records in main memory are, combined into a partially full block, and are output to stable storage., 313. The silicon chips used for data, processing are called, a) RAM chips, b) ROM chips, c) Micro processors, d) PROM chips, Answer: d, Explanation: PROM is Programmable, Read Only Memory., 314. Which of the following is used, for manufacturing chips?, a) Control bus, b) Control unit, c) Parity unit, d) Semiconductor, Answer: d, Explanation: A semiconductor is a, material which has electrical, conductivity between that of a, , 65, , conductor such as copper and that of, an insulator such as glass., 315. What was the name of the first, commercially available, microprocessor chip?, a) Intel 308, b) Intel 33, c) Intel 4004, d) Motorola 639, Answer: c, Explanation: The Intel 4004 is a 4-bit, central processing unit (CPU), released by Intel Corporation in 1971, 316. Which lock should be obtained, to prevent a concurrent transaction, from executing a conflicting read,, insert or delete operation on the, same key value., a) Higher-level lock, b) Lower-level lock, c) Read only lock, d) Read write, Answer: a, Explanation: Operations acquire, lower-level locks while they execute,, but release them when they, complete; the corresponding, transaction must however retain a, higher-level lock in a two-phase, manner to prevent concurrent
Page 65 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, transactions from executing, conflicting actions., , backup site where all the data from, the primary site are replicated., , 317. Once the lower-level lock is, released, the operation cannot be, undone by using the old values of, updated data items, and must instead, be undone by executing a, compensating operation; such an, operation is called, a) Logical operation, b) Redo operation, c) Logical undo operation, d) Undo operation, , 319. Remote backup system must be, _________ with the primary site., a) Synchronised, b) Separated, c) Connected, d) Detached but related, , Answer: a, Explanation: It is important that the, lower-level locks acquired during an, operation are sufficient to perform a, subsequent logical undo of the, operation., , Answer: a, Explanation: We can achieve high, availability by performing transaction, processing at one site, called the, primary site, and having a remote, backup site where all the data from, the primary site are replicated., , 318. The remote backup site is, sometimes also called the, a) Primary Site, b) Secondary Site, c) Tertiary Site, d) None of the mentioned, , 320. The backup is taken by, a) Erasing all previous records, b) Entering the new records, c) Sending all log records from, primary site to the remote backup, site, d) Sending selected records from, primary site to the remote backup, site, , Answer: b, Explanation: We can achieve high, availability by performing transaction, processing at one site, called the, primary site, and having a remote, , Answer: c, Explanation: We can achieve high, availability by performing transaction, processing at one site, called the, primary site, and having a remote, , 66
Page 66 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, backup site where all the data from, the primary site are replicated., 321. When the __________ the, backup site takes over processing and, becomes the primary., a) Secondary fails, b) Backup recovers, c) Primary fails, d) None of the mentioned, Answer: c, Explanation: When the original, primary site recovers, it can either, play the role of remote backup, or, take over the role of primary site, again., 322. The simplest way of transferring, control is for the old primary to, receive __________ from the old, backup site., a) Undo logs, b) Redo Logs, c) Primary Logs, d) All of the mentioned, Answer: c, Explanation: If control must be, transferred back, the old backup site, can pretend to have failed, resulting, in the old primary taking over., , 67, , 323. In the __________ phase, the, system replays updates of all, transactions by scanning the log, forward from the last checkpoint., a) Repeating, b) Redo, c) Replay, d) Undo, Answer: b, Explanation: Undo brings the, previous contents., 324. The actions which are played in, the order while recording it is called, ______________ history., a) Repeating, b) Redo, c) Replay, d) Undo, Answer: a, Explanation: Undo brings the, previous contents., 325. A special redo-only log record <, Ti, Xj, V1> is written to the log, where, V1 is the value being restored to data, item Xj during the rollback. These log, records are sometimes called, a) Log records, b) Records, c) Compensation log records, d) Compensation redo records
Page 67 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, Answer: c, Explanation: Such records do not, need undo information since we, never need to undo such an undo, operation., 326. The process of designating sub, groupings within the entity set is, called as _______, a) Specialization, b) Division, c) Aggregation, d) Finalization, Answer: a, Explanation: The process of, designating sub-groupings within the, entity set is called as specialization., Specialization allows us to distinguish, among entities., 327. State true or false: Specialization, can be applied only once, a) True, b) False, , Answer: a, Explanation: We can apply, specialization multiple times to refine, a design. An entity set may also be, specialized by more than one, distinguishing feature., , 68, , 328. Which of the following is the, specialization that permits multiple, sets, a) Superclass specialization, b) Disjoint specialization, c) Overlapping specialization, d) None of the mentioned, Answer: c, Explanation: Overlapping, specialization is the type of, specialization that permits multiple, sets. But disjoint specialization does, not permit multiple sets. Disjoint, specialization permits at most one, set., 329. The similarities between the, entity set can be expressed by which, of the following features?, a) Specialization, b) Generalization, c) Uniquation, d) Inheritance, Answer: b, Explanation: The similarities between, the entity set can be expressed by, the generalization feature. It is a, containment o the relationship that, exists between a higher level entity, set and one or more lower level, entity sets.
