Page 1 :
Tissues
Page 2 :
ANIMAL TISSUES, 1. In unicellular organisms (single celled organisms) all the, basic physiological activities are done by the same cell., 2. In multicellular organisms, there are millions of cells in, their body., 3. But all these cells are not alike. They are differentiated to, perform different functions., 4. The similar cells form a group to perform a specific, function., 5. similar cells having a specific function are grouped together, and they are called tissue., Shibu Abdullah
Page 3 :
Tissue definition, Tissues can be defined as a group of similar cells, which are structurally and functionally differentiated to, perform a specific function., Cells of a tissue have same origin., , Each organ of the body is formed by several types of, tissues., The part of science dealing with plant and animal, tissues is known as histology., The term tissue is coined by Bichat in 1792., , Shibu Abdullah
Page 4 :
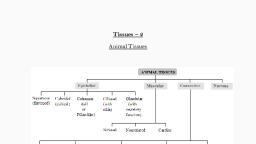
Types of Tissues, Based on the function and structure, animals tissues, are grouped into four major types. They are,, , Shibu Abdullah, , 1., , Epithelial Tissues, , 2., , Connective tissues, , 3., , Muscular Tissues, , 4., , Nervous Tissues
Page 5 :
Epithelial Tissue, , , It is made of closely-packed cells arranged in sheets., , , , usually consists of a single layer of cells, certain cases there may, be more than one layer., , , , derived from endoderm., , , , cells - closely connected, via cellular junctions., , , , Epithelium has two distinct surfaces, apical surface and Basal, surface., , , , The apical surface is exposed to the body cavity or exterior, while, the basal surface is adjacent to the underlying., , , , Epithelia contain no blood vessels (they are non-vascular) and are, dependent upon the underlying connective tissue for nutrients., , Shibu Abdullah
Page 6 :
Epithelial Tissue, Epithelial tissues form the protective covering and, inner lining of the body and organs., Epithelia form the surface of the skin;, it forms the lining of the various cavities and tubes of, the body,, covers the internal organs., It is found in skin as well as the lining of the mouth and, nasal cavity, inner lining of the GI tract, lungs, urinary, bladder, exocrine glands, vagina and more., Shibu Abdullah
Page 7 :
Types, Epithelial cells are of three types based on their three shapes,, squamous (flattened), cuboidal, columnar, Simple epithelium, - consists of one cell layer, Stratified epithelium, - has more than one layer., , Shibu Abdullah
Page 8 :
Functions, , , they are boundaries between masses of cells and a cavity or space., , , , epithelium of the skin protects the underlying tissues from, mechanical damage, ultraviolet light, dehydration and invasion by, bacteria., , , , epithelium of the intestine secretes digestive enzymes into the, intestine and absorbs the products of digestion from it., , , , epithelium also lines our air passages and the alveoli of the lungs. It, secretes mucus which keeps it from drying out and traps inhaled, dust particles., , , , Epithelial cells secrete enzymes, hormones, sweat, saliva, etc., , , , Most of its cells have cilia on their apical surface that helps to, protect entry of dust particles., , Shibu Abdullah
Page 9 :
Connective Tissue, occurs throughout the body., , most abundant type in human body., They are named connective tissues because of their, special function of linking and supporting other, tissues/organs of the body., Each cells of this tissue is called fibroblast., In this, cells are separated by non-living extracellular, material which is called matrix. (ground substance)., This matrix can be liquid or rigid. This matrix contains, fibers of structural protein which is called collagen or, elastin.
Page 10 :
Connective Tissue
Page 11 :
Connective Tissue, The fibers provide strength, elasticity and flexibility to, the tissue., Depending upon the nature of the matrix and collagen,, connective tissues can be classified into three main, categories., , 1. Loose connective tissue, 2. Dense connective tissue, 3. Specialized connective tissues
Page 12 :
Loose connective tissue, Loose connective tissue has cells and fibers loosely, arranged in a semi-fluid ground substance, for example, areolar tissue present beneath the skin., It serves as a support framework for epithelium., , Adipose tissue is another type of loose connective, tissue located mainly beneath the skin., , Shibu Abdullah
Page 13 :
Dense connective tissue, In this tissue, specialized connective tissue fibres and, fibroblasts are compactly packed., Orientation of fibres shows a regular or irregular, pattern., In the regular connective tissues, the collagen fibres, are present in rows between many parallel bundles of, fibres., In irregular connective tissue, fibroblasts and many, fibres (mostly collagen) that is oriented differently. Eg., Tendons and Ligaments., , Shibu Abdullah
Page 14 :
Specialised connective tissues, Cartilage, bones and blood are various types of, Specialised connective tissue., The intercellular material of cartilage is solid and, flexible and resists compression., , Cartilage is present in the tip of nose, outer ear joints,, between adjacent bones of the vertebral column, limbs, and hands in adults., The cells of cartilage are called chondrocytes., , Shibu Abdullah
Page 15 :
Specialised connective tissues, Bones have a hard and non-flexible ground substance, rich in calcium salts and collagen fibres which give, bone its strength., It is the main tissue that provides structural frame to, the body., Bones support and protect softer tissues and organs., The bone cells are called osteocytes., , Shibu Abdullah
Page 16 :
Specialised connective tissues, , Blood is a fluid connective tissue containing plasma,, red blood cells (RBC), white blood cells (WBC) and, platelets., , It is the main circulating fluid that helps in the transport, of various substances., , Shibu Abdullah
Page 17 :
Muscle Tissue, Muscle tissues are a special type of tissues which are, specialized for contraction., The cells of the muscle tissues are elongated and, spindle shaped. They are known as muscle fibers., They contain the contractile proteins actin and, myosin., These proteins interact with each other to shorten and, elongate muscle during contraction and elongation., , Muscles play an active role in all the movements of the, body., Shibu Abdullah
Page 18 :
Skeletal muscles, Skeletal muscle tissue is closely attached to skeletal, bones., In a typical muscle skeletal muscle fibres are bundled, together in a parallel fashion., , Here the muscles are striated., A sheath of tough connective tissue encloses several, bundles of muscle fibres., , Shibu Abdullah
Page 19 :
Smooth muscles, Here muscle fibres taper at both ends (fusiform) and, do not show striations., They are seen as bundled together in a connective, tissue sheath., , The wall of internal organs such as the blood vessels,, stomach and intestine contains this type of muscle, tissue., Smooth muscles are ‘involuntary’ as their functioning, cannot be directly controlled., , Shibu Abdullah
Page 20 :
Cardiac muscles, Cardiac muscle tissue is a contractile tissue present, only in the heart., Here the muscles show a branched appearance., Cell junctions fuse the plasma membranes of cardiac, muscle cells and make them stick together, Communication junctions at some fusion points allow, the cells to contract as a unit, i.e., when one cell, receives a signal to contract, its neighbors are also, stimulated to contract.
Page 21 :
Nervous tissue, is specialized for communication., , The brain, spinal cord, and peripheral Nerves are, composed of Nervous tissues., The tissue consists of two major cell types: neurons, and glial cells., Neurons communicate with each other via electrical, and chemical signals., Neurons are excitable cells., , They have nucleated cell bodies and two types of, elongated cellular processes: dendrites-which receive, signals, and axons-which send signals., Shibu Abdullah
Page 22 :
Nervous tissue, Neuroglial cells constitute the rest of the neural, system., , These cells protect and support neurons., Neuroglia makes up more than one half the volume of, neural tissue in our body., , They maintain proper ion concentrations in the fluid, surrounding neurons, generating myelin, and cleaning, up debris., , Shibu Abdullah
Page 23 :
Thank You..