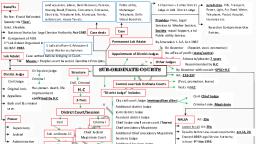
Page 1 :
ENROUTE 2KAS NOTES, Judiciary System of India, • The Indian constitution has established an integrated, judicial system with the Supreme Court at the top and high, Courts below it., • Under the high Court there come the subordinate Courts,, i.e. district Courts and other lower Courts., , Supreme Court, • The Supreme Court of India was inaugurated on 28, January, 1950., • Article 124 to 147 of Part V of the Indian constitution deals, with the Supreme Court., , Organization, • At present Supreme Court consists of 33 judges and one, chief justice., • Originally there were only 8 judges in the Supreme Court., , Appointment of Judges, • The chief justice of India is appointed by the president after, consultation with other judges of the Supreme Court., • The other judges of the Supreme Court are appointed by the, President of India after consulting the chief justice of India., , Qualification of Judges
Page 2 :
• He should be an Indian citizen., • he/she has been a judge of one or more High Courts, for at, least 5 years, or, • he/she has been an advocate in one or more High Courts for, at least 10 years, or, • He/she is in the opinion of the President, a distinguished, jurist., , Oath and Salary, • The judges of the Supreme Court make the oath and, affirmation before the President of India, or some person, appointed by him., • The salaries, allowances, leave etc. are decided by the, Parliament from time to time, • The retired chief justice and judges are entitled to 50% of, their last drawn salary as monthly pension., , Tenure, • The constitution has no fix tenure for the judges of Supreme, Court but there are some provisions in this matter and these, are:, • He/she holds office until the age of 65 years., • He/she can resign from the office by writing to the President., • He/she can be removed by the President on the, recommendation of the parliament., , Removal of Judges, • A judge can be removed from his office by the President of, India., • The President issues order only if the address has been made, by the parliament regarding this.
Page 3 :
• The address must be supported by special majority in each, house., • The ground of removal can be proved misbehavior or, incapacity., • The removal motion must be signed by at least 100, members of lok sabha and 50 members of rajya sabha., • The speaker can admit and refuse the motion., • If the motion is accepted, the speaker constitutes a threemember body to investigate the matter., • The committee consist of one chief justice of Supreme, Court, one chief justice of a high Court and a prominent, jurist., • After the motion is passed by the committee and by both, houses of the Parliament, the motion is then presented, before the President., • Finally the president passes the order of removing of the, judge., • Note: No judge of the Supreme Court has been impeached so, far., , Acting Chief Justice, • The president appoints an acting chief justice of the, Supreme Court if the CJI is temporary absent., • The office of Chief justice is vacant., • The chief justice is unable to perform his/her duties., , Ad-hoc Judges, • When there is lack of Quorum in the Supreme Court to hold, any session, the Chief justice can appoint judges of High, Court as a temporary judge or ad-hoc judge of the Supreme, Court.
Page 4 :
• The judge so appointed should be qualified to be appointed, as a judge of the Supreme Court., • While a judge of the high Court acts as the ad-hoc judge of, the Supreme Court, he enjoys all the privileges and powers., , Retired Judges, • The CJI can request the retired judges of the Supreme, Court or a retired judge of the High Court to act as a judge, for a temporary period., • In order to do this he/she needs the consent of the president, and the also of the person appointed., , Independence of Supreme Court, Security of Tenure, • The judges of the SC are given security of tenure., • Once appointed, they retain their office until the age of 65, years., • They can be removed only by a presidential order on, grounds of proven misbehavior and/or incapacity., , Salaries and Allowances, • The judges of the SC enjoy good salaries and allowances and, these cannot be decreased except in the case of a financial, emergency., • The expenses of the SC are charged on the Consolidated, Fund of India.
Page 5 :
Powers and Jurisdiction, • The SC’s powers and jurisdiction can only be added by the, Parliament and not be curtailed., • The conduct of any judge of the Supreme Court in the, discharge of his/her duties cannot be questioned in the, legislature., • The SC has the power to punish any person for its contempt,, as per Article 129., , Separation of the Judiciary from the Executive, • The constitution directs the state to take steps to separate, the judiciary from the executive., , No practice after the Retirement, • The judges are the Supreme Court cannot act in any Court, or authority in the Indian Territory., , Powers & jurisdiction of Supreme Court, Original Jurisdiction, • Dispute between the Central Government and one or more, States., • Dispute between the central Government and one or more, States on one side and one or more States on the other side.
Page 6 :
• Dispute between two or more States., , Writ Jurisdiction, • Matters regarding the enforcement of Fundamental Rights., • The SC can issue writs, directions, or orders including writs, in the nature of mandamus, habeas corpus, quo warranto,, prohibition and certiorari., , Appellate Jurisdiction, • Supreme Court is the highest Court of Appeal in India., • The SC also has the power to direct the transfer of a, criminal or civil case from the High Court in one State to the, High Court in another State., • It can also transfer cases from one subordinate Court to, another State High Court, • If the SC deems that cases involving the same questions of, law are pending before it and one or more High Courts, and, that these are significant questions of law, it can withdraw, the cases before the High Court or Courts and dispose of all, these cases itself., • The Arbitration and Conciliation Act, 1996 gives the SC the, authority to initiate international commercial arbitration., , Advisory Jurisdiction, • Article 143 of the Indian constitution authorizes the, President to seek the opinion of the Supreme Court in these, two categories:
Page 7 :
• On any law or fact of public importance., • On the dispute arising out of any treaty or agreement that, was signed before the enactment of the constitution., • In the first instance the Supreme Court may or may not give, its opinion. But in the second instance the Supreme Court, must tender its opinion to the president., • The opinion given by the Supreme Court are not binding to, the President., , Judicial Review, • The Supreme Court can check the legality of the, constitutional amendments., • If the amendments are found to be violating the basic, structure of the constitution or infringe the fundamental, rights of the citizens then the SC can declare this kind of, amendments as null and void, , Other powers of SC, • SC decides on the matter related to the election of President, and Vice-president., • It also enquires the conduct and behavior of the Chairman, of UPSC., • SC can re-review its own judgment or order., • The law made by Supreme Court is binding on all Court in, India. All authorities shall act in aid of the SC., • SC has the power to superintendence over all Courts and, tribunals in the country.
Page 8 :
Important Articles Related to SC, •, •, •, •, •, , Art 124 - Establishment and constitution of SC, Art 129 - Supreme Court to be a Court of record, Art 131 - Original jurisdiction of the Supreme Court, Art 137 - Review of Judgments of the SC, Art 143 - Power of President to consult the SC, , QUESTIONS, 1. Detail how a Supreme Court judge can be removed from his, position?, , 2. Explain the provisions that provide and ensures the, independence of Supreme court?, , 3. What are the qualifications required to be appointed as a, Supreme Court Judge?, , 4. Write a short note on powers and jurisdiction of Supreme, Court?