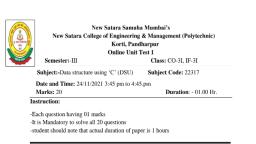
Page 1 :
Quick Sort Algorithm, Sorting is a way of arranging items in a systematic manner. Quicksort is the widely used sorting algorithm, that makes n log n comparisons in average case for sorting an array of n elements. It is a faster and highly, efficient sorting algorithm. This algorithm follows the divide and conquer approach. Divide and conquer, is a technique of breaking down the algorithms into subproblems, then solving the subproblems, and, combining the results back together to solve the original problem., Quick sort is a highly efficient sorting algorithm and is based on partitioning of array of data into smaller arrays. A, large array is partitioned into two arrays one of which holds values smaller than the specified value, say pivot,, based on which the partition is made and another array holds values greater than the pivot value., , Divide: In Divide, first pick a pivot element. After that, partition or rearrange the array into two sub-arrays, such that each element in the left sub-array is less than or equal to the pivot element and each element, in the right sub-array is larger than the pivot element., Conquer: Recursively, sort two subarrays with Quicksort., Combine: Combine the already sorted array., Quicksort picks an element as pivot, and then it partitions the given array around the picked pivot element., In quick sort, a large array is divided into two arrays in which one holds values that are smaller than the, specified value (Pivot), and another array holds the values that are greater than the pivot., After that, left and right sub-arrays are also partitioned using the same approach. It will continue until the, single element remains in the sub-array., , Choosing the pivot, Picking a good pivot is necessary for the fast implementation of quicksort. However, it is typical to, determine a good pivot. Some of the ways of choosing a pivot are as follows o, , Pivot can be random, i.e. select the random pivot from the given array., , o, , Pivot can either be the rightmost element of the leftmost element of the given array.
Page 2 :
o, , Select median as the pivot element., , Algorithm, Algorithm:, , 1. QUICKSORT (array A, start, end), 2. {, 3., , 1 if (start < end), , 4., , 2{, , 5. 3 p = partition(A, start, end), 6. 4 QUICKSORT (A, start, p - 1), 7. 5 QUICKSORT (A, p + 1, end), 8. 6 }, 9. }, Partition Algorithm:, The partition algorithm rearranges the sub-arrays in a place., , 1. PARTITION (array A, start, end), 2. {, 3., , 1 pivot ? A[end], , 4., , 2 i ? start-1, , 5., , 3 for j ? start to end -1 {, , 6., , 4 do if (A[j] < pivot) {, , 7., , 5 then i ? i + 1, , 8., , 6 swap A[i] with A[j], , 9., , 7 }}, , 10. 8 swap A[i+1] with A[end], 11. 9 return i+1, 12. }, , Working of Quick Sort Algorithm, Now, let's see the working of the Quicksort Algorithm.
Page 3 :
To understand the working of quick sort, let's take an unsorted array. It will make the concept more clear, and understandable., Let the elements of array are -, , In the given array, we consider the leftmost element as pivot. So, in this case, a[left] = 24, a[right] = 27, and a[pivot] = 24., Since, pivot is at left, so algorithm starts from right and move towards left., , Now, a[pivot] < a[right], so algorithm moves forward one position towards left, i.e. -, , Now, a[left] = 24, a[right] = 19, and a[pivot] = 24., Because, a[pivot] > a[right], so, algorithm will swap a[pivot] with a[right], and pivot moves to right, as -
Page 4 :
Now, a[left] = 19, a[right] = 24, and a[pivot] = 24. Since, pivot is at right, so algorithm starts from left and, moves to right., As a[pivot] > a[left], so algorithm moves one position to right as -, , Now, a[left] = 9, a[right] = 24, and a[pivot] = 24. As a[pivot] > a[left], so algorithm moves one position to, right as -, , Now, a[left] = 29, a[right] = 24, and a[pivot] = 24. As a[pivot] < a[left], so, swap a[pivot] and a[left], now, pivot is at left, i.e. -
Page 5 :
Since, pivot is at left, so algorithm starts from right, and move to left. Now, a[left] = 24, a[right] = 29, and, a[pivot] = 24. As a[pivot] < a[right], so algorithm moves one position to left, as -, , Now, a[pivot] = 24, a[left] = 24, and a[right] = 14. As a[pivot] > a[right], so, swap a[pivot] and a[right], now, pivot is at right, i.e. -, , Now, a[pivot] = 24, a[left] = 14, and a[right] = 24. Pivot is at right, so the algorithm starts from left and, move to right.