Page 68 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, 330. Higher level entity sets are, designated by the term _________, a) Sub class, b) Super class, c) Parent class, d) Root class, , Answer: d, Explanation: Machine definition is not, a generalization constraint. Condition, defined, user defined, disjoint and, overlapping are 4 generalization, constraints., , Answer: b, Explanation: Higher level entity sets, can also be designated by the term, super class. In the similar manner, lower level entity sets can also be, designated by the term sub class., , 333. Condition defined generalization, constraint is also said to be ________, a) Attribute defined, b) Constraint defined, c) Value defined, d) Undefined, , 331. State true or false: The, attributes of the higher level entity, sets are inherited by the attributes of, the lower level entity sets, a) True, b) False, , Answer: a, Explanation: Condition defined, generalization constraint is also said, to be attribute defined., , Answer: a, Explanation: The attributes of the, higher level entity sets are inherited, by the attributes of the lower level, entity sets. But the inverse is not true, in this case., 332. Which of the following is not a, generalization constraint?, a) Condition-defined, b) User defined, c) Disjoint, d) Machine defined, , 69, , 334. Which of the following is not a, feature of a good relational design?, a) Specifying primary keys, b) Specifying foreign keys, c) Preserving integrity constraints, d) Allowing redundancy of attributes, Answer: d, Explanation: Allowing redundancy of, attributes makes it very difficult for, data extraction. So, It is not a good, relational design feature., 335. The dependency rules specified, by the database designer are known
Page 69 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, as _______, a) Designer dependencies, b) Database rules, c) Functional dependencies, d) None of the mentioned, Answer: c, Explanation: The dependency rules, specified by the database designer, are known as functional, dependencies. The normal forms are, based on functional dependencies., 336. If the decomposition is unable to, represent certain important facts, about the relation, then such a, decomposition is called as?, a) Lossless decomposition, b) Lossy decomposition, c) Insecure decomposition, d) Secure decomposition, Answer: b, Explanation: If the decomposition is, unable to represent certain, important facts about the relation,, then such a decomposition is called, as lossy decomposition. Lossy, decompositions should be avoided as, they result in the loss of data., 337. An instance of a relation that, satisfies all real world constraints is, known as?, , 70, , a) Proper relation, b) Ideal relation, c) Perfect relation, d) Legal relation, Answer: d, Explanation: A relation that satisfies, all the real world constraints is called, as a legal relation. An instance of a, legal relation is called as a legal, instance., 338. If K → R then K is said to be the, _______ of R, a) Candidate key, b) Foreign key, c) Super key, d) Domain, Answer: c, Explanation: If K → R then k is said to, be the superkey of R i.e. K uniquely, identifies every tuple in the relation, R., 339. X → Y holds on a schema k(K) if?, a) At least one legal instance satisfies, the functional dependency, b) No legal instance satisfies the, functional dependency, c) Each and every legal instance, satisfies the functional dependency, d) None of the mentioned
Page 70 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, Answer: c, Explanation: X → Y holds on a schema, k(K) if each and every legal instance, satisfies the functional dependency., Even if one instance does not satisfy, the functional dependency X→ Y, does not hold on a schema., 340. X→ Y is trivial if?, a) X ⊂ Y, b) Y ⊂ X, c) X ⊇ Y, d) None of the mentioned, Answer: a, Explanation: X→ Y is said to be trivial, if X is a subset of Y. Thus X ⊂ Y, implies X→Y is trivial., 341. Which of the following is not a, condition for X→ Y in Boyce codd, normal form?, a) X → Y is trivial, b) X is the superkey for the relational, schema R, c) Y is the superkey for the relational, schema R, d) All of the mentioned, Answer: c, Explanation: Y does not need to be a, superkey of the relation for the given, functional dependency to satisfy, BCNF. X→ Y must be trivial and X, , 71, , must be the superkey of the relation, R., 342. Which of the following is used to, express database consistency?, a) Primary keys, b) Functional dependencies, c) Check clause, d) All of the mentioned, Answer: d, Explanation: Primary keys, Functional, dependencies, Check clause are all, used to express database, consistency., 343. _________ introduces the, Management Data Warehouse, (MDW) to SQL Server Management, Studio for streamlined performance, troubleshooting., a) SQL Server 2005, b) SQL Server 2008, c) SQL Server 2012, d) SQL Server 2014, Answer: b, Explanation: MDW is a set of, components that enable a database, developer or administrator to quickly, track down problems that could be, causing performance degradation.
Page 71 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, 344. Point out the correct statement., a) MDW consist of three components, b) SQL Server Express instances can, be targets, c) Setting up the MDW is a one-step, process, d) All of the mentioned, Answer: a, Explanation: MDW consists of three, components: Data Collector, MDW, database and MDW reports., 345. Which of the following mode, allows for the collection and, uploading of data to occur on, demand?, a) Non-cached mode, b) Cached mode, c) Mixed mode, d) All of the mentioned, Answer: a, Explanation: In non-cached mode,, collection and upload are on the, same schedule., 346. Which of the following scenario, favours cached mode?, a) Continuous collection of data, b) Less frequent uploads, c) Data collection and uploading of, jobs on different schedules, , 72, , d) All of the mentioned, , Answer: d, Explanation: Cached mode uses, separate schedules for collection and, upload., 347. Point out the wrong statement., a) The Data Collection is performed, primarily through SSIS packages that, control the collection frequency on, the target, b) You should change the database, name after creation, c) Do not change any of the job, specifications for the data collection, and upload jobs, d) None of the mentioned, Answer: b, Explanation: You should not change, the database name after creation,, because all of the jobs created to, manage the database collection refer, to the database by the original name, and will generate errors if the name, is changed., 348. Which of the following is the, best Practice and Caveat for, Management Data Warehouse?, a) Use a centralized server for the, MDW database
Page 72 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, b) The XML parameters for a single TSQL collection item can have multiple, <Query> elements, c) Use a distributed server for the, MDW database, d) All of the mentioned, , warehouse schema that is required, for the Server Activity?, a) snapshots.query_stat, b) snapshots.os_latch_stats, c) snapshots.active_sessions, d) all of the mentioned, , Answer: a, Explanation: Centralized server allows, you to use a single point for viewing, reports for multiple instances., , Answer: b, Explanation:, snapshots.os_latch_stats is a System, level resource table., , 349. ____________ stores, information about how the, management data warehouse reports, should group and aggregate, performance counters., a) core.snapshots_internal, b), core.supported_collector_types_inter, nal, c) core.wait_categories, d), core.performance_counter_report_gr, oup_items, , 351. Which of the following is syntax, for sp_add_collector_type, procedure?, a) core.sp_add_collector [, @collector_type_uid = ], ‘collector_type_uid’, b) core.sp_add_collector_type [, @collector_type_uid = ]., c) core.sp_add_collector_type [, @collector_type_uid = ], ‘collector_type_uid’, d) none of the mentioned, , Answer: d, Explanation: core.wait_categories, contains the categories used to group, wait types according to wait_type, characteristic., 350. Which of the following table is, used in the management data, , 73, , Answer: c, Explanation:, core.sp_add_collector_type adds a, new entry to the, core.supported_collector_types view, in the management data warehouse, database.
Page 73 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, 352. What does collector_type_id, stands for in the following code, snippet?, core.sp_remove_collector_type [, @collector_type_uid = ], ‘collector_type_uid’, a) uniqueidentifier, b) membership role, c) directory, d) none of the mentioned, Answer: a, Explanation: collector_type_uid is the, GUID for the collector type., 353. Which of the following clustering, type has characteristic shown in the, below figure?, , a) Partitional, b) Hierarchical, c) Naive bayes, d) None of the mentioned, Answer: b, Explanation: Hierarchical clustering, groups data over a variety of scales, , 74, , by creating a cluster tree or, dendrogram., 354. Point out the correct statement., a) The choice of an appropriate, metric will influence the shape of the, clusters, b) Hierarchical clustering is also called, HCA, c) In general, the merges and splits, are determined in a greedy manner, d) All of the mentioned, Answer: d, Explanation: Some elements may be, close to one another according to, one distance and farther away, according to another., 355. Which of the following is finally, produced by Hierarchical Clustering?, a) final estimate of cluster centroids, b) tree showing how close things are, to each other, c) assignment of each point to, clusters, d) all of the mentioned, Answer: b, Explanation: Hierarchical clustering is, an agglomerative approach., 356. Which of the following is, required by K-means clustering?
Page 74 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, a) defined distance metric, b) number of clusters, c) initial guess as to cluster centroids, d) all of the mentioned, , 359. Hierarchical clustering should be, primarily used for exploration., a) True, b) False, , Answer: d, Explanation: K-means clustering, follows partitioning approach., , Answer: a, Explanation: Hierarchical clustering is, deterministic., , 357. Point out the wrong statement., a) k-means clustering is a method of, vector quantization, b) k-means clustering aims to, partition n observations into k, clusters, c) k-nearest neighbor is same as kmeans, d) none of the mentioned, , 360. Which of the following function, is used for k-means clustering?, a) k-means, b) k-mean, c) heatmap, d) none of the mentioned, , Answer: c, Explanation: k-nearest neighbor has, nothing to do with k-means., 358. Which of the following, combination is incorrect?, a) Continuous – euclidean distance, b) Continuous – correlation similarity, c) Binary – manhattan distance, d) None of the mentioned, Answer: d, Explanation: You should choose a, distance/similarity that makes sense, for your problem., , 75, , Answer: a, Explanation: K-means requires a, number of clusters., 361. Which of the following clustering, requires merging approach?, a) Partitional, b) Hierarchical, c) Naive Bayes, d) None of the mentioned, Answer: b, Explanation: Hierarchical clustering, requires a defined distance as well., 362. K-means is not deterministic and, it also consists of number of, iterations.
Page 75 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, a) True, b) False, Answer: a, Explanation: K-means clustering, produces the final estimate of cluster, centroids., 363. Which of the following term is, appropriate to the below figure?, , a) Large Data, b) Big Data, c) Dark Data, d) None of the mentioned, Answer: b, Explanation: Big data is a broad term, for data sets so large or complex that, traditional data processing, applications are inadequate., 364. Point out the correct statement., a) Machine learning focuses on, prediction, based on known, properties learned from the training, data, b) Data Cleaning focuses on, prediction, based on known, properties learned from the training, data, , 76, , c) Representing data in a form which, both mere mortals can understand, and get valuable insights is as much a, science as much as it is art, d) None of the mentioned, Answer: d, Explanation: Visualization is, becoming a very important aspect., 365. Which of the following, characteristic of big data is relatively, more concerned to data science?, a) Velocity, b) Variety, c) Volume, d) None of the mentioned, Answer: b, Explanation: Big data enables, organizations to store, manage, and, manipulate vast amounts of disparate, data at the right speed and at the, right time., 366. Which of the following analytical, capabilities are provided by, information management company?, a) Stream Computing, b) Content Management, c) Information Integration, d) All of the mentioned
Page 76 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, Answer: d, Explanation: With stream computing,, store less, analyze more and make, better decisions faster., 367. Point out the wrong statement., a) The big volume indeed represents, Big Data, b) The data growth and social media, explosion have changed how we look, at the data, c) Big Data is just about lots of data, d) All of the mentioned, Answer: c, Explanation: Big Data is actually a, concept providing an opportunity to, find new insight into your existing, data as well guidelines to capture and, analysis your future data., 368. Which of the following step is, performed by data scientist after, acquiring the data?, a) Data Cleansing, b) Data Integration, c) Data Replication, d) All of the mentioned, Answer: a, Explanation: Data cleansing, data, cleaning or data scrubbing is the, process of detecting and correcting, (or removing) corrupt or inaccurate, , 77, , records from a record set, table, or, database., 369. 3V’s are not sufficient to, describe big data., a) True, b) False, Answer: a, Explanation: IBM data scientists, break big data into four dimensions:, volume, variety, velocity and veracity., 370: Which of the following applied, on warehouse?, a) write only, b) read only, c) both a & b, d) none of these, Answer:B, 371: Data can be store , retrive and, updated in …, a) SMTOP, b) OLTP, c) FTP, d) OLAP, Answer:B
Page 77 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, 372: Which of the following is a good, alternative to the star schema?, , Answer:C, , a) snow flake schema, , 375: Which of the following is true for, Classification?, , b) star schema, , a) A subdivision of a set, , c) star snow flake schema, , b) A measure of the accuracy, , d) fact constellation, , c) The task of assigning a, classification, , Answer :D, 373: Patterns that can be discovered, from a given database are which, type…, a) More than one type, b) Multiple type always, c) One type only, d) No specific type, Answer :A, 374:Background knowledge is…, a) It is a form of automatic learning., b) A neural network that makes use, of a hidden layer, c) The additional acquaintance used, by a learning algorithm to facilitate, the learning process, d) None of these, , 78, , d) All of these, Answer:A, 376: Data mining is?, a) time variant non-volatile collection, of data, b) The actual discovery phase of a, knowledge, c) The stage of selecting the right, data, d) None of these, Answer -:B, 377: ——- is not a data mining, functionality?, A) Clustering and Analysis, B) Selection and interpretation, C) Classification and regression
Page 78 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, D) Characterization and, Discrimination, Answer -:B, 378: Which of the following can also, applied to other forms?, a) Data streams & Sequence data, b) Networked data, c) Text & Spatial data, d) All of these, Answer -:D, 379:Which of the following is general, characteristics or features of a target, class of data?, a) Data selection, b) Data discrimination, c) Data Classification, c) Data Characterization, Answer -:D, 380: ——– is the out put of KDD…, a) Query, b) Useful Information, c) Data, , d) information, Answer -:B, 381: What is noise?, a) component of a network, b) context of KDD and data mining, c) aspects of a data warehouse, d) None of these, Answer -:B, 382.Firms that are engaged in, sentiment mining are analyzing data, collected from?, A. social media sites., B. in-depth interviews., C. focus groups., D. experiments., E. observations., Answer -:A. social media sites., Which of the following forms of data, mining assigns records to one of a, predefined set of classes?, (A). Classification, (B). Clustering, (C). Both A and B, (D). None, , 79
Page 79 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, Answer -:(B). Clustering, , Answer -:C, , 383. What is the adaptive system, management?, , 386. A class of learning algorithm that, tries to find an optimum classification, of a set of examples using the, probabilistic theory is named as …, , a) machine language techniques, b) machine learning techniques, c) machine procedures techniques, d) none of these, Answer -:B, 384. An essential process used for, applying intelligent methods to, extract the data patterns is named as, …, , a) Bayesian classifiers, b) Dijkstra classifiers, c) doppler classifiers, d) all of these, Answer -:A, 387. Which of the following can be, used for finding deep knowledge?, , a) data mining, , a) stacks, , b) data analysis, , b) algorithms, , c) data implementation, , c) clues, , d) data computation, , d) none of these, , Answer -:A, , Answer -:C, , 385. Classification and regression are, the properties of…, , 388. We define a ______ as a, subdivison of a set of examples into, a number of classes., , a) data analysis, b) data manipulation’, c) data mining, d) none of these, , 80, , a) kingdom, b) tree, c) classification
Page 80 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, d) array, , c) hybrid database, , Answer -:C, , d) none of these, , 389. Group of similar objects that, differ significantly from other objects, is named as …, , Answer -:B, , a) classification, b) cluster, c) community, d) none of these, Answer -:B, 390. Combining different type of, methods or information is …., , 392. What is the strategic value of, data mining?, a) design sensitive, b) cost sensitive, c) technical sensitive, d) time sensitive, Answer -:D, , a) analysis, , 393. The amount of information with, in data as opposed to the amount of, redundancy or noise is known as …, , b) computation, , a) paragraph content, , c) stack, , b) text content, , d) hybrid, , c) information content, , Answer -:D, , d) none of these, , 391. What i sthe name of database, having a set of databases from, different vendors, possibly using, different database paradigms?, , Answer -:C, , a) homogeneous database, , b) learning by analyzing, , b) heterogeneous database, , c) learning by generalizing, , 81, , 394. What is inductive learning?, a) learning by hypothesis
Page 81 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, d) none of these, , Answer -:D, , Answer -:C, , 398: Patterns that can be discovered, from a given database are which, type…, , 395: Which of the following applied, on warehouse?, a) write only, b) read only, c) both a & b, d) none of these, Answer -:B, 396: Data can be store , retrive and, updated in …, a) SMTOP, b) OLTP, , a) More than one type, b) Multiple type always, c) One type only, d) No specific type, Answer -:A, 399:Background knowledge is…, a) It is a form of automatic learning., b) A neural network that makes use, of a hidden layer, , d) OLAP, , c) The additional acquaintance used, by a learning algorithm to facilitate, the learning process, , Answer -:B, , d) None of these, , 397: Which of the following is a good, alternative to the star schema?, , Answer -:C, , c) FTP, , a) snow flake schema, , 400: Which of the following is true for, Classification?, , b) star schema, , a) A subdivision of a set, , c) star snow flake schema, , b) A measure of the accuracy, , d) fact constellation, , 82
Page 82 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, c) The task of assigning a, classification, , into lines or records, d) None of the mentioned, , d) All of these, Answer -:A, 401. As companies move past the, experimental phase with Hadoop,, many cite the need for additional, capabilities, including, _______________, a) Improved data storage and, information retrieval, b) Improved extract, transform and, load features for data integration, c) Improved data warehousing, functionality, d) Improved security, workload, management, and SQL support, Answer: d, Explanation: Adding security to, Hadoop is challenging because all the, interactions do not follow the classic, client-server pattern., 402. Point out the correct statement., a) Hadoop do need specialized, hardware to process the data, b) Hadoop 2.0 allows live stream, processing of real-time data, c) In Hadoop programming, framework output files are divided, , 83, , Answer: b, Explanation: Hadoop batch processes, data distributed over a number of, computers ranging in 100s and 1000s., 403. According to analysts, for what, can traditional IT systems provide a, foundation when they’re integrated, with big data technologies like, Hadoop?, a) Big data management and data, mining, b) Data warehousing and business, intelligence, c) Management of Hadoop clusters, d) Collecting and storing unstructured, data, Answer: a, Explanation: Data warehousing, integrated with Hadoop would give a, better understanding of data., 404. Hadoop is a framework that, works with a variety of related tools., Common cohorts include, ____________, a) MapReduce, Hive and HBase, b) MapReduce, MySQL and Google, Apps
Page 83 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, c) MapReduce, Hummer and Iguana, d) MapReduce, Heron and Trumpet, , d) A sound Cutting’s laptop made, during Hadoop development, , Answer: a, Explanation: To use Hive with HBase, you’ll typically want to launch two, clusters, one to run HBase and the, other to run Hive., , Answer: c, Explanation: Doug Cutting, Hadoop, creator, named the framework after, his child’s stuffed toy elephant., , 405. Point out the wrong statement., a) Hardtop processing capabilities are, huge and its real advantage lies in the, ability to process terabytes &, petabytes of data, b) Hadoop uses a programming, model called “MapReduce”, all the, programs should confirm to this, model in order to work on Hadoop, platform, c) The programming model,, MapReduce, used by Hadoop is, difficult to write and test, d) All of the mentioned, Answer: c, Explanation: The programming, model, MapReduce, used by Hadoop, is simple to write and test., 406. What was Hadoop named after?, a) Creator Doug Cutting’s favorite, circus act, b) Cutting’s high school rock band, c) The toy elephant of Cutting’s son, , 84, , 407. All of the following accurately, describe Hadoop, EXCEPT, ____________, a) Open-source, b) Real-time, c) Java-based, d) Distributed computing approach, Answer: b, Explanation: Apache Hadoop is an, open-source software framework for, distributed storage and distributed, processing of Big Data on clusters of, commodity hardware., 408. __________ can best be, described as a programming model, used to develop Hadoop-based, applications that can process massive, amounts of data., a) MapReduce, b) Mahout, c) Oozie, d) All of the mentioned
Page 84 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, Answer: a, Explanation: MapReduce is a, programming model and an, associated implementation for, processing and generating large data, sets with a parallel, distributed, algorithm., 409. __________ has the world’s, largest Hadoop cluster., a) Apple, b) Datamatics, c) Facebook, d) None of the mentioned, Answer: c, Explanation: Facebook has many, Hadoop clusters, the largest among, them is the one that is used for Data, warehousing., 410. Facebook Tackles Big Data With, _______ based on Hadoop., a) ‘Project Prism’, b) ‘Prism’, c) ‘Project Big’, d) ‘Project Data’, Answer: a, Explanation: Prism automatically, replicates and moves data wherever, it’s needed across a vast network of, computing facilities., , 85, , 411. IBM and ________ have, announced a major initiative to use, Hadoop to support university courses, in distributed computer, programming., a) Google Latitude, b) Android (operating system), c) Google Variations, d) Google, Answer: d, Explanation: Google and IBM, Announce University Initiative to, Address Internet-Scale., 412. Point out the correct statement., a) Hadoop is an ideal environment for, extracting and transforming small, volumes of data, b) Hadoop stores data in HDFS and, supports data, compression/decompression, c) The Giraph framework is less useful, than a MapReduce job to solve graph, and machine learning, d) None of the mentioned, Answer: b, Explanation: Data compression can, be achieved using compression, algorithms like bzip2, gzip, LZO, etc., Different algorithms can be used in
Page 85 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, different scenarios based on their, capabilities., , d) Relational Database Management, System, , 413. What license is Hadoop, distributed under?, a) Apache License 2.0, b) Mozilla Public License, c) Shareware, d) Commercial, , Answer: a, Explanation: The Hadoop Distributed, File System (HDFS) is designed to, store very large data sets reliably,, and to stream those data sets at high, bandwidth to the user., , Answer: a, Explanation: Hadoop is Open Source,, released under Apache 2 license., , 416. What was Hadoop written in?, a) Java (software platform), b) Perl, c) Java (programming language), d) Lua (programming language), , 414. Sun also has the Hadoop Live CD, ________ project, which allows, running a fully functional Hadoop, cluster using a live CD., a) OpenOffice.org, b) OpenSolaris, c) GNU, d) Linux, Answer: b, Explanation: The OpenSolaris Hadoop, LiveCD project built a bootable CDROM image., 415. Which of the following genres, does Hadoop produce?, a) Distributed file system, b) JAX-RS, c) Java Message Service, , 86, , Answer: c, Explanation: The Hadoop framework, itself is mostly written in the Java, programming language, with some, native code in C and command-line, utilities written as shell-scripts., 417. A ________ serves as the master, and there is only one NameNode per, cluster., a) Data Node, b) NameNode, c) Data block, d) Replication, Answer: b, Explanation: All the metadata related, to HDFS including the information
Page 86 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, about data nodes, files stored on, HDFS, and Replication, etc. are stored, and maintained on the NameNode., 418. Point out the correct statement., a) DataNode is the slave/worker node, and holds the user data in the form of, Data Blocks, b) Each incoming file is broken into, 32 MB by default, c) Data blocks are replicated across, different nodes in the cluster to, ensure a low degree of fault, tolerance, d) None of the mentioned, , Answer: a, Explanation: There can be any, number of DataNodes in a Hadoop, Cluster., 419. HDFS works in a __________, fashion., a) master-worker, b) master-slave, c) worker/slave, d) all of the mentioned, Answer: a, Explanation: NameNode servers as, the master and each DataNode, servers as a worker/slave, , 87, , 420. ________ NameNode is used, when the Primary NameNode goes, down., a) Rack, b) Data, c) Secondary, d) None of the mentioned, Answer: c, Explanation: Secondary namenode is, used for all time availability and, reliability., 421. Point out the wrong statement., a) Replication Factor can be, configured at a cluster level (Default, is set to 3) and also at a file level, b) Block Report from each DataNode, contains a list of all the blocks that, are stored on that DataNode, c) User data is stored on the local file, system of DataNodes, d) DataNode is aware of the files to, which the blocks stored on it belong, to, , Answer: d, Explanation: NameNode is aware of, the files to which the blocks stored, on it belong to., 422. Which of the following scenario, may not be a good fit for HDFS?
Page 87 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, a) HDFS is not suitable for scenarios, requiring multiple/simultaneous, writes to the same file, b) HDFS is suitable for storing data, related to applications requiring low, latency data access, c) HDFS is suitable for storing data, related to applications requiring low, latency data access, d) None of the mentioned, Answer: a, Explanation: HDFS can be used for, storing archive data since it is, cheaper as HDFS allows storing the, data on low cost commodity, hardware while ensuring a high, degree of fault-tolerance., 423. The need for data replication, can arise in various scenarios like, ____________, a) Replication Factor is changed, b) DataNode goes down, c) Data Blocks get corrupted, d) All of the mentioned, Answer: d, Explanation: Data is replicated across, different DataNodes to ensure a high, degree of fault-tolerance., 424. ________ is the slave/worker, node and holds the user data in the, , 88, , form of Data Blocks., a) DataNode, b) NameNode, c) Data block, d) Replication, Answer: a, Explanation: A DataNode stores data, in the [HadoopFileSystem]. A, functional filesystem has more than, one DataNode, with data replicated, across them., 425. HDFS provides a command line, interface called __________ used to, interact with HDFS., a) “HDFS Shell”, b) “FS Shell”, c) “DFS Shell”, d) None of the mentioned, Answer: b, Explanation: The File System (FS), shell includes various shell-like, commands that directly interact with, the Hadoop Distributed File System, (HDFS)., 426. HDFS is implemented in, _____________ programming, language., a) C++, b) Java
Page 88 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, c) Scala, d) None of the mentioned, , relational database management, system developed by Microsoft., , Answer: b, Explanation: HDFS is implemented in, Java and any computer which can run, Java can host a NameNode/DataNode, on it., , 429. Point out the correct statement., a) Documents can contain many, different key-value pairs, or key-array, pairs, or even nested documents, b) MongoDB has official drivers for a, variety of popular programming, languages and development, environments, c) When compared to relational, databases, NoSQL databases are, more scalable and provide superior, performance, d) All of the mentioned, , 427. For YARN, the ___________, Manager UI provides host and port, information., a) Data Node, b) NameNode, c) Resource, d) Replication, Answer: c, Explanation: All the metadata related, to HDFS including the information, about data nodes, files stored on, HDFS, and Replication, etc. are stored, and maintained on the NameNode., 428. Which of the following is not a, NoSQL database?, a) SQL Server, b) MongoDB, c) Cassandra, d) None of the mentioned, Answer: a, Explanation: Microsoft SQL Server is a, , 89, , Answer: d, Explanation: There are also a large, number of unofficial or communitysupported drivers for other, programming languages and, frameworks., 430. Which of the following is a, NoSQL Database Type?, a) SQL, b) Document databases, c) JSON, d) All of the mentioned, Answer: b, Explanation: Document databases
Page 89 :
Database Management Systems Unit – 4 MCQs, pair each key with a complex data, structure known as a document., 431. Which of the following is a widecolumn store?, a) Cassandra, b) Riak, c) MongoDB, d) Redis, Answer: a, Explanation: Wide-column stores, such as Cassandra and HBase are, optimized for queries over large, datasets, and store columns of data, together, instead of rows., 432. Point out the wrong statement., a) Non Relational databases require, that schemas be defined before you, can add data, b) NoSQL databases are built to allow, the insertion of data without a, predefined schema, c) NewSQL databases are built to, allow the insertion of data without a, predefined schema, d) All of the mentioned, Answer: a, Explanation: There’s also no way,, using a relational database, to, effectively address data that’s, , 90, , completely unstructured or unknown, in advance.
Page 90 :
DIWAKAR EDUCATION HUB, , System Software and Operating, System Unit – 5 MCQs, As per updated syllabus, DIWAKAR EDUCATION HUB, , 2020, , THE LEARN WITH EXPERTIES