Page 6 :
Now, a[pivot] = 24, a[left] = 24, and a[right] = 24. So, pivot, left and right are pointing the same element., It represents the termination of procedure., Element 24, which is the pivot element is placed at its exact position., Elements that are right side of element 24 are greater than it, and the elements that are left side of element, 24 are smaller than it., , Now, in a similar manner, quick sort algorithm is separately applied to the left and right sub-arrays. After, sorting gets done, the array will be -, , Quicksort complexity, Now, let's see the time complexity of quicksort in best case, average case, and in worst case. We will also, see the space complexity of quicksort., , 1. Time Complexity, Case, , Time Complexity, , Best Case, , O(n*logn), , Average Case, , O(n*logn)
Page 7 :
Worst Case, o, , O(n2), , Best Case Complexity - In Quicksort, the best-case occurs when the pivot element is the middle, element or near to the middle element. The best-case time complexity of quicksort is O(n*logn)., , o, , Average Case Complexity - It occurs when the array elements are in jumbled order that is not, properly ascending and not properly descending. The average case time complexity of quicksort, is O(n*logn)., , o, , Worst Case Complexity - In quick sort, worst case occurs when the pivot element is either greatest, or smallest element. Suppose, if the pivot element is always the last element of the array, the worst, case would occur when the given array is sorted already in ascending or descending order. The, worst-case time complexity of quicksort is O(n2)., , Though the worst-case complexity of quicksort is more than other sorting algorithms such as Merge, sort and Heap sort, still it is faster in practice. Worst case in quick sort rarely occurs because by changing, the choice of pivot, it can be implemented in different ways. Worst case in quicksort can be avoided by, choosing the right pivot element., , 2. Space Complexity, Space Complexity, , O(n*logn), , Stable, , NO, , o, , The space complexity of quicksort is O(n*logn)., , Implementation of quicksort, Now, let's see the programs of quicksort in different programming languages., Program: Write a program to implement quicksort in C language., , 1. #include <stdio.h>, 2. /* function that consider last element as pivot,, 3. place the pivot at its exact position, and place, 4. smaller elements to left of pivot and greater, 5. elements to right of pivot. */, 6. int partition (int a[], int start, int end), 7. {, 8., , int pivot = a[end]; // pivot element
Page 8 :
9., , int i = (start - 1);, , 10., 11., , for (int j = start; j <= end - 1; j++), , 12., , {, , 13., , // If current element is smaller than the pivot, , 14., , if (a[j] < pivot), , 15., , {, , 16., , i++; // increment index of smaller element, , 17., , int t = a[i];, , 18., , a[i] = a[j];, , 19., , a[j] = t;, , 20., , }, , 21., , }, , 22., , int t = a[i+1];, , 23., , a[i+1] = a[end];, , 24., , a[end] = t;, , 25., , return (i + 1);, , 26. }, 27., 28. /* function to implement quick sort */, 29. void quick(int a[], int start, int end) /* a[] = array to be sorted, start = Starting index, end = Ending inde, x */, 30. {, 31., , if (start < end), , 32., , {, , 33., , int p = partition(a, start, end); //p is the partitioning index, , 34., , quick(a, start, p - 1);, , 35., , quick(a, p + 1, end);, , 36., , }, , 37. }, 38., 39. /* function to print an array */, 40. void printArr(int a[], int n), 41. {, 42., , int i;, , 43., , for (i = 0; i < n; i++), , 44., , printf("%d ", a[i]);, , 45. }, 46. int main()
Page 9 :
47. {, 48., , int a[] = { 24, 9, 29, 14, 19, 27 };, , 49., , int n = sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]);, , 50., , printf("Before sorting array elements are - \n");, , 51., , printArr(a, n);, , 52., , quick(a, 0, n - 1);, , 53., , printf("\nAfter sorting array elements are - \n");, , 54., , printArr(a, n);, , 55., 56., 57. }, , return 0